Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Which One Is Best?
There are two main types of frequencies to be compared: low frequency vs high frequency inverters. The inverter frequency determines the desired application''s compatibility, efficiency,
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
Here, we will provide a detailed comparison and analysis of these two inverters from multiple scenarios and perspectives to better understand power-frequency inverters and
Get a quote
Why Frequency Inverters Are More Suitable for Off-Grid
The power frequency inverter has a strong impact resistance due to the use of a large-capacity power frequency transformer, which can easily cope with the current shock generated by the
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
Among them, power frequency inverter and high frequency inverter are two common inverter types, each with different characteristics and
Get a quote
MDT-MVMD-based frequency modulation for photovoltaic energy storage
Due to the rapid advances in renewable energy technologies, the growing integration of renewable sources has led to reduced resources for Fast Frequency Response
Get a quote
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Which
There are two main types of frequencies to be compared: low frequency vs high frequency inverters. The inverter frequency determines the desired
Get a quote
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency Inverters and High
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power efficiency, space saving, or suitability for...
Get a quote
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Learn the key differences between high frequency inverters and low frequency inverters. Discover which one suits your power needs for efficiency and surge capacity.
Get a quote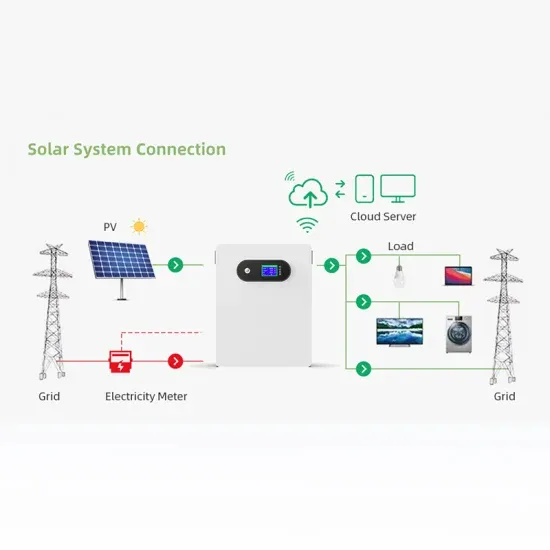
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get a quote
Frequency vs High-Frequency Inverters: The Best Choice for Off
With the rapid development of renewable energy worldwide, solar inverters have become a core component of off-grid power systems. As an importer, choosing the right off-grid inverter often
Get a quote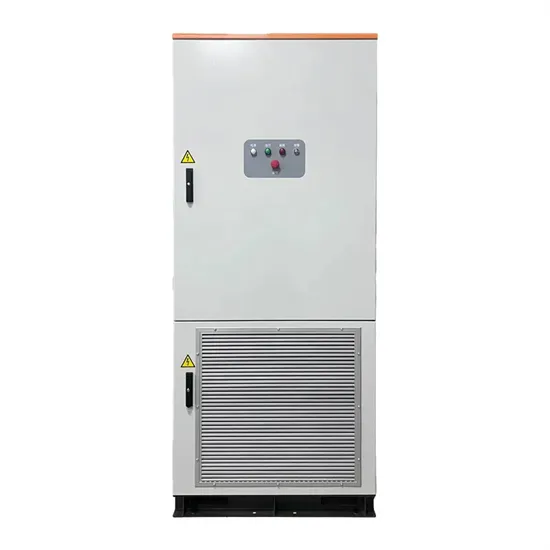
Fast Grid Frequency Support from Distributed Energy
A mathematical (eigenvalue) analysis of the frequency stability of power systems containing both conventional generation and high levels of inverter-based resources with
Get a quote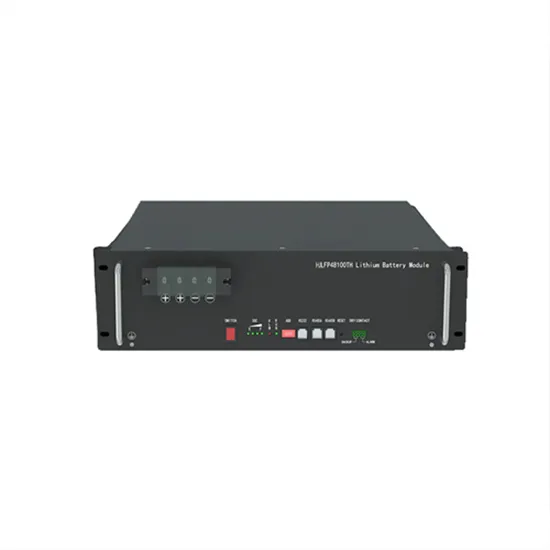
Inverter Competition: Comparison of High Frequency and Power Frequency
High-frequency inverters provide a greater conversion efficiency and are smaller in size. The frequency of power frequency inverter is usually around 50Hz, while the frequency of
Get a quote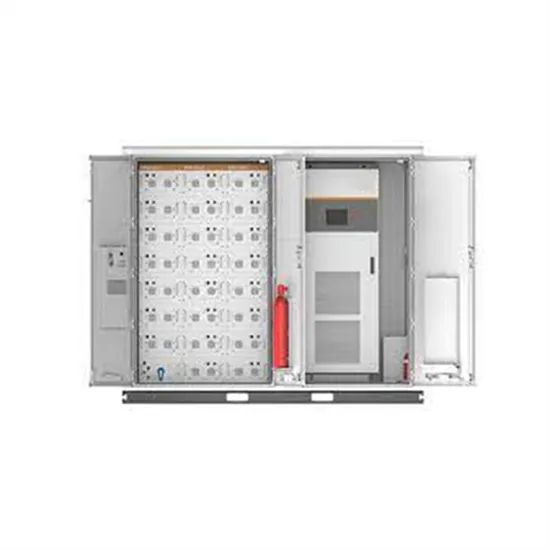
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get a quote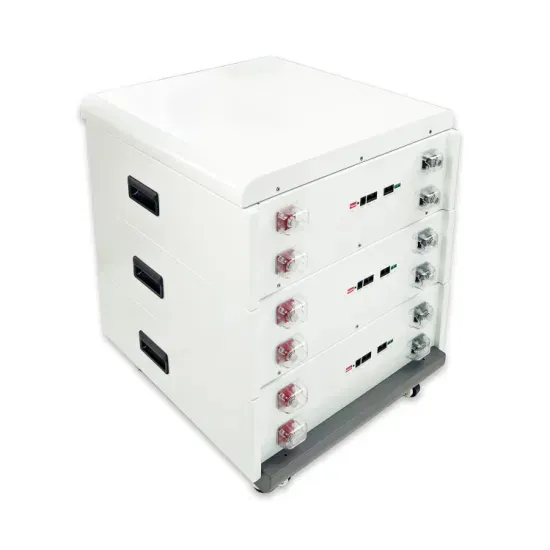
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power
Get a quote
