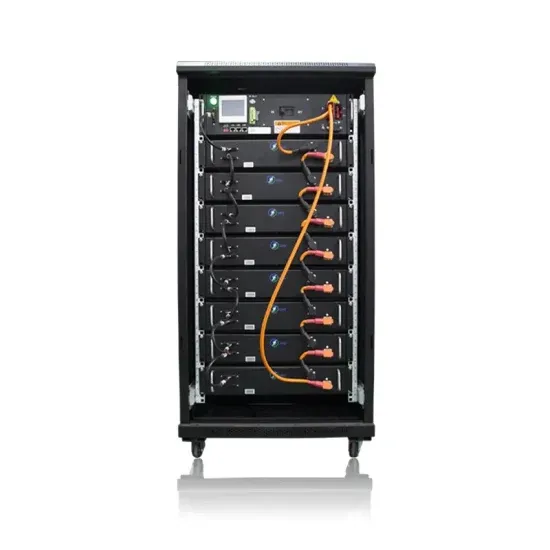
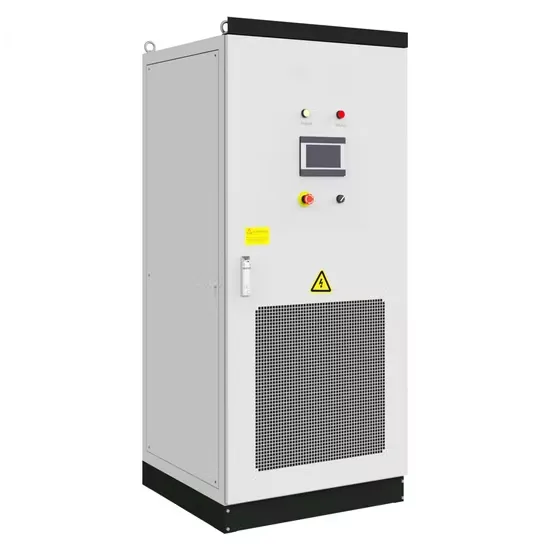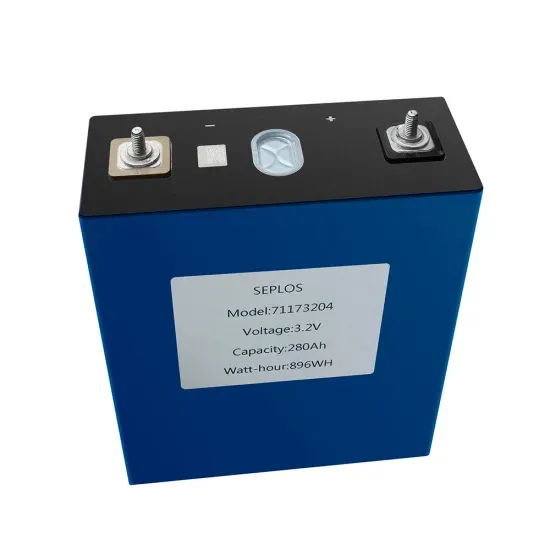
32 Common Faults in Inverters and Their Solutions
When the inverter is in operation, a low output voltage from a unit can lead to a three-phase output imbalance, resulting in an over-voltage unit
Get a quote
Inverter Voltage Calculator, Formula, Inverter Voltage Calculation
It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC). The output voltage of an inverter is
Get a quote
What is the Peak Output Power of a Power Inverter?
The continuous output power is the rated output power, and the peak output power is generally twice the rated output power. It is worth mentioning that the operating
Get a quote
Understanding inverter voltage
A 12V to 240V inverter is a pivotal device designed to convert direct current (DC) power from a 12-volt battery into alternating current (AC) power with a nominal output of 240 volts.
