Comparing Inverter Solutions: Silicon vs. Wide
This article explores the differences between inverters based on silicon power devices and those utilizing WBG technologies, evaluating their
Get a quote
Advantages and Disadvantages of Multilevel Inverter
In recent years, multilevel inverters have grown in popularity in medium and high-power applications. There are several advantages of multilevel inverters over two-level
Get a quote
Induction Coil Design Considerations for High
The use of wide band gap (WBG) semiconductor switches in power converters is increasing day by day due to their superior chemical and
Get a quote
Review on Silicon Carbide based High-Fundamental
ABSTRACT This article provides a comprehensive review of Silicon Carbide (SiC) based inverters designed for High-Speed (HS) drive applications, which require higher output frequencies to
Get a quote
Review on Multilevel Inverters: Topologies, Control and
Each type of multilevel inverter has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of a specific topology depends on factors such as the application requirements, voltage levels
Get a quote
SiC MOSFET vs. Si IGBT: SiC MOSFET advantages
Two types of inverters are used in modern DC to AC motor drive applications: silicon IGBTs and silicon carbide MOSFETs. Historically, Si IGBTs are the most common, but
Get a quote
Drawbacks and Benefits of High Switching Frequency
I was reading about Benefits of High Switching Frequency, I found the following: Smaller converter can be cheaper – up to a certain power
Get a quote
Advantages of Low Frequency Inverters vs. High Frequency Inverters
Inverters can be classified into two main types: low frequency inverters and high frequency inverters. Each type of inverter has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high
Get a quote
Review on Silicon Carbide-Based High-Fundamental Frequency Inverters
The review analyzes approximately 70 recent three-phase SiC inverter designs, categorizing them by topology, specifically two-level, Neutral Point Clamped (NPC), T-type, and Multilevel, and
Get a quote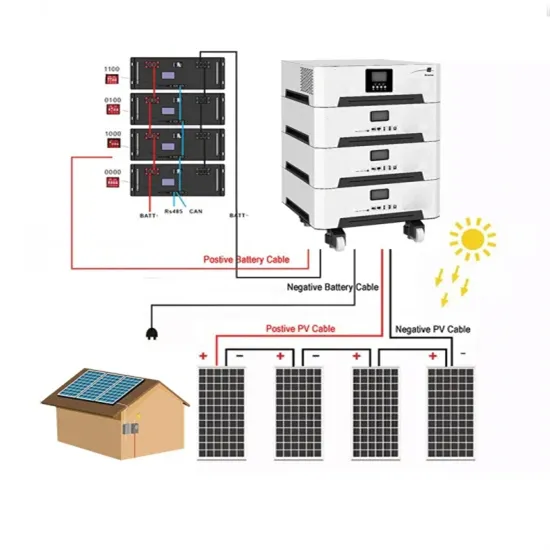
Types of Deye Hybrid Inverters: Features and Benefits Explained
Discover the different types of Deye hybrid inverters, their features, and how they can help optimize your solar energy system for better efficiency and savings.
Get a quote
SiC MOSFET vs. Si IGBT: SiC MOSFET advantages
Two types of inverters are used in modern DC to AC motor drive applications: silicon IGBTs and silicon carbide MOSFETs. Historically, Si
Get a quote
AN-1973 Benefits and Challenges of High-Frequency