Difference Between High-Frequency (HF) and Low-Frequency
Are you trying to figure out the differences between High-Frequency (HF) and Low Frequency (LF) Solar Inverters? Choosing the right one can be a bit confusing,especially if
Get a quote
Inverter Competition: Comparison of High Frequency
High-frequency inverters provide a greater conversion efficiency and are smaller in size. The frequency of power frequency inverter is usually
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get a quote
What is Frequency Regulation in Energy Storage?
Learn how energy storage frequency regulation enhances grid stability, balances supply and demand, and provides fast-response ancillary services.
Get a quote
Which is Better: Low Frequency or High Frequency Inverter?
When it comes to choosing an inverter for your home or business, one of the most important decisions you will make is whether to go with a low-frequency or high-frequency
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency Inverter: Which is Better?
Among them, power frequency inverter and high frequency inverter are two common inverter types, each with different characteristics and application scenarios. So,
Get a quote
Preventive primary frequency response control of energy storage
An preventive adjustment scheme is proposed to dynamically determine the primary frequency response parameters (PFRP) of energy storage system (ESS), like deadband and
Get a quote
Microsoft Word
Use Energy Storage for Primary Frequency Control in Power Grids Shutang You Abstract— Frequency stability of power systems becomes more vulnerable with the increase of solar
Get a quote
Load frequency control and dynamic response improvement using energy
Energy storage element is a precious solution presented to combat the non-desirable transient conditions on load frequency and power sharing. Among different storage
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Which energy storage inverter is better power frequency or high frequency ]
What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency inverters?
Low-frequency Inverters are designed to handle high-surge loads, typically 2-5 times their rated power output. This makes them perfect for refrigerators, compressors, or air conditioners requiring extra power during startup. High-frequency inverters typically have 1.5-2 times their rated power, which limits their surge capacity.
Are power frequency inverters good?
In contrast, power frequency inverters can maintain high efficiency and stability under heavy load or overload. Output waveform quality: The output waveform quality of power frequency inverters is usually better than that of high frequency inverters.
Why are frequency drive inverters more efficient?
Efficiency and energy consumption: Because frequency drive inverters use high-frequency switching technology, their switching losses and iron losses are relatively small, so their efficiency is usually higher than that of power frequency inverters.