Get a quote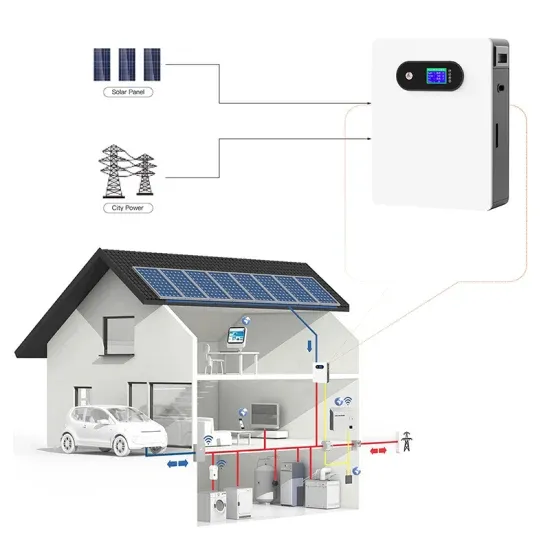
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
Maximum Power Point Tracking or MPPT refers to the optimal voltage level at which the inverter can extract the most power from the solar panels. So, for efficient power
Get a quote
How to Troubleshoot and Fix Common Inverter Problems
Here are some steps to follow: Check the input voltage. The input voltage to the inverter should be within the specified range. If the input voltage is too low or
Get a quote
Why there is no output voltage after the inverter is powered on?
According to the working flow of the inverter circuit, the driving pulse required by the inverter circuit is generated by the CPU and is amplified by the drive circuit. Therefore, the
Get a quote
I have voltage on my neutral wire for a 220 volt ac inverter and
Why does my white neutral conductor has voltage on it? Is a 220 VAC from a DC to AC Inverter circuit supply. The outlet is like a normal American 110 VAC socket but I requested
Get a quote
Power inverter
OverviewInput and outputBatteriesApplicationsCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.
Get a quote
An inverter has a periodic output voltage with the output
An inverter has a periodic output voltage with the output waveform as shown in figure. When the conduction angle α = 120°, the rms fundamental component of the output voltage is
Get a quote
What Are The Components Of An Inverter
Discover what are the components of an inverter, including the DC input source, power electronics circuit, and control systems. Learn how inverters transform DC to AC power
Get a quote
Power inverter
The input voltage, output voltage and frequency, and overall power handling depend on the design of the specific device or circuitry. The inverter does not produce any power; the power
Get a quote
Inverter has no output voltage
VPIC has received some questions about the status of the inverter without output voltage from you. Today, we will clearly explain the cause and show you how to fix it.
Get a quote
Single Phase Half Bridge Inverter | R Load | RL Load
The output voltage waveform (rectangular) and various current waveforms for different load characteristics are drawn in Fig. 11.47 (b)- (f). In the Single
Get a quote
Single-Phase Inverters
Inverters are crucial components in power electronics because they transform DC input voltage to AC output voltage. Talking about single-phase inverters, these convert a DC input source into
Get a quote
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working
Get a quote
CHAPTER4
the input voltage a three-phase inverter has to be used. The inverter is build of switching devices, thus the way in which the switching takes place in the inverter gives the required output. In this
Get a quote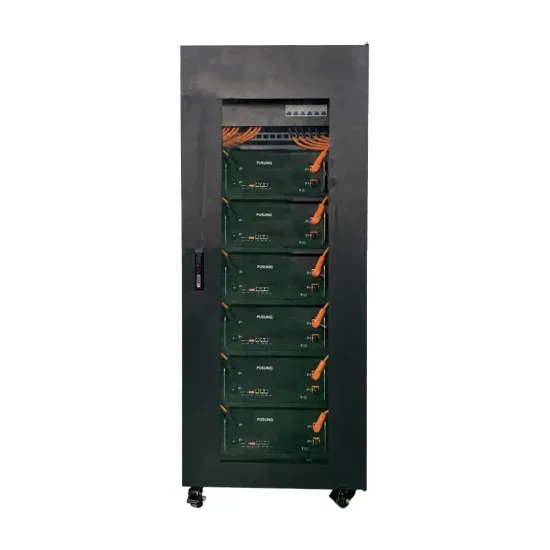
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and
Get a quote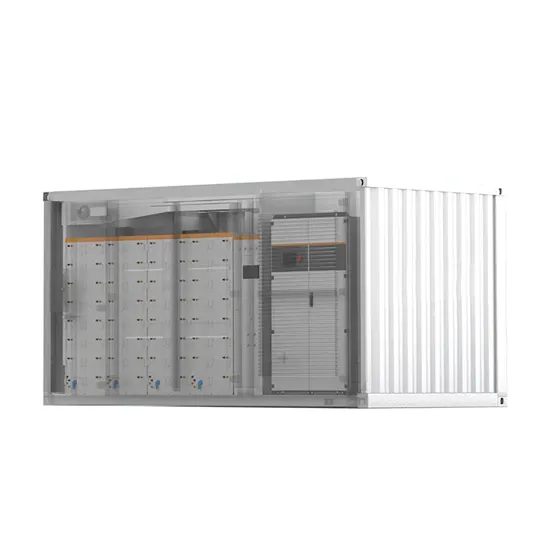
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
According to the output voltage and current phases, inverters are divided into two main categories. Single-phase inverters and three-phase inverters. These
Get a quote
What does the inverter voltage specifications represent?
