Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power calculations and inverter
Get a quote
How does an inverter work?
We''ll start the introduction by explaining the inverter device''s mechanism in detail. The inverter device''s role is to control the voltage and frequency of the power
Get a quote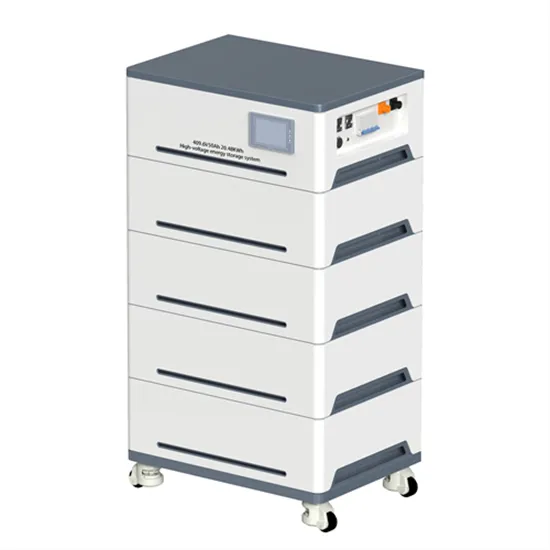
Power inverter
OverviewInput and outputBatteriesApplicationsCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
A typical power inverter device or circuit requires a stable DC power source capable of supplying enough current for the intended power demands of the system. The input voltage depends on the design and purpose of the inverter. Examples include: • 12 V DC, for smaller consumer and commercial inverters that typically run fro
Get a quote
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What Is The
Input Power Specification Here are some important specifications that you need to know about input power inverters. Input Voltage: The input
Get a quote
Changing inverter voltage output?
Modern switching regulated power supplies will still pull about the same power by pulling less current at the higher voltage, but an old style linear regulator will have to drop the
Get a quote
Harmonics and Noise in Photovoltaic (PV) Inverter and the
1. Introduction PV inverters use semiconductor devices to transform the DC power into controlled AC power by using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) switching. PWM switching is the most
Get a quote
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
In bigger household appliances, electricity works a different way. The power supply that comes from the outlet in your wall is based on
Get a quote
Inverter Voltage Calculator, Formula, Inverter Voltage Calculation
It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC). The output voltage of an inverter is
Get a quote
Understanding inverter voltage
A 12V to 240V inverter is a pivotal device designed to convert direct current (DC) power from a 12-volt battery into alternating current (AC) power with a nominal output of 240 volts.
Get a quote
INVERTERS
The word ''inverter'' in the context of power-electronics denotes a class of power conversion (or power conditioning) circuits that operates from a dc voltage source or a dc current source and
Get a quote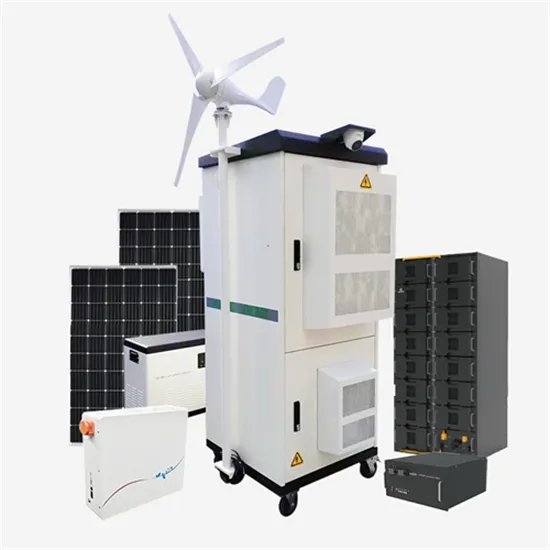
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC). The output voltage of an inverter is
Get a quote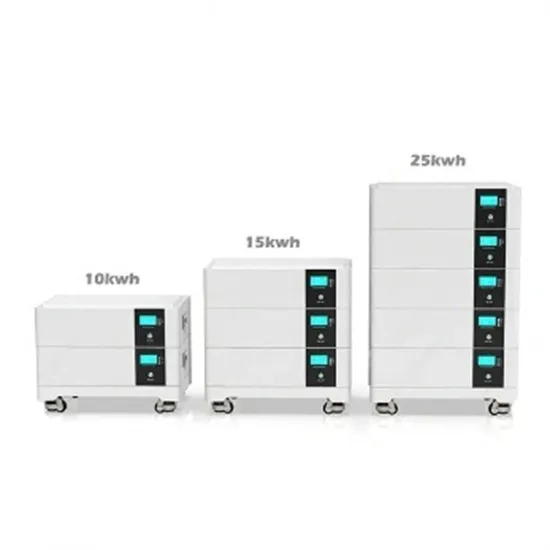
How Power Inverter Generates Reactive Power
Learn how power inverters generate reactive power to support voltage stability and enhance system efficiency. Understand the role of phase control and its importance for
Get a quote
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What Is The
Input Power Specification Here are some important specifications that you need to know about input power inverters. Input Voltage: The input voltage supplied from the DC source to the
Get a quote
How do inverters convert DC electricity to AC?
