Base stations and networks
Base stations enable mobile communications Mobile phones and other mobile devices require a network of base stations in order to function. The base station antennas transmit and receive
Get a quote
What is a 5G base station?
A 5G Base Station, also Known as A GNB (Next-Generation Nodeb), is a fundamental component of the fifth-generation (5G) Wireless Network Infrastructure. It serves
Get a quote
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, Type
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get a quote
What is a 5G Base Station?
These base stations are pivotal in delivering the high-speed, low-latency connectivity that 5G promises. A 5G base station is a critical component in a mobile network
Get a quote
What is 5G NR Base Station Types
5G New Radio (NR) base stations, also known as gNBs, are classified into different types based on their deployment scenarios, frequency ranges, and technical requirements.
Get a quote
Optimization of 5G base station coverage based on self-adaptive
Research on base station coverage methods Base station coverage optimization refers to the optimization of the number and placement of base stations to ensure
Get a quote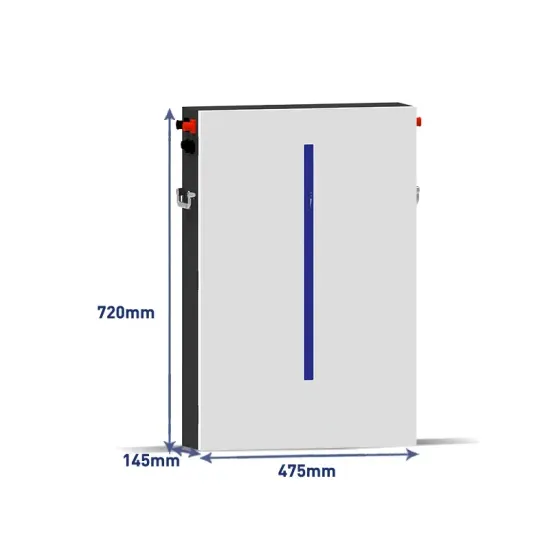
What Is a Base Station? Exploring the Core of 5G Networks and
Receiving and transmitting signals: The base station is both the transmitter and receiver of mobile phone signals. Network access: It converts wireless signals
Get a quote
5G NR Base Station Classes: Type 1-C, Type 1-H,
Learn about the different classes of 5G NR base stations (BS), including Type 1-C, Type 1-H, Type 1-O, and Type 2-O, and their specifications.
Get a quote
Location of 5G base station antenna in substation
Aiming at the engineering problem that 5G base station antenna is difficult to locate efficiently in complex electromagnetic environment, a two
Get a quote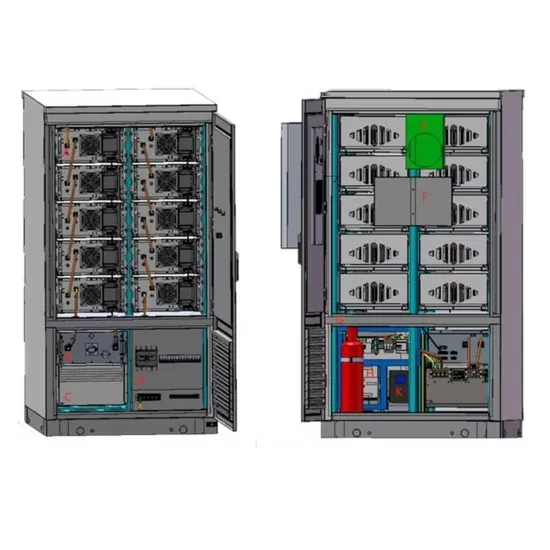
5G NR Base Station types
5G NR Base Station types BS type 1-C requirements are applied at the BS antenna connector (port A) for a single transmitter or receiver with a full complement of transceivers for the
