5G NR Total Transmit Power | Maximum Cell Transmit Power
It''s crucial for the network to manage total transmit power effectively to ensure reliable communication, efficient use of resources, and compliance with regulatory limits.
Get a quote
Quick guide: components for 5G base stations and antennas
Your 5G base-station design and 5G antenna components will need to address not only technical challenges, but also aesthetics, weather and security requirements. This guide
Get a quote
Signal Analysis in 5G NR Base Station Transmitters:
5G Base StationTest Requirements for Base Station Transmitters Your 5G NR measurement application on your signal analyzer should be able
Get a quote
Dynamic Power Management for 5G Small Cell Base Station
5G networks with small cell base stations are attracting significant attention, and their power consumption is a matter of significant concern. As the increase of the expectation, concern for
Get a quote
5G Transmit Power and Antenna radiation
The RF output power is strongly depending on the available bandwidth and on the target data rate. Output power is typically limited by the EMF constraints of the site.
Get a quote
base station in 5g
A 5G base station, also known as a gNodeB (gNB), is a critical component of a 5G network infrastructure. It plays a central role in enabling wireless communication between user
Get a quote
What is a base station and how are 4G/5G base
In comparison to 4G base stations, 5G base stations often require more than twice as much electricity. The operators have two options to think
Get a quote
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O,
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get a quote
Unveiling the 5G Base Station: The Backbone of Next-Gen
4. Power Supply and Cooling Systems 5G base stations require robust power supply and cooling systems to ensure reliable and efficient operation. These systems provide the necessary
Get a quote
A Review on 5G Sub-6 GHz Base Station Antenna
Modern wireless networks such as 5G require multiband MIMO-supported Base Station Antennas. As a result, antennas have multiple ports to
Get a quote
TS 138 113
The present document specifies the applicable requirements, procedures, test conditions, performance assessment and performance criteria for NR base stations and associated
Get a quote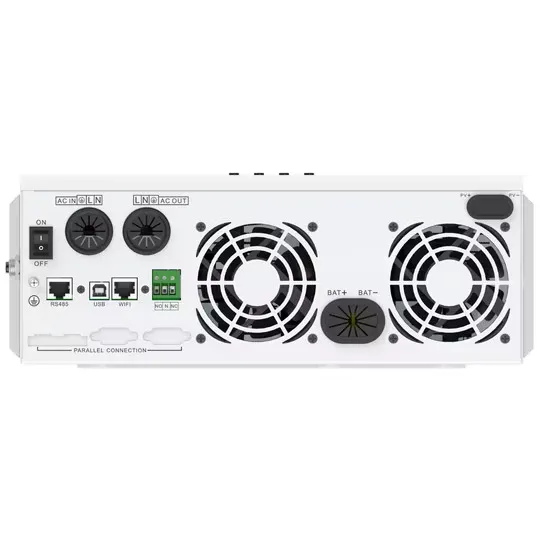
Front Line Data Study about 5G Power Consumption
The two figures above show the actual power consumption test results of 5G base stations from different manufacturers, ZTE and HUAWEI, in Guangzhou and
Get a quote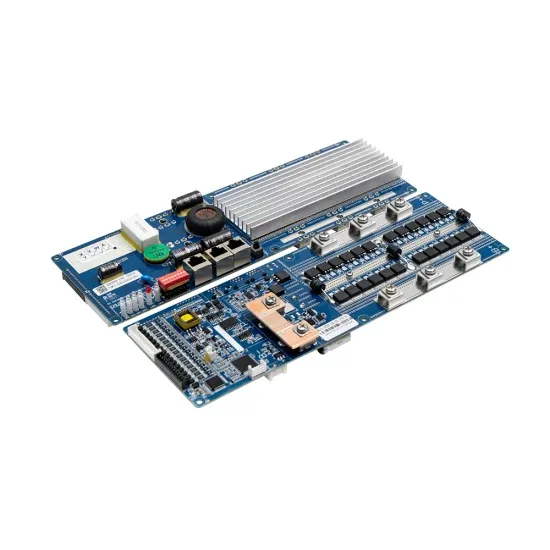
Selecting the Right Supplies for Powering 5G Base Stations
Additionally, these 5G cells will also include more integrated antennas to apply the massive multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) techniques for reliable connections. As a result, a
Get a quote
An Introduction to 5G and How MPS Products Can Optimize a Base Station
Although this latest generation of technology is incredibly innovative, 5G poses challenges such as widespread adoption and efficiency. This article described the basics of 5G and introduced
Get a quote
An Introduction to 5G and How MPS Products Can Optimize
What Is 5G? 5G is a global wireless standard that was released in 2019, and it is the fifth generation for cellular network technology, with previous generations being 1G through 4G. In
Get a quote
What is the Power Consumption of a 5G Base Station?