In bigger household appliances, electricity works a different way. The power supply that comes from the outlet in your wall is based on alternating current (AC), where the
Get a quote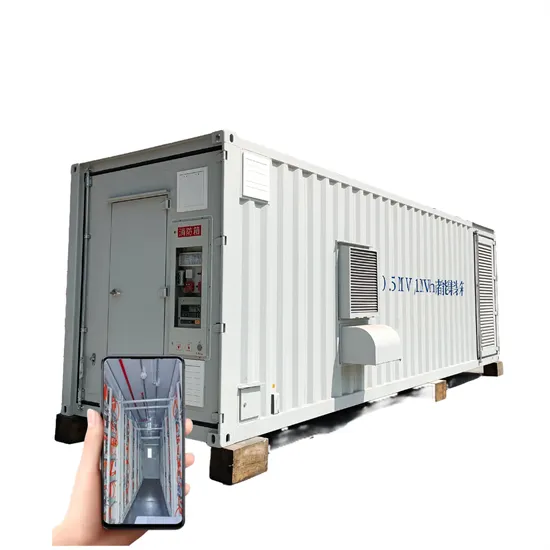
Inverter Basics | inverter
An inverter takes input from a DC (direct current) power supply and generates an AC (alternating current) output, typically at a voltage comparable to that of your standard
Get a quote
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
An inverter (or power inverter) is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage. While DC power is common in small gadgets, most
Get a quote
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
Get a quote
What is the output voltage of the inverter? Learn some basics
When installing an inverter for the motor, it usually saves more than 10% of the power consumption. The output characteristic is not the usual sinusoidal AC voltage, so if you use
Get a quote
Power inverter
The AC output voltage of a power inverter is often regulated to be the same as the grid line voltage, typically 120 or 240 VAC at the distribution level, even when there are changes in the
Get a quote
How does an inverter control current?