Get a quote
5G Base Station Chips: Driving Future Connectivity by 2025
The evolution of wireless technology has brought the world to the brink of a connectivity revolution. As 5G networks become the backbone of modern communication, 5G
Get a quote
What is 5G Small Cell? A complete guide | emnify Blog
They are best suited for providing outdoor coverage, either extending a macrocell''s coverage or offloading traffic in areas with high demand. 5G small cell use cases 5G small cell
Get a quote
Types of 5G NR Base Stations: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding these base stations is crucial for network planners, engineers, and businesses looking to optimize connectivity. This article provides a detailed overview of the different types
Get a quote
5G NR Base Station Types
Macro Cell Base Station (eNB or gNB): Description: Macro cell base stations are designed for wide-area coverage, typically deployed outdoors to provide extensive coverage in
Get a quote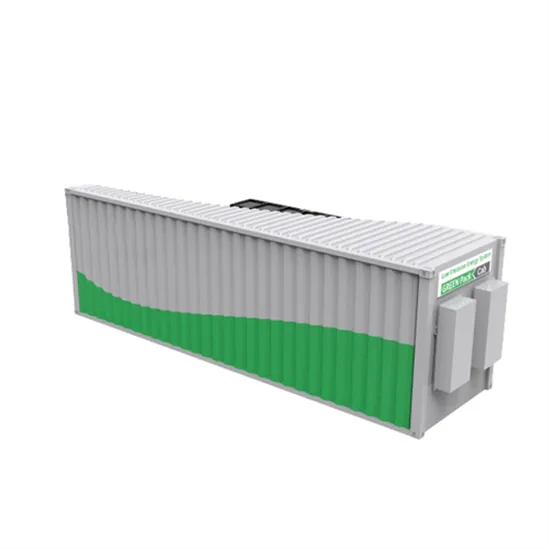
COMONENTS OR 5G BASE STATIONS AND ANTENNAS
STATIONS base-station connects other wireless devices s to (baseband unit in wireless stations). Whatever you''re designing, cost, ease of installation and assembly and, of course, goes for a
Get a quote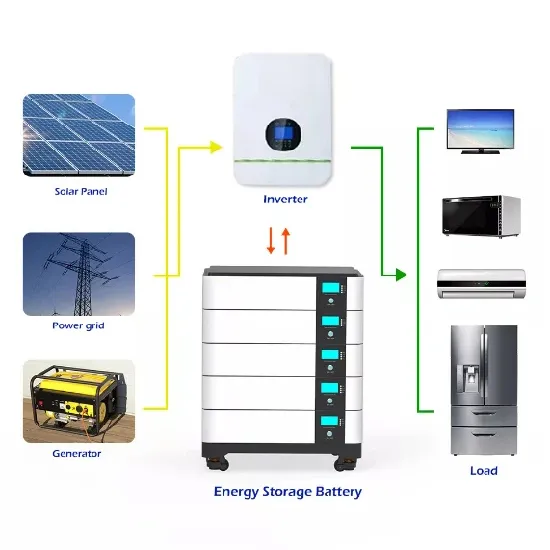
COMONENTS OR 5G BASE STATIONS AND ANTENNAS
With the demand for 5G coverage accelerating, it''s a race to build and deploy base-station components and antenna mast systems. Upgrading 4G base stations by software to non
Get a quote
Quick guide: components for 5G base stations and antennas
Rated IP65, they''re also ideal for outdoor use, protecting your base-station equipment from dust and water ingress. Six head styles and seven grip ranges. Available in
Get a quote
An Introduction to 5G and How MPS Products Can Optimize
The base station is a critical component for 5G operation. The base station is comprised of two main components: the active antenna unit (AAU) and the baseband unit (BBU) (see Figure 1).
Get a quote
What is 5G CPE? What is the difference with ONU?
