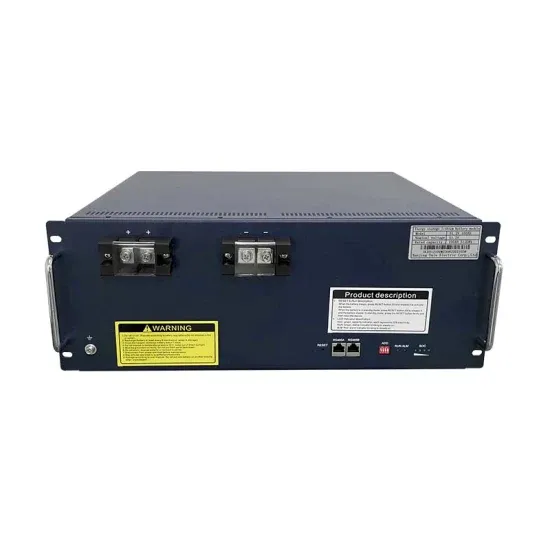
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Learn the key differences between high frequency inverters and low frequency inverters. Discover which one suits your power needs for efficiency and surge capacity.
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Line-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters: A Technical Deep Dive for Engineers In the world of power electronics, the inverter is a cornerstone technology, responsible for the
Get a quote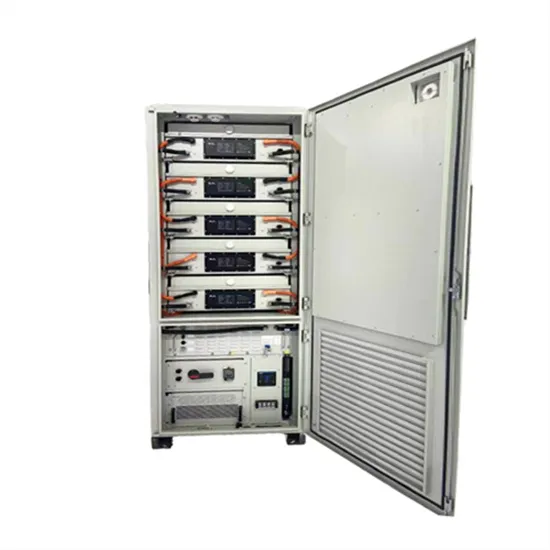
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High
High-frequency inverters represent a more modern approach, engineered to overcome the size and weight limitations of their line-frequency counterparts. The topology is
Get a quote
Inverters High or Low Frequency
Largely the high frequency inverter area is dominated by Chinese manufacturers that produce in general poor quality devices, but they are cheap. The more expensive quality
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
Yes, high-frequency inverters are generally more efficient, often achieving up to 95-99% efficiency compared to low-frequency models. Their smaller transformers and faster switching reduce
Get a quote
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size and weight, etc., and compares
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
Yes, high-frequency inverters are generally more efficient, often achieving up to 95-99% efficiency compared to low-frequency models. Their
Get a quote