The two go hand-in-hand. If, on average, you''re providing slightly more current than the load sinks, the voltage will be increasing as you charge the output capacitance, since
Get a quote
How to Calculate the Maximum Output Power of a Power Inverter
With home systems from batteries from 12V to 48V, the power inverter will always step up the voltage; thus, the current will be lower at the output of the inverter. With step up inverters, the
Get a quote
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
Combination of pulses of different length and voltage results in a multi-stepped modified square wave, which closely matches the sine wave shape. The low
Get a quote
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
Combination of pulses of different length and voltage results in a multi-stepped modified square wave, which closely matches the sine wave shape. The low frequency inverters typically
Get a quote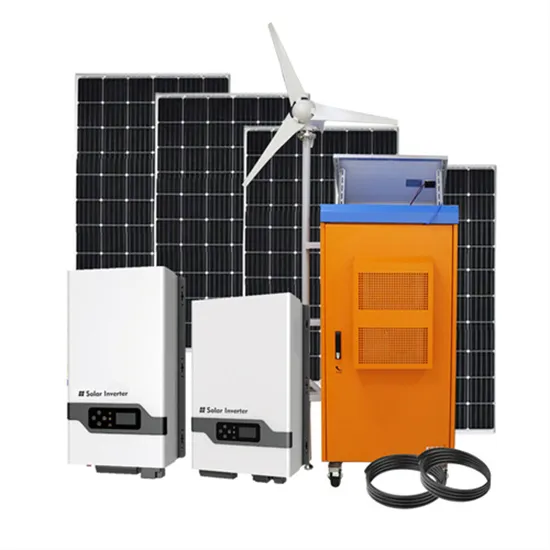
A Guide to Solar Inverters: How They Work & How to
What is a solar power inverter? How does it work? A solar inverter is really a converter, though the rules of physics say otherwise. A solar power inverter
Get a quote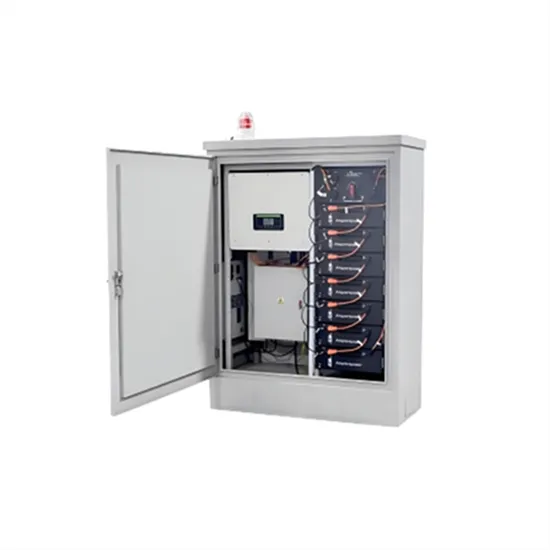
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
An inverter (or power inverter) is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage. While DC power is common
Get a quote
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
The nominal AC output power represents the rated power output of the solar inverter under standard operating conditions. It indicates the maximum power
Get a quote
What is the output voltage of the inverter? Learn some
When installing an inverter for the motor, it usually saves more than 10% of the power consumption. The output characteristic is not the usual sinusoidal AC
Get a quote
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
The output voltage and current waveform of the inverter circuit, vo, and io respectively, are assumed to be AC quantities. These are stated in terms of RMS values normally while the
Get a quote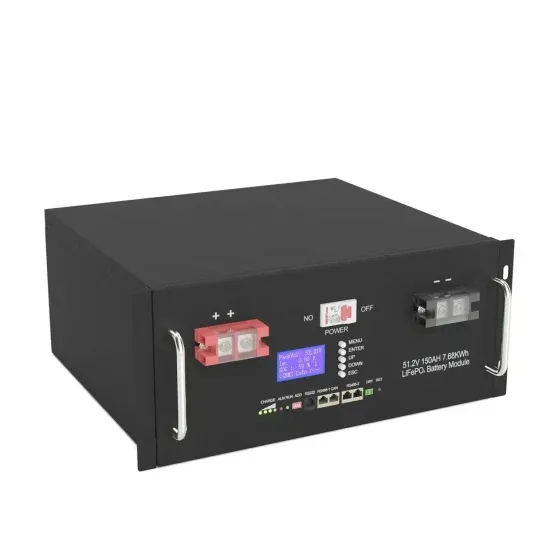
Voltage Control Using Inverter Reactive Power Control
4. Constant reactive power mode In this mode, the inverter either injects or absorbs a constant amount of reactive power, independent of real
Get a quote
Troubleshooting Inverter Problems: A Step-by-Step Guide
Inverters play a crucial role in many modern systems, converting DC power from sources like batteries or solar panels into AC power that can be used by household
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What voltage does the inverter output ]
What is the output voltage of an inverter?
It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC). The output voltage of an inverter is determined by the DC input voltage and the modulation index.