Ericsson has been able to innovate a 5G base station that consumes only 20% energy when the traffic is low compared to a normal setup. This achieves through advanced
Get a quote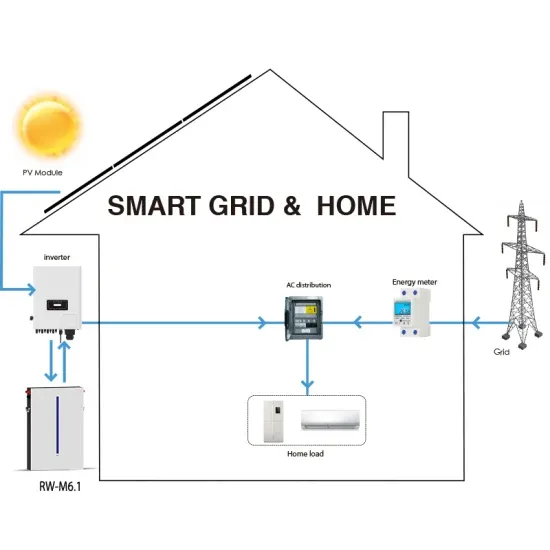
What is a 5G Base Station?
These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises. A 5G base station is a critical component in a mobile network
Get a quote
Building a Better –48 VDC Power Supply for 5G and Next
Figure 3. A power supply for a 5G macro base station block diagram. Highlighted ICs The MAX15258 is a high voltage multiphase boost controller with an I 2 C digital interface designed
Get a quote
What is a base station and how are 4G/5G base stations different?
In comparison to 4G base stations, 5G base stations often require more than twice as much electricity. The operators have two options to think about in the 5G network planning
Get a quote
What is 5G base station architecture?
What are your power requirements? 5G base stations typically need more than twice the amount of power of a 4G base station. In 5G network planning, cellular operators
Get a quote
5G NR Base Station types
Home > Technical Articles > 5G NR Base Station types As per 3GPP specifications for 5G NR, it defines three classes for 5G NR base stations: Wide Area Base Station Medium Range Base
Get a quote
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H,
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What is the voltage of the 5G base station ]
What are the different types of 5G NR base stations?
This article describes the different classes or types of 5G NR Base Stations (BS), including BS Type 1-C, BS Type 1-H, BS Type 1-O, and BS Type 2-O. 5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB.
What is a 5G base station?
As the world continues its transition into the era of 5G, the demand for faster and more reliable wireless communication is skyrocketing. Central to this transformation are 5G base stations, the backbone of the next-generation network. These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises.
Will 4G base stations be upgraded to non-standalone 5G?
Upgrading 4G base stations by software to non-standalone (NSA) 5G will still require hardware changes. It will act as an interim, but it will still not satisfy the need for true 5G network architecture. The number of base stations needed increases with each generation of mobile technology to support higher levels of data traffic.
How much power does a 5G system need?
To keep the power density per MHz similar to LTE systems, the 100MHz 3.5GHz spectrum will require 5x 80 W, which is not easy to be achieved. 5G trials need to define a realistic output power trade-off between coverage, power consumption, EMF limits, and performance.
What are the advantages of a 5G base station?
Massive MIMO: The use of a large number of antennas allows the base station to serve multiple users simultaneously by forming multiple beams and spatially multiplexing signals. Modulation Techniques: 5G base stations support advanced modulation schemes, such as 256-QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation), to achieve higher data rates.
What is 5G NR BS?