Comparing Carrier-Based PWM Techniques in High
This article explores the potential of carrier-based pulse width modulation techniques such as sawtooth, triangular, and sinusoidal, and
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
High-frequency inverters represent a more modern approach, engineered to overcome the size and weight limitations of their line-frequency counterparts. The topology is
Get a quote
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size
Get a quote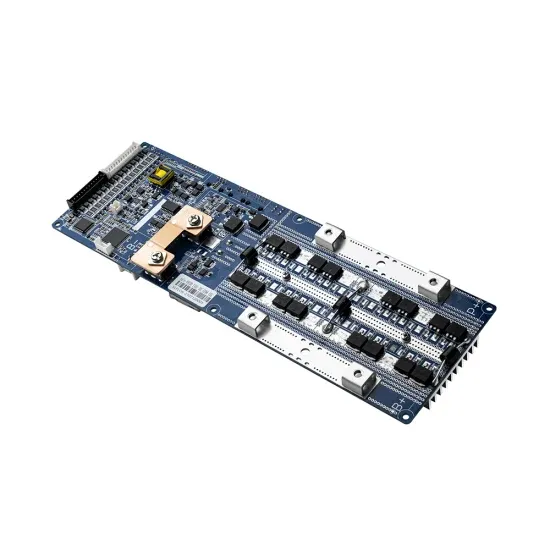
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in Modern
High-frequency inverters are known for their high efficiency, which is one of their most significant advantages. By operating at higher frequencies, typically in
Get a quote
Performance evaluation of hybrid multilevel inverter with a high
This proposed work deals with the implementation of a single-phase topology with using hybrid for multilevel inverters. It is observed that the proposed structure improves the
Get a quote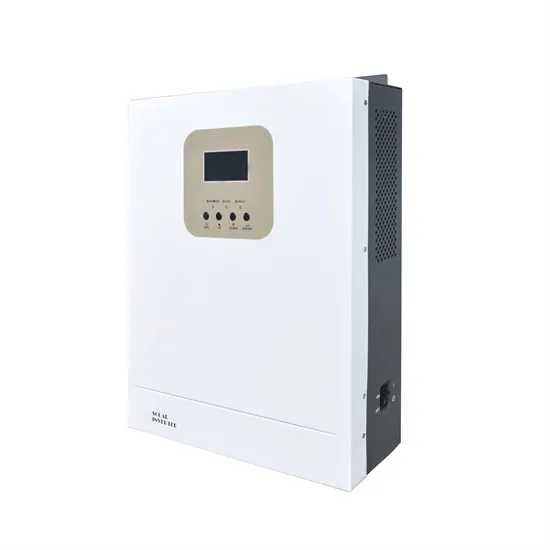
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get a quote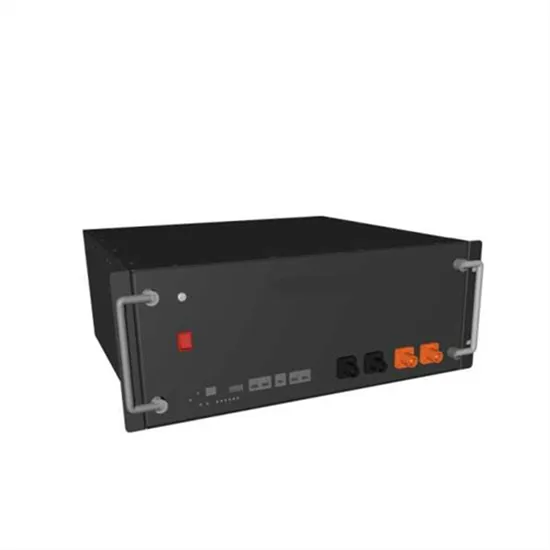
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Introduction What is a High Frequency Inverter? What is a Low Frequency Inverter? Introduction By the early 1980s, pure sine wave inverters had become more commercially available,
Get a quote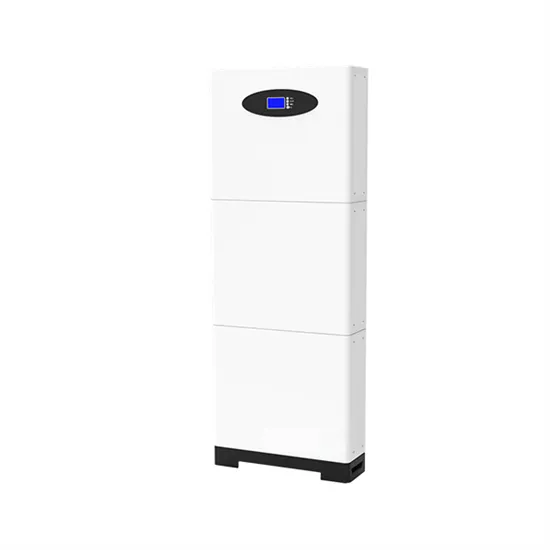
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