What do you need to know about input power inverters?
Here are some important specifications that you need to know about input power inverters. Input Voltage: The input voltage supplied from the DC source to the inverter follows the inverter voltage specifications, which start from 12V, 24V, or 48V.
How does a power inverter work?
The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry. The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source.
How much power does an inverter need?
It’s important to note what this means: In order for an inverter to put out the rated amount of power, it will need to have a power input that exceeds the output. For example, an inverter with a rated output power of 5,000 W and a peak efficiency of 95% requires an input power of 5,263 W to operate at full power.
How does a battery affect the output power of an inverter?
The continuous output power of any inverter can be influenced by the battery providing the DC input voltage. The battery must be sufficiently large to supply the high current required by a sizable inverter without causing the battery voltage to drop excessively low, which could lead to the inverter shutting down.
How do inverter input and output work?
They work by converting the power obtained from the DC source, which is the input source of the inverter, into AC, which is the output source of the inverter, and then distributing it to various devices that require AC sources. In this article, we will discuss inverter input and output and their relationships. What is an Inverter Input?
Guess what you want to know
-
 What voltage does the inverter output
What voltage does the inverter output
-
 What does a wide voltage inverter mean
What does a wide voltage inverter mean
-
 Is the inverter output voltage 233v normal
Is the inverter output voltage 233v normal
-
 Inverter working output voltage is high
Inverter working output voltage is high
-
 New energy inverter output voltage
New energy inverter output voltage
-
 Inverter has voltage output
Inverter has voltage output
-
 How much is the inverter output voltage adjusted to
How much is the inverter output voltage adjusted to
-
 What is the voltage of a 7800w inverter
What is the voltage of a 7800w inverter
-
 What is the output voltage of a 3-watt photovoltaic panel
What is the output voltage of a 3-watt photovoltaic panel
-
 Is there voltage on one side of the inverter output
Is there voltage on one side of the inverter output
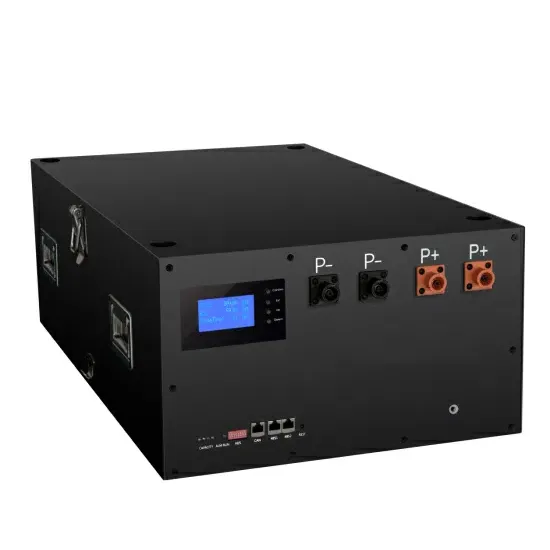
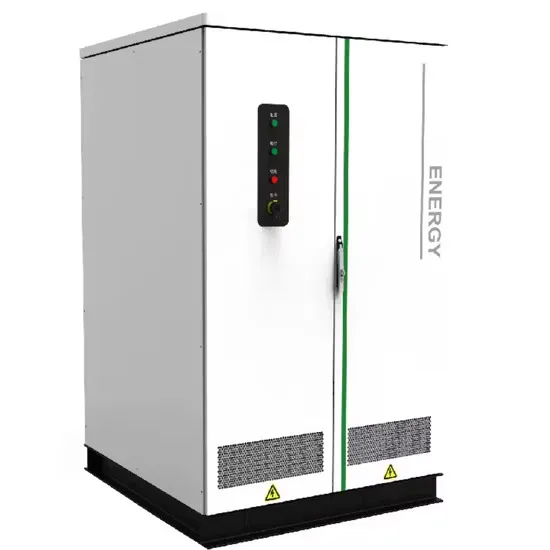
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