Besides solution size, a well-designed high switching frequency regulator has the advantage of a faster transient response and reduced output voltage ripple. There are a few considerations to
Get a quote
A Practical Study on Three-Level Hybrid SiC/Si Inverters
A Practical Study on Three-Level Hybrid SiC/Si Inverters This article highlights Infineon Technologies Italia S.r.l - Austria AG demonstration of the
Get a quote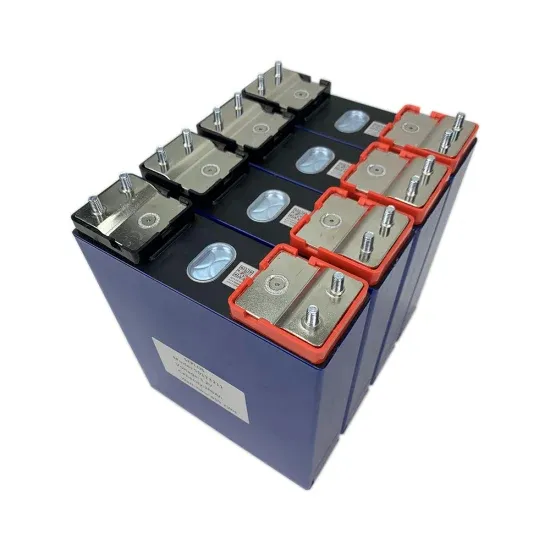
Inverter types and classification | AE 868: Commercial Solar
Now that we understand why we need an inverter for PV systems, it is time to introduce the different types of inverters that exist in the market and discover the advantages and
Get a quote
Ferrite Core Transformers: Their Pros, Cons & Uses
Ferrite core transformers are a cornerstone of modern electronic devices, offering numerous advantages due to their unique material
Get a quote
Comparing Inverter Solutions: Silicon vs. Wide Bandgap Power
This article explores the differences between inverters based on silicon power devices and those utilizing WBG technologies, evaluating their advantages, disadvantages,
Get a quote
Multilevel Inverter
A multilevel converter has several advantages over a conventional two-level converter that uses high switching frequency pulse width modulation (PWM). The attractive features of a multilevel
Get a quote
SCR as a Switch, its Advantages, Disadvantages and
A Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) is a switch to control power flow. It conducts when triggered and remains on until the current drops below
Get a quote
(PDF) Review on Silicon Carbide based High-Fundamental
Furthermore, the paper reviews industrial SiC prototypes, recent advancements in SiC device technologies, and various configurations (discrete, parallel, and module),
Get a quote
(PDF) Review on Silicon Carbide based High-Fundamental Frequency
Furthermore, the paper reviews industrial SiC prototypes, recent advancements in SiC device technologies, and various configurations (discrete, parallel, and module),
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency Inverter: Which is
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high efficiency, but they also have the
Get a quote
Silicon (Si): 5 Advantages and Disadvantages
Explore 5 key advantages and disadvantages of silicon (Si) in various applications. Learn about its properties, advantages, and disadvantages.
Get a quote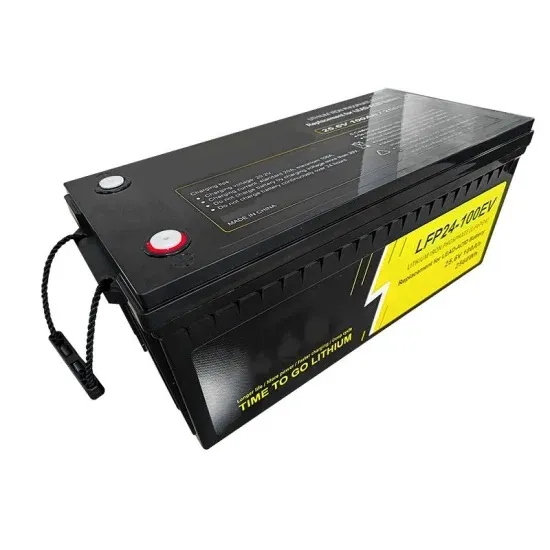
Review on Silicon Carbide based High-Fundamental
ABSTRACT This article provides a comprehensive review of Silicon Carbide (SiC) based inverters designed for High-Speed (HS) drive applications, which require higher output frequencies to...