High-frequency inverters are well-suited for applications requiring a pure sine wave output, high efficiency, and a compact size. These inverters are ideal for powering sensitive electronic
Get a quote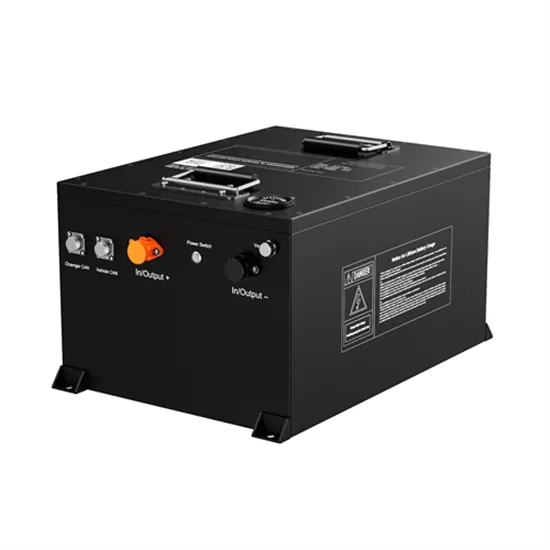
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
With the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the benefits of compact size, high efficiency, and lightweight but also have the
Get a quote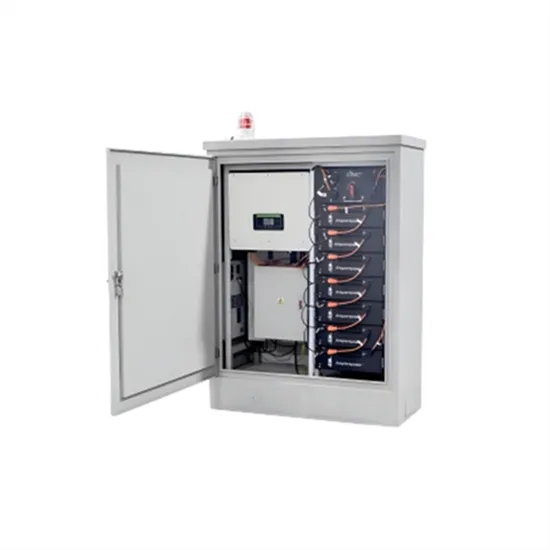
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
High-frequency inverters are well-suited for applications requiring a pure sine wave output, high efficiency, and a compact size. These inverters are ideal for
Get a quote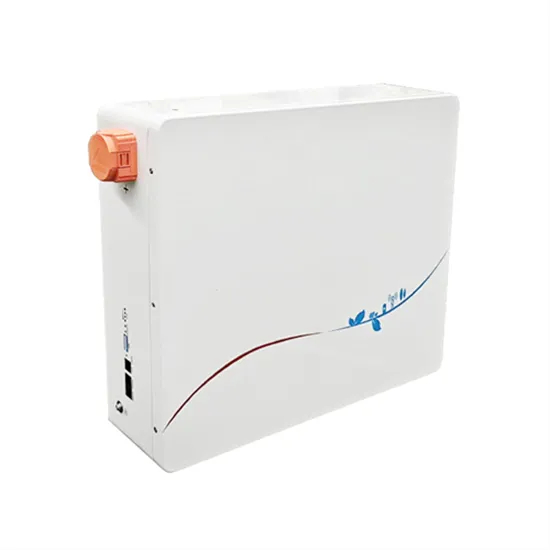
Circuit structure of high-frequency inverter.
Download scientific diagram | Circuit structure of high-frequency inverter. from publication: Power Quality Control System of High-Power-Density Switching
Get a quote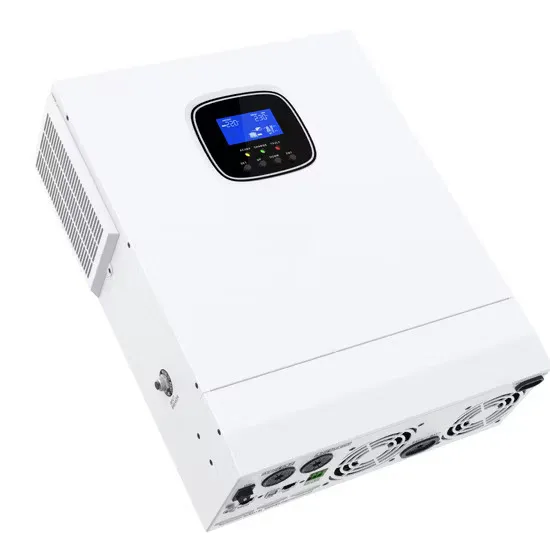
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency, typically above 20
Get a quote
What''s The Difference between A High Frequency And Low Frequency
In contrast, low-frequency inverters provide a stable and consistent performance, which is ideal for applications where power quality is of utmost importance. Their efficiency may be slightly lower
Get a quote
Frequency vs High-Frequency Inverters: The Best Choice for Off
Discover why frequency inverters excel in off-grid use with superior shock resistance, stable inductive load performance, and long lifespan. Make smarter choices for reliable power.