This is the inverter''s AC range (relating to its nominal output). Since grid voltage fluctuates constantly, the inverter has to adjust to that voltage within a given window. For instance, the
Get a quote
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
According to the output voltage and current phases, inverters are divided into two main categories. Single-phase inverters and three-phase inverters. These categories are briefly
Get a quote
Interpreting inverter datasheet and main parameters | AE 868
Inverter Start-up voltage Aside from the operating voltage range, another main parameter is the start-up voltage. It is the lowest acceptable voltage that is needed for the inverter to kick on.
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The ability of an inverter to accurately convert DC to AC, operate within specified voltage and current limits, and incorporate safety and control features such as MPPT, transfer switches,
Get a quote
Why there is no output voltage after the inverter is
According to the working flow of the inverter circuit, the driving pulse required by the inverter circuit is generated by the CPU and is amplified by the
Get a quote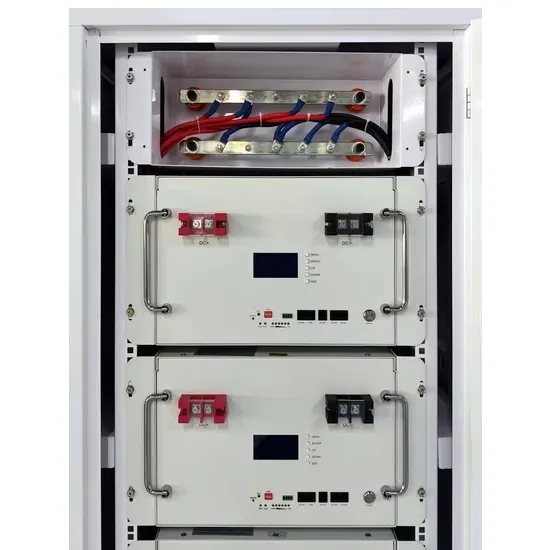
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
VPIC has received some questions about the status of the inverter without output voltage from you. Today, we will clearly explain the cause and show you how
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Inverter has voltage output]
What is the output voltage of an inverter?
It describes the output voltage of an inverter, which converts direct current (DC) from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC). The output voltage of an inverter is determined by the DC input voltage and the modulation index.
What do you need to know about input power inverters?
Here are some important specifications that you need to know about input power inverters. Input Voltage: The input voltage supplied from the DC source to the inverter follows the inverter voltage specifications, which start from 12V, 24V, or 48V.
What are the characteristics of an output inverter?
The output produced by the inverter is an alternating current (AC) that is usually used to power various kinds of electronic devices needed in everyday life such as lights, fans, televisions, and so on. Here are some characteristics of the output inverter. Output Voltage: must match the connected device to prevent damage.
What is an example of a power inverter?
Common examples are refrigerators, air-conditioning units, and pumps. AC output voltage This value indicates to which utility voltages the inverter can connect. For inverters designed for residential use, the output voltage is 120 V or 240 V at 60 Hz for North America. It is 230 V at 50 Hz for many other countries.
How do inverter input and output work?
They work by converting the power obtained from the DC source, which is the input source of the inverter, into AC, which is the output source of the inverter, and then distributing it to various devices that require AC sources. In this article, we will discuss inverter input and output and their relationships. What is an Inverter Input?
What is a power inverter?
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Inverter output voltage is slow
Inverter output voltage is slow
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
 Inverter has voltage output
Inverter has voltage output
-
 Is the inverter voltage output high or low
Is the inverter voltage output high or low
-
 Inverter output 800v voltage
Inverter output 800v voltage
-
 Inverter working output voltage is high
Inverter working output voltage is high
-
 The inverter has a high voltage output
The inverter has a high voltage output
-
 Inverter voltage output is too low
Inverter voltage output is too low
-
 Inverter output voltage returns to zero
Inverter output voltage returns to zero
-
 Does the inverter output have fine-tuning voltage
Does the inverter output have fine-tuning voltage
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