Get a quote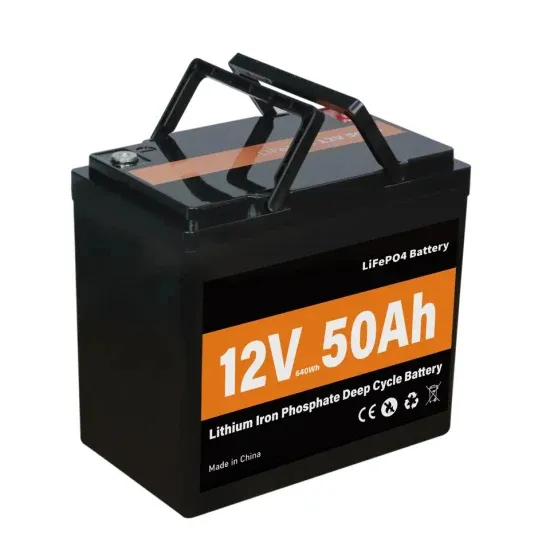
Drawbacks and Benefits of High Switching Frequency
So different operating frequencies each have their own challenges; start-up is particularly difficult at higher operating frequencies and some converters utilise for times when
Get a quote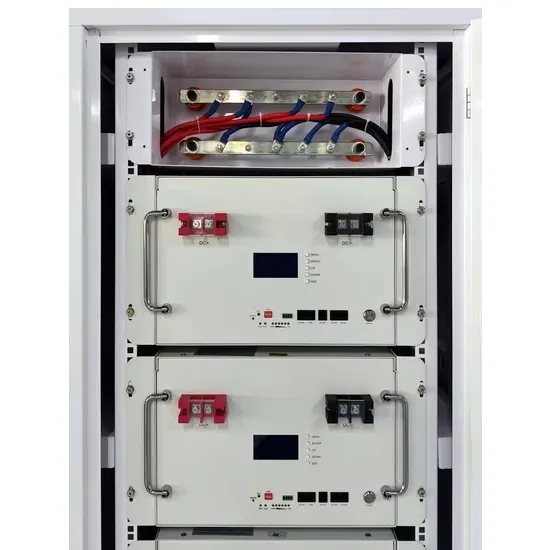
GaN Advantages and Disadvantages
GaN Advantages GaN devices have a variety of advantages, making them especially suited to a variety of applications. Significant GaN advantages include: High
Get a quote
Voltage Fed Full Bridge DC-DC & DC-AC Converter High
ABSTRACT The High-Frequency Inverter is mainly used today in uninterruptible power supply systems, AC motor drives, induction heating and renewable energy source systems. The
Get a quote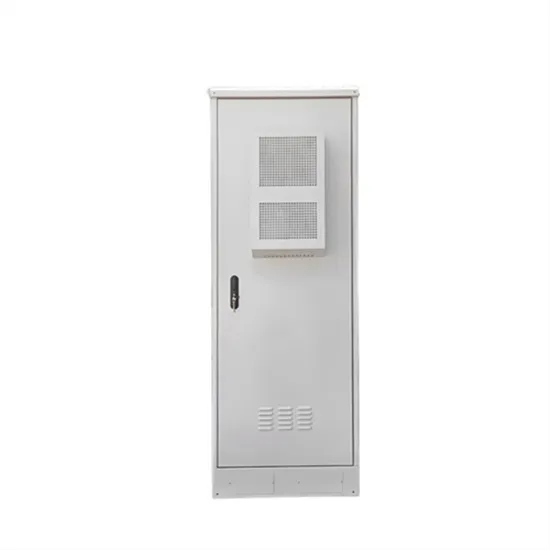
Review on Silicon Carbide-Based High-Fundamental Frequency
The review analyzes approximately 70 recent three-phase SiC inverter designs, categorizing them by topology, specifically two-level, Neutral Point Clamped (NPC), T-type, and Multilevel, and
Get a quote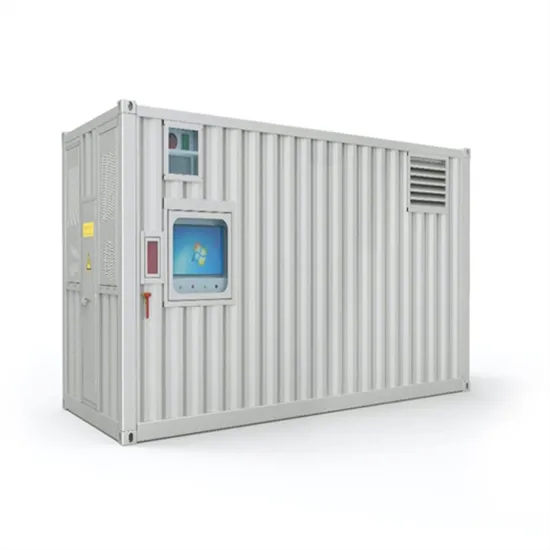
6 FAQs about [Advantages and disadvantages of dual silicon high frequency inverter]
What are the advantages of high frequency inverters?
Volume and weight: Since high frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology and compact circuit design, their size and weight are usually much smaller than power frequency inverters. This gives high frequency inverters significant advantages in mobile power supplies, aerospace, electric vehicles, and other fields.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a multilevel converter?
Switching frequency: Multilevel converters can operate at both fundamental switching frequency and high switching frequency PWM. It should be noted that lower switching frequency usually means lower switching loss and higher efficiency. Unfortunately, multilevel converters do have some disadvantages.
Are high-frequency inverters a good choice?
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high efficiency, but they also have the problem of relatively poor output waveform quality.
Why do silicon based inverters require bulky cooling solutions?