What are the advantages of high frequency inverters?
Volume and weight: Since high frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology and compact circuit design, their size and weight are usually much smaller than power frequency inverters. This gives high frequency inverters significant advantages in mobile power supplies, aerospace, electric vehicles, and other fields.
What is a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverter: High frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology to chop DC power at high frequency through high-frequency switching tubes (such as IGBT, MOSFET, etc.), and then convert high-frequency pulses into stable alternating current through high-frequency transformers and filter circuits.
Are high-frequency inverters a good choice?
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high efficiency, but they also have the problem of relatively poor output waveform quality.
Guess what you want to know
-
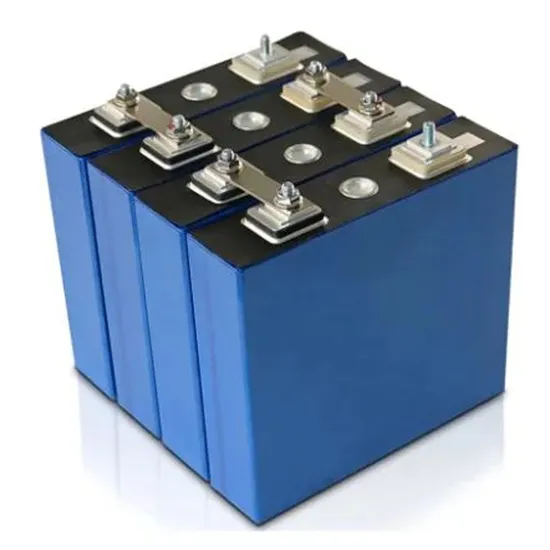 Energy storage high frequency inverter
Energy storage high frequency inverter
-
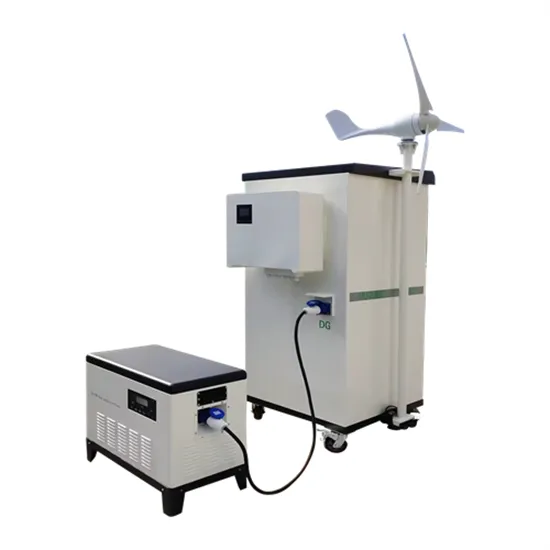 Which energy storage power supply is better in Vietnam
Which energy storage power supply is better in Vietnam
-
 Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
-
 Industrial frequency inverter high power solar energy
Industrial frequency inverter high power solar energy
-
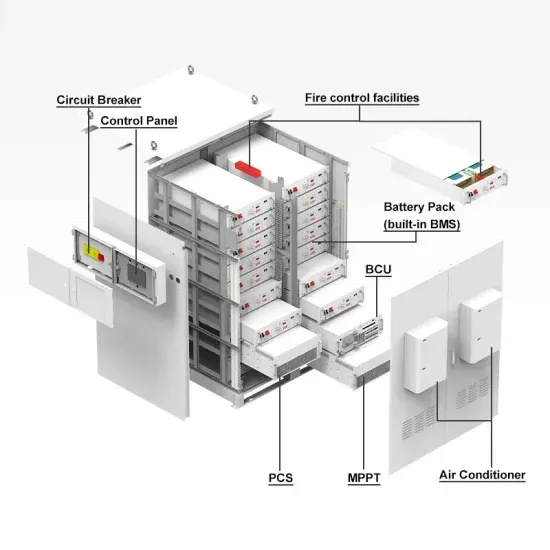 5kva high frequency power inverter
5kva high frequency power inverter
-
 Kenya high power energy storage equipment quotation
Kenya high power energy storage equipment quotation
-
 Which category does the energy storage power supply belong to
Which category does the energy storage power supply belong to
-
 Energy storage power station operating frequency 50hz
Energy storage power station operating frequency 50hz
-
 Power grid energy storage frequency regulation service
Power grid energy storage frequency regulation service
-
 Brunei Energy Storage Frequency Regulation Power Station
Brunei Energy Storage Frequency Regulation Power Station
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