5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB. These 5G NR BS operate in two frequency ranges: FR1 and FR2. (../../assets/5G-NR-BS-Channel-Bandwidths.jpg). Table 1: Frequency Ranges
Guess what you want to know
-
 What is the voltage of the mobile base station power
What is the voltage of the mobile base station power
-
 What is the minimum voltage of a communication base station
What is the minimum voltage of a communication base station
-
 What kind of base station is the 5G outdoor signal base station
What kind of base station is the 5G outdoor signal base station
-
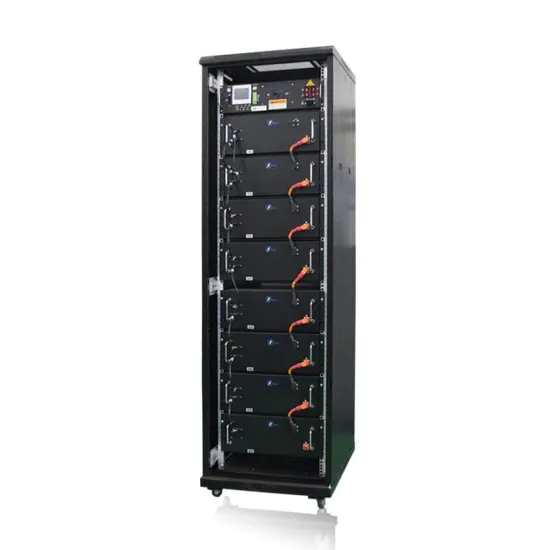 What is Oceania Communications 5G base station
What is Oceania Communications 5G base station
-
 How many watts of voltage does a 5G base station use
How many watts of voltage does a 5G base station use
-
 How big is the battery of an outdoor 5G base station
How big is the battery of an outdoor 5G base station
-
 A brief description of the 5G communication base station power supply construction process
A brief description of the 5G communication base station power supply construction process
-
 China s hybrid energy 5G base station equipment
China s hybrid energy 5G base station equipment
-
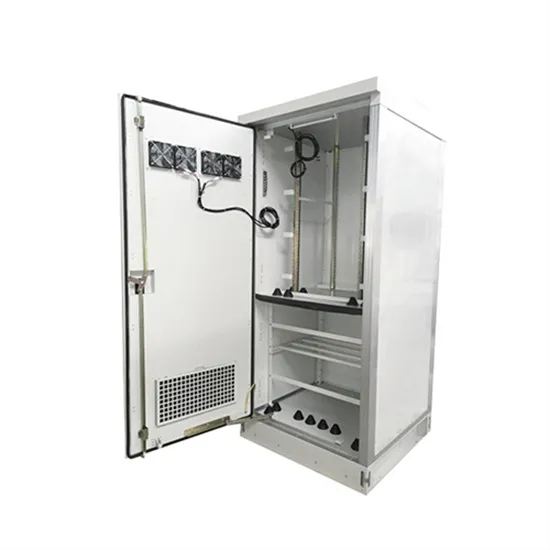 5g micro base station China hybrid energy
5g micro base station China hybrid energy
-
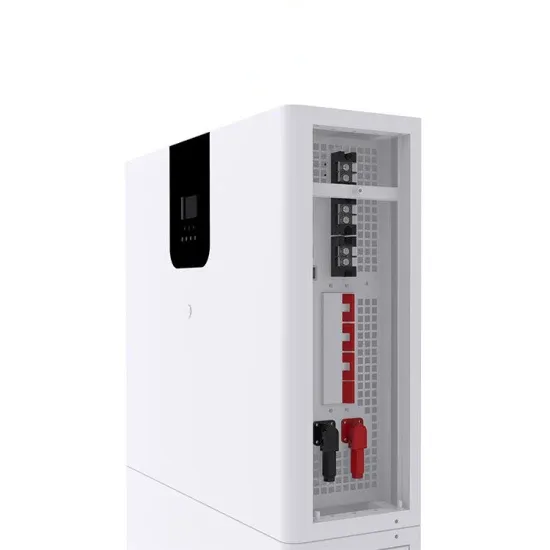 What does the Uzbekistan communication base station inverter include
What does the Uzbekistan communication base station inverter include
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