The relatively slow switching frequency of IGBTs results in higher energy losses in applications demanding rapid switching, such as high-speed motor drives. Additionally, silicon-based inverters often require bulky cooling solutions due to higher heat dissipation, which increases system size and weight.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a WBG based inverter?
Currently, GaN is utilized in DC/DC converters and on-board chargers, where its higher switching frequency (with high du/dt values) offers the greatest advantages. Despite these advantages, WBG-based inverters come with challenges. The higher cost of SiC and GaN devices compared to silicon counterparts remains a barrier to widespread adoption.
What are the disadvantages of a multilevel inverter?
Multilevel inverters (MLI) have become increasingly popular in recent years for medium voltage and high-power applications. However, these devices also come with a number of other built-in disadvantages, such as a greater number of switches, a greater need for sources, and intricate control mechanisms.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Is the Swedish 299A high frequency inverter a dual silicon inverter
Is the Swedish 299A high frequency inverter a dual silicon inverter
-
 Simple sinusoidal high frequency inverter design
Simple sinusoidal high frequency inverter design
-
 Pulse inverter is divided into high frequency and low frequency
Pulse inverter is divided into high frequency and low frequency
-
 Taipei No 3 38000v high frequency inverter
Taipei No 3 38000v high frequency inverter
-
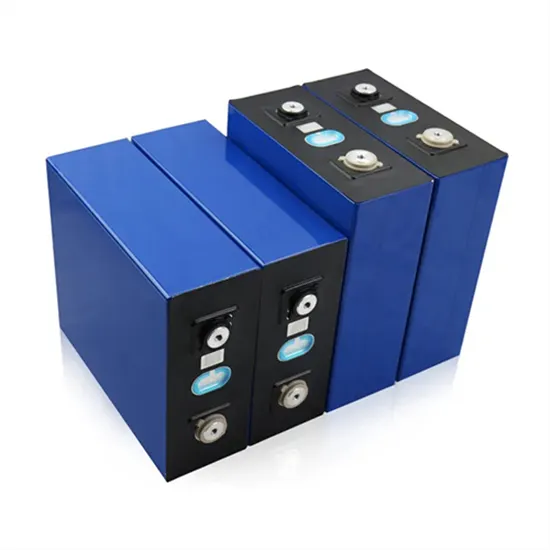 High frequency inverter continuously turned on
High frequency inverter continuously turned on
-
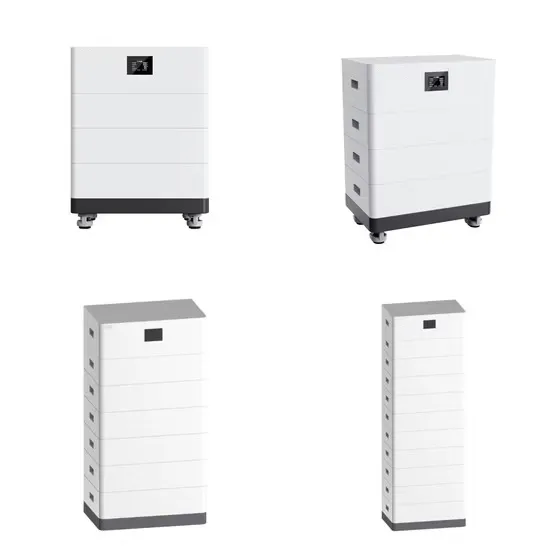 High frequency inverter quality
High frequency inverter quality
-
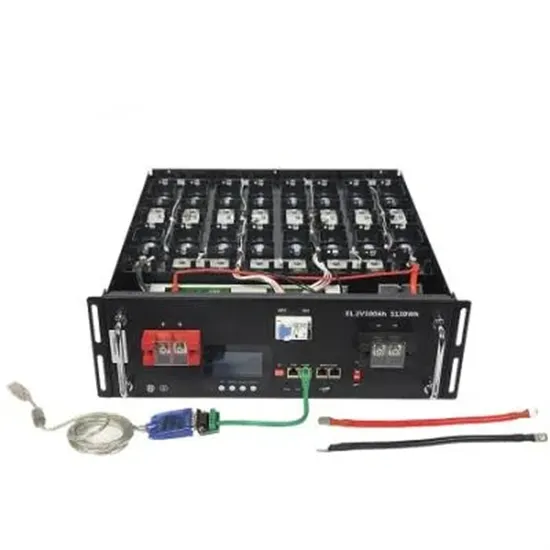 5kva high frequency power inverter
5kva high frequency power inverter
-
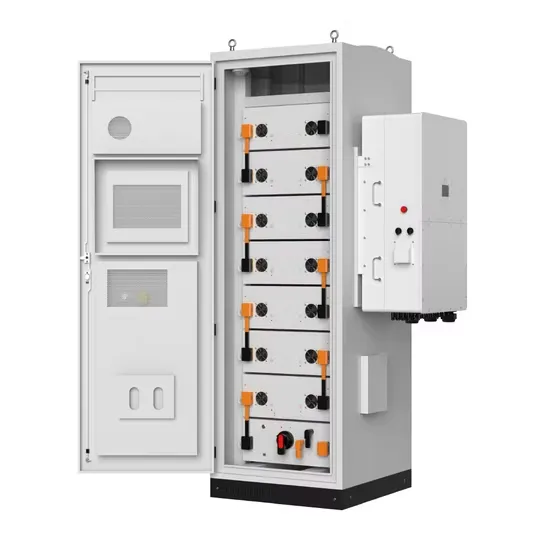 Which energy storage inverter is better power frequency or high frequency
Which energy storage inverter is better power frequency or high frequency
-
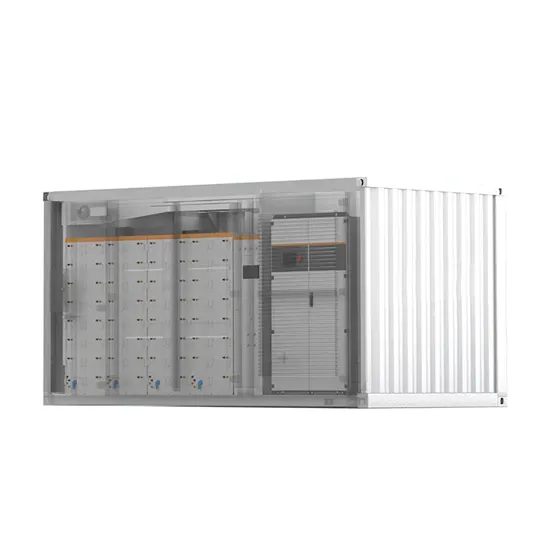 High frequency inverter 38kw
High frequency inverter 38kw
-
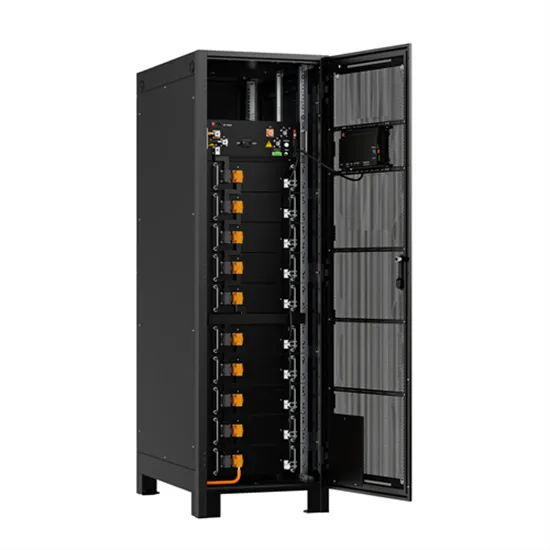 52Hz low frequency high efficiency home inverter
52Hz low frequency high efficiency home inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
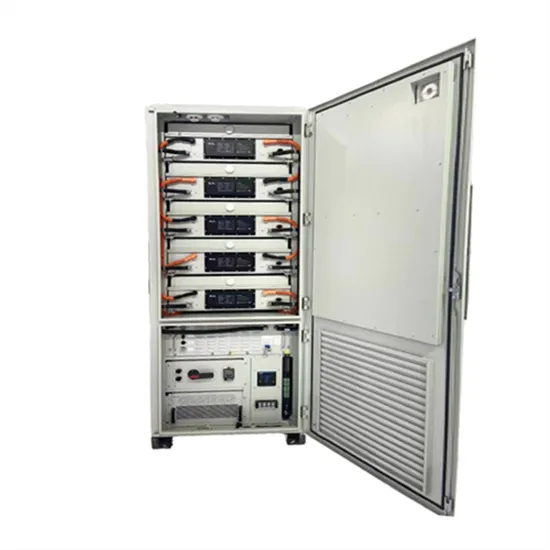
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


