When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings
Rated voltage refers to the nominal voltage that the inverter is engineered to work with. For grid-tied systems, this is typically 220V or 230V in most countries.
Get a quote
The 3 Most Common Faults on Inverters and how to
At IDS we have a wealth of inverter experience. We have been an ABB Partner for over 20 years and are used to supporting clients with a variety of inverter
Get a quote
Common faults and solutions for inverters
However, inverters may encounter various faults during operation. This article will introduce the common faults of inverters in detail, including
Get a quote
32 Common Faults in Inverters and Their Solutions
GUIDE Inverters, which convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), are critical components in various applications, including
Get a quote
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
The start-up voltage is the minimum voltage potential needed for the inverter to start functioning. For effective performance, it is recommended
Get a quote
7 Simple Inverter Circuits you can Build at Home
These 7 inverter circuits might look simple with their designs, but are able to produce a reasonably high power output and an efficiency of around 75%. Learn how to build
Get a quote
Will reducing inverter output voltage during load-shedding, make
I''ll add that roughly matching your inverter''s voltage with the typical utility voltage means that the changeover relays have an easier life and with load shedding, they will work hard.
Get a quote
Inverter Initial Diagnostic and Maintenance Guide final
Output Voltage Multi-meter: Check the output AC voltage. Expected Voltage: Ensure it matches the regional voltage (e.g., 120V or 230V). Rated Output: Confirm it aligns with inverter
Get a quote
What are the differences between 220VAC, 230VAC and
After the harmonization, manufacturers started designing end devices according to new 230Vac nominal voltage, but you can still find 220Vac and 240Vac devices aimed for other markets
Get a quote
Difference Between 220V & 380V 3-Phase Power
Understanding the difference between 220V and 380V three-phase power supplies, including how inverters handle these voltage levels. Learn
Get a quote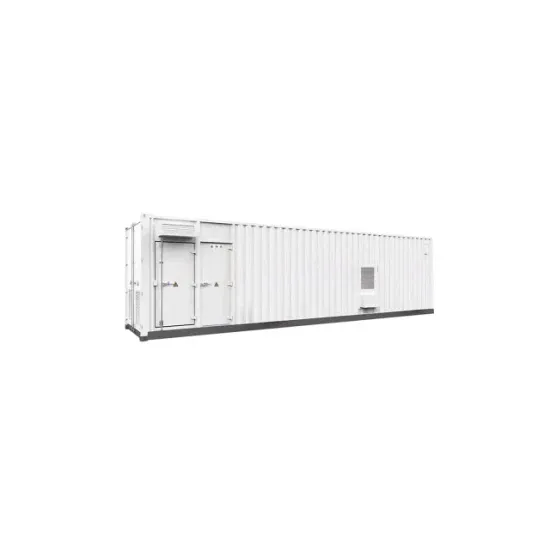
What is the optimal AC output voltage for inverter?
If the inverter is set to SA grid code, it will only tolerate voltages of 230V±10%, which means that it would have disconnected and go into
Get a quote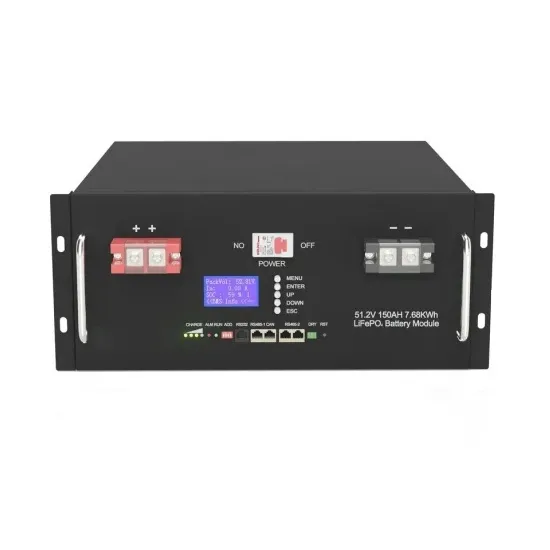
UPS Explained
The backfeed relay opens immediately open to prevent the inverter output voltage connecting to the input. The battery provides power to a DC Boost circuit which converts the low level DC
Get a quote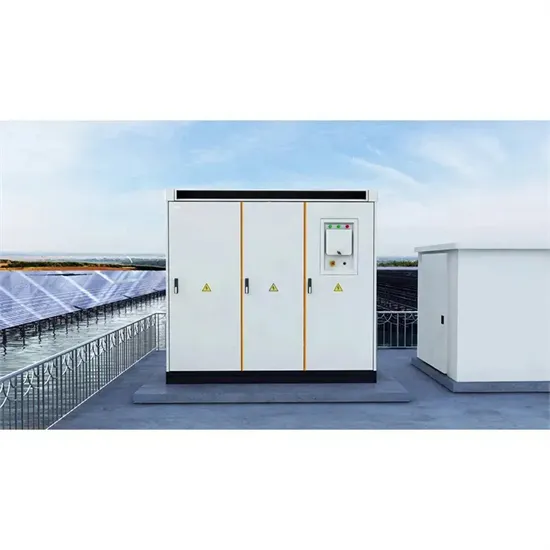
Inverter too high output voltage than normal, problem?