5G CPE is a type of 5G terminal outfit. It receives 5G signal from operator''s base station, and also converts it into WiFi or wired signal, allowing more local
Get a quote
Base Station Transmits: 5G
Many 5G base stations do not have an RF test port. For this reason, over-the-air (OTA) measurements must be made. Certain field spectrum analyzers offer a comprehensive
Get a quote
Technical Requirements and Market Prospects of 5G Base Station
5G networks use a broader range of spectrum resources, particularly the millimeter-wave bands (24 GHz and above). Base station chips must be capable of efficiently
Get a quote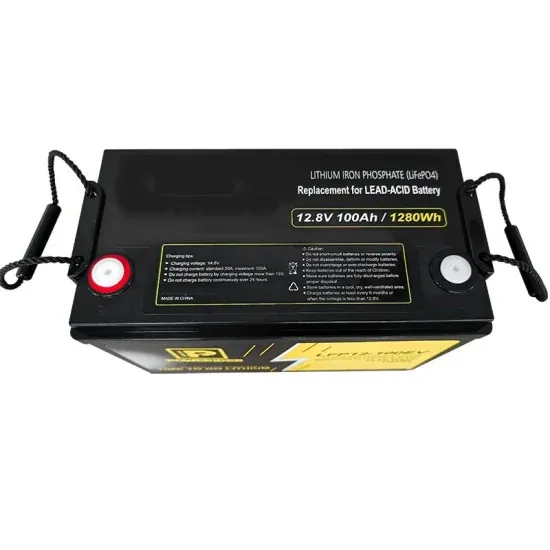
6 FAQs about [What kind of base station is the 5G outdoor signal base station]
What are 5G NR base stations?
5G New Radio (NR) base stations, also known as gNBs, are classified into different types based on their deployment scenarios, frequency ranges, and technical requirements. Here’s a detailed technical explanation of the various 5G NR base station types: 1. Classification by Frequency Range
What are the components of a 5G base station?
Key Components of A 5G Base Station: Antennas and Radios: The Base Station Includes Antennas and Radio Units Responsible for Transmitting and Receiving Signals. Multiple antennas may be used for MOMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), Enhancing Coverage, Capacity, and Overall Network Efficiency.
What are the 3GPP specifications for 5G NR base stations?
The 3GPP specifications define several classes of 5G NR base stations: Frequency Range: Operates in FR1. Requirements: Conducted requirements at individual antenna connectors. Use Case: Suitable for macro and small cell deployments where the focus is on conducted measurements. Frequency Range: Operates in FR1.
Will a 4G base station be upgraded to a 5G network?
ation components and antenna mast systems. Upgrading 4G base stations by software to non-standalone (N A) 5G will still require hardware changes. It will act as an interim, but it will still not satisfy the need for true 5G network architecture. The number of base stations needed increases with each generation of mobile technolo
What is 5G NR BS?
5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless cellular standard, succeeding LTE/LTE-A. It adheres to 3GPP specifications from Release 15 onwards. In 5G NR, the Base Station (BS) is referred to as a gNB. These 5G NR BS operate in two frequency ranges: FR1 and FR2. (../../assets/5G-NR-BS-Channel-Bandwidths.jpg). Table 1: Frequency Ranges
What frequency bands do 5G base stations use?
Utilization of Frequency Spectrum: 5g Base Stations Operate in specific Frequency Bands Allocated for 5G Communication. These bands include Sub-6 GHz Frequencies for Broader Coverage and Millimeter-Wave (Mmwave) Frequencies for Higher Data Rates.