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get a quote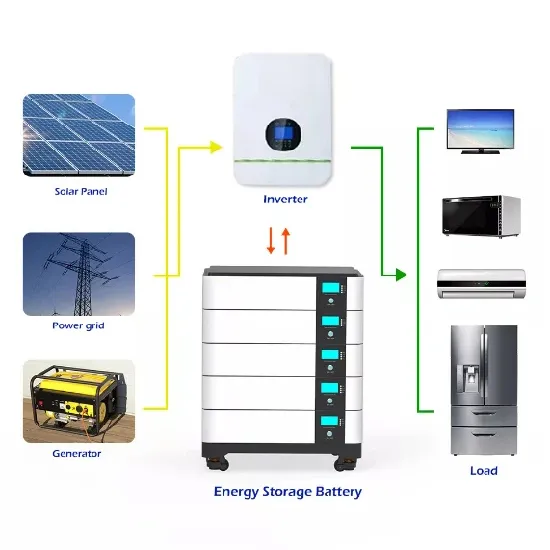
Low vs High frequency inverters | DIY Solar Power Forum
If you intend to run high inductive loads such as motors found on AC watermakers, a low frequency inverter will be more reliable. If you just want to run resistive loads like water
Get a quote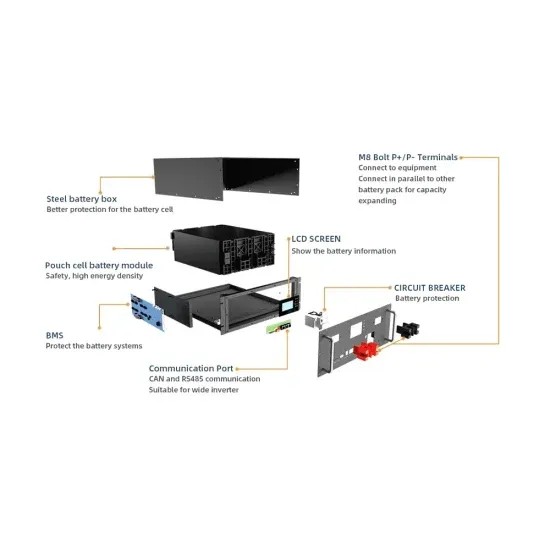
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in Modern Applications
High-frequency inverters are known for their high efficiency, which is one of their most significant advantages. By operating at higher frequencies, typically in the range of tens or hundreds of
Get a quote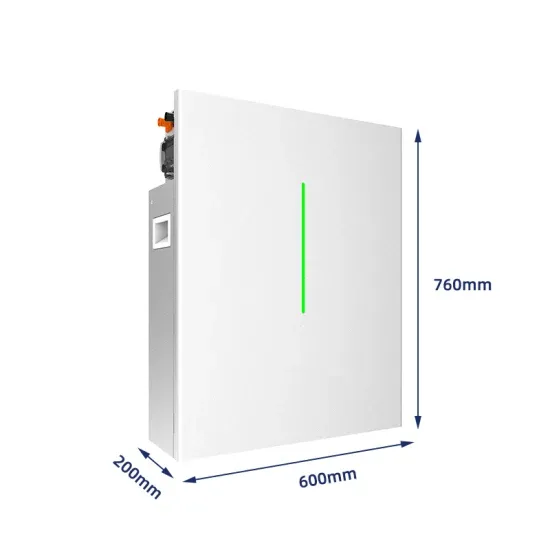
Impact of Multiple Grid-Connected Solar PV Inverters
This paper evaluates the behaviour of high-frequency harmonics in the 2–20 kHz range due to the parallel operation of multiple solar PV
Get a quote
High Frequency Inverters Supplier Nigeria | Vantom Power
Looking for the best high-frequency inverters in Nigeria? Find top-quality inverters from the leading solar energy system manufacturer.