It has a detection voltage range of 180V to 260V and turns on when the electricity voltage is higher or lower when it is set to UPS Mode. Its detection mode is higher (they do not
Get a quote
Voltage Troubles? A Guide to Diagnosing Inverter Low Voltage
Many people face issues with inverter low voltage at some point in their lives. In this blog post, we will guide you on how to diagnose and potentially fix these problems.
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
Inverters can be classed according to their power output. The following information is not set in stone, but it gives you an idea of the classifications and general power ranges associated with
Get a quote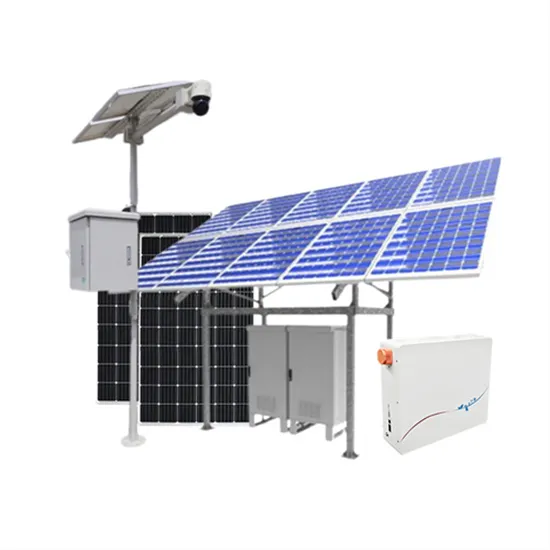
Understanding inverter voltage
An abnormally high inverter output voltage may indicate a malfunction in the voltage regulation circuit. Addressing this issue promptly is crucial to prevent potential damage
Get a quote
What is the optimal AC output voltage for inverter?
If the inverter is set to SA grid code, it will only tolerate voltages of 230V±10%, which means that it would have disconnected and go into backup/ups mode when the grid voltage
Get a quote
Maximum voltage output from inverter
Re: Maximum voltage output from inverter - what''s normal? Don''t want to step to far out but lets just share what I''ve seen. Fan in the bedroom, runs at a certain RPM. I then
Get a quote
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
The start-up voltage is the minimum voltage potential needed for the inverter to start functioning. For effective performance, it is recommended to confirm if the solar panel''s
Get a quote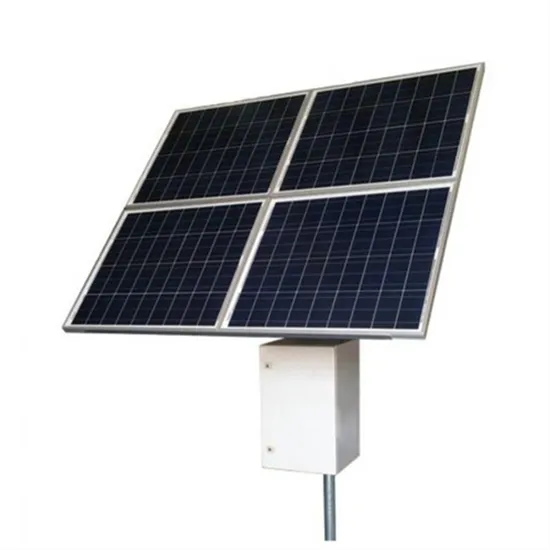
How Does Input Voltage Affect a Grid-Tie Inverter?
In the photovoltaic grid-tie inverter, there are many input voltage technical parameters: Maximum DC input voltage, MPPT operating voltage
Get a quote
Matrix Standalone Inverter
The Matrix Standalone Inverter is a 1U, 19-inch rack mount module with output up to 2000VA/2000W (at 110/115/120 or 208/220/230/240V ac, 50 or 60Hz) from -48V dc input. The
Get a quote
What is the output voltage of the inverter? Learn some basics
Regarding the structure of the inverter, the output voltage is not a normal three-phase power, but a DC voltage that is hashed to have a function equivalent to that used for a three-phase motor.