Guess what you want to know
-
 How big is the battery of an outdoor 5G base station
How big is the battery of an outdoor 5G base station
-
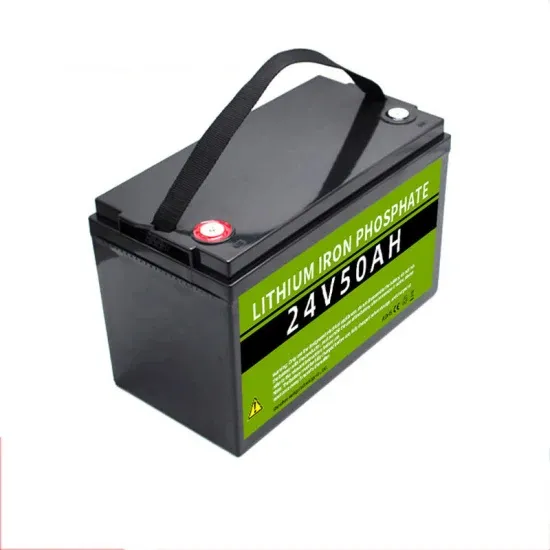
 Cook Islands 5G base station outdoor cabinet manufacturer
Cook Islands 5G base station outdoor cabinet manufacturer
-
 Sweden s outdoor 5G base station
Sweden s outdoor 5G base station
-
 Mobile 5G outdoor base station small
Mobile 5G outdoor base station small
-
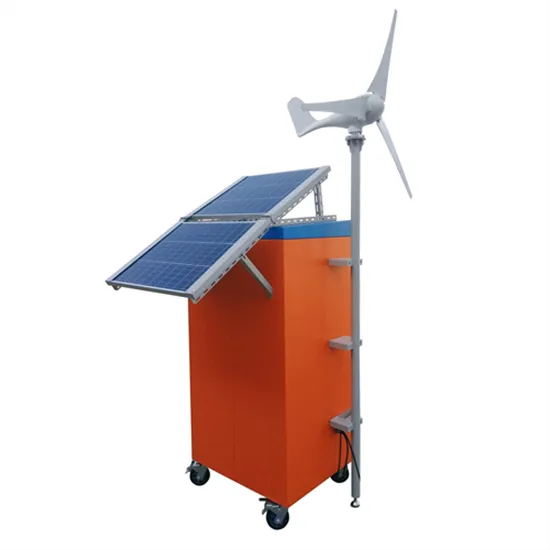
 What is the photovoltaic outdoor base station
What is the photovoltaic outdoor base station
-
 What equipment does the mobile outdoor base station have
What equipment does the mobile outdoor base station have
-
 Outdoor 5G base station within the 5th ring road in Algeria
Outdoor 5G base station within the 5th ring road in Algeria
-
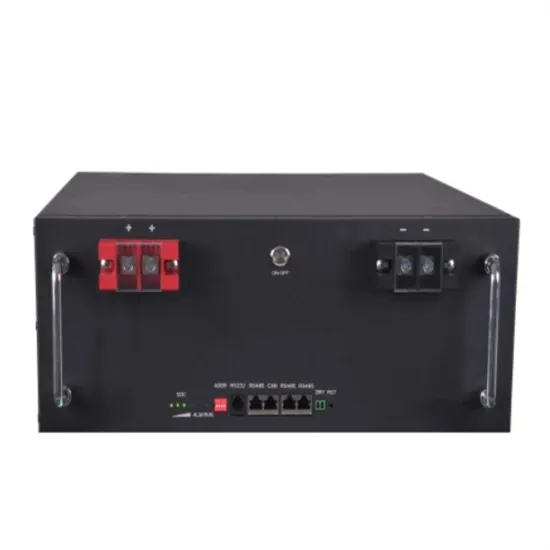
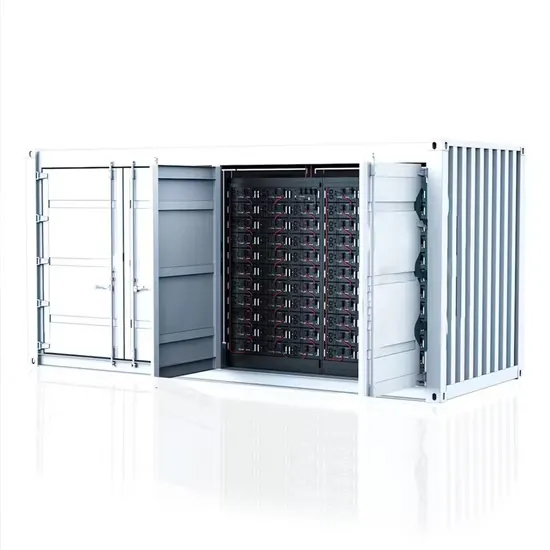 What kind of project is the base station energy management system
What kind of project is the base station energy management system
-
 What is Oceania Communications 5G base station
What is Oceania Communications 5G base station
-
 Algeria Communications 5G signal base station
Algeria Communications 5G signal base station
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