Get a quote
Everything to Know Low Frequency Inverters
Low-frequency inverters, characterized by their use of transformers for electrical isolation, play a crucial role in a variety of high-reliability applications. This
Get a quote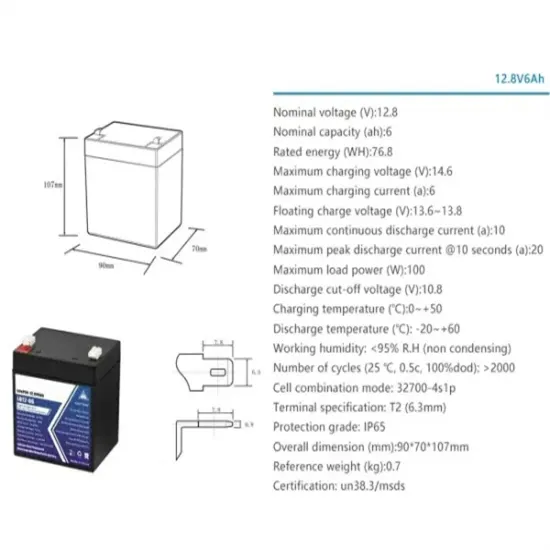
High Frequency Inverters Supplier in Ghana | Vantom Power
Looking for the best high-frequency inverters in Ghana? Find top-quality inverters from the leading solar energy system manufacturer.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [High frequency inverter quality]
Are high-frequency inverters better than low-frequency?
Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers. Efficiency: High-frequency inverters are generally more efficient than low-frequency inverters for maintaining a constant load for lighter loads. However, they may struggle with high surge currents or heavy loads.
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
Why are high frequency inverters more efficient?
In contrast, high-frequency inverters can use smaller-sized and lighter-weight components due to their use of higher frequencies, resulting in smaller overall size and weight. Efficiency: Since the high frequency inverter uses high-frequency switches for inversion, its switching loss is relatively small, so it has higher conversion efficiency.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Efficiency: Low-frequency inverters are known for their robustness and ability to handle high surge currents, making them suitable for powering heavy-duty appliances or equipment with high starting currents, such as motors and compressors.
Does victron use a high frequency inverter?
Victron combines both inverters, which they call Hybrid HF or Combined high frequency and line frequency technologies. What frequency inverter does growatt use? Growatt uses a high-frequency inverter. Which one is best? Low or high frequency? The best inverter is the low-frequency inverter.
How much does a high frequency inverter weigh?
That unit (Phocos PSW-H 5kw/120v) weighs around 110 lbs. I'm also considering it for my off-grid build, but I believe high frequency inverters generally weigh less and can double power on a surge for a couple seconds.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Which energy storage inverter is better power frequency or high frequency
Which energy storage inverter is better power frequency or high frequency
-
 Timor-Leste 110kw high quality inverter for sale
Timor-Leste 110kw high quality inverter for sale
-
 Korea 15kw high quality inverter quotation
Korea 15kw high quality inverter quotation
-
 Cambodia high frequency power inverter
Cambodia high frequency power inverter
-
 Dominican 45kw high quality inverter quotation
Dominican 45kw high quality inverter quotation
-
 High frequency inverter square wave
High frequency inverter square wave
-
 Grenada high frequency inverter installation
Grenada high frequency inverter installation
-
 Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
-
 Yaounde 30kw high quality inverter price
Yaounde 30kw high quality inverter price
-
 High frequency inverter produces 1200v
High frequency inverter produces 1200v
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