Get a quote
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings should you pay
Rated voltage refers to the nominal voltage that the inverter is engineered to work with. For grid-tied systems, this is typically 220V or 230V in most countries. For off-grid systems, it might be
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
Inverters can be classed according to their power output. The following information is not set in stone, but it gives you an idea of the classifications
Get a quote
What is the output voltage of the inverter? Learn some
Regarding the structure of the inverter, the output voltage is not a normal three-phase power, but a DC voltage that is hashed to have a function equivalent to
Get a quote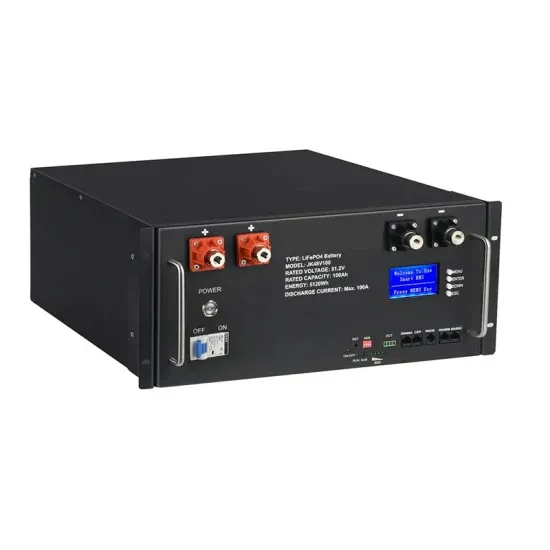
How to Choose an Off-grid Inverter? | inverter
Use a multimeter and other tools to check the inverter''s output voltage and current, ensuring they are within the normal range. Check the
Get a quote
What does the inverter voltage specifications represent?
This is the inverter''s AC range (relating to its nominal output). Since grid voltage fluctuates constantly, the inverter has to adjust to that voltage within a given window.
Get a quote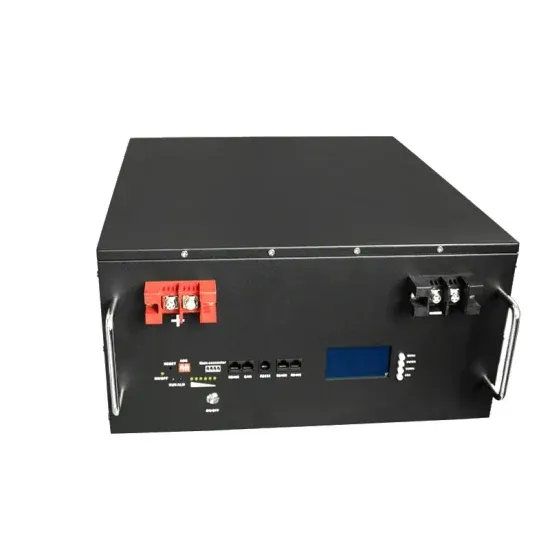
6 FAQs about [Is the inverter output voltage 233v normal ]
Can a 230 volt inverter go into backup/up mode?
If the inverter is set to SA grid code, it will only tolerate voltages of 230V±10%, which means that it would have disconnected and go into backup/ups mode when the grid voltage dropped to "196.5 V". Yeah I assumed there was some fine print I'm missing, thanks for clearing that up It is more about the voltage than the frequency
How many MPPT inputs does an inverter have?
Most inverters come with two MPPT inputs, allowing them to track two different arrays with different voltage profiles. Minimum startup voltage is the lowest voltage at which an inverter will begin operation. The minimum startup voltage 4 tells you the lowest point the inverter needs to begin functioning.
What voltage does an inverter use?
In different countries, the applicable AC voltage is different, and most countries use 110v, 120v output inverter voltage. You can confirm on the search engine or see how much AC voltage the home appliance label uses. How can the quality of inverter output voltage be measured?
How much voltage should a 230 volt inverter be?
The voltage is not required to be exactly 230 V. There is a tolerance. 5% (if that's what it is), gives you 11.5V either way. Anyway, I have set my inverter for our safety code, and I leave it to disconnect when it sees fit.
What are the input specifications of a solar inverter?
The input specifications of an inverter concern the DC power originating from the solar panels and how effectively the inverter can handle it. The maximum DC input voltage is all about the peak voltage the inverter can handle from the connected panels. The value resonates with the safety limit for the inverter.
What is the maximum input voltage for a residential inverter?
Typically, residential inverters have a maximum input voltage between 500V and 1000V. Choosing one with a higher rating ensures greater flexibility and better performance in different weather conditions.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Does the inverter output have fine-tuning voltage
Does the inverter output have fine-tuning voltage
-
 What voltage does the inverter output
What voltage does the inverter output
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
 Is the inverter voltage output high or low
Is the inverter voltage output high or low
-
 Normal voltage range of photovoltaic inverter
Normal voltage range of photovoltaic inverter
-
 Inverter working output voltage is high
Inverter working output voltage is high
-
 Inverter voltage output is too low
Inverter voltage output is too low
-
 How much is the inverter output voltage adjusted to
How much is the inverter output voltage adjusted to
-
 Inverter output voltage is slow
Inverter output voltage is slow
-
 Is there voltage on one side of the inverter output
Is there voltage on one side of the inverter output
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


