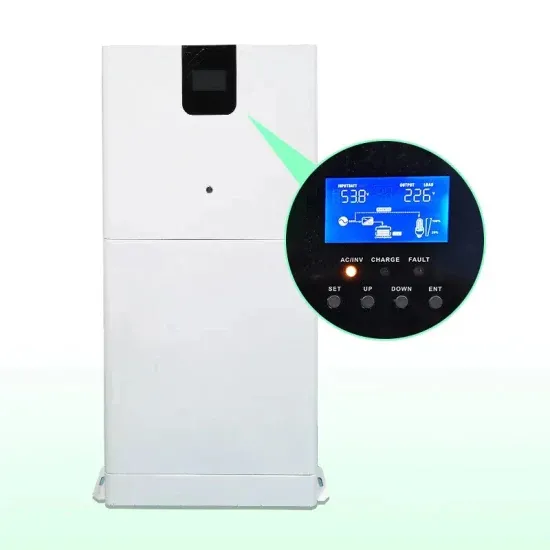
Surge Protection for Cell Sites
Moreover, the base station contains secondary systems like cooling or emergency power supply, which might also need extra surge protection. For safeguarding the base
Get a quote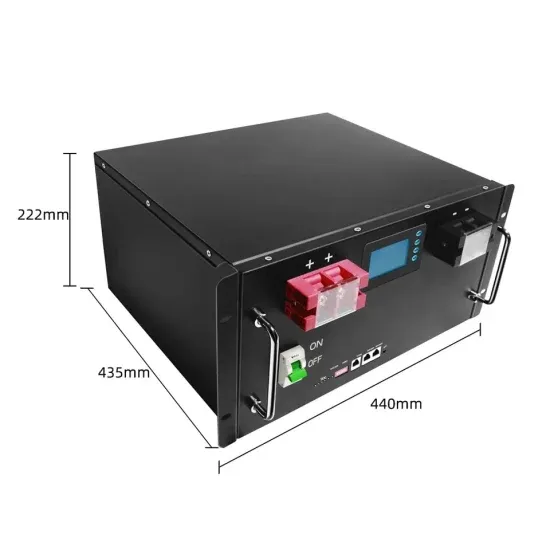
Mobile as base station--How do I power this thing? : r/gmrs
For an extra margin of error, and so the power supply isn''t running at 100% capacity, you''ll want to find something rated closer to 10 or 15 amps (what most lighter sockets
Get a quote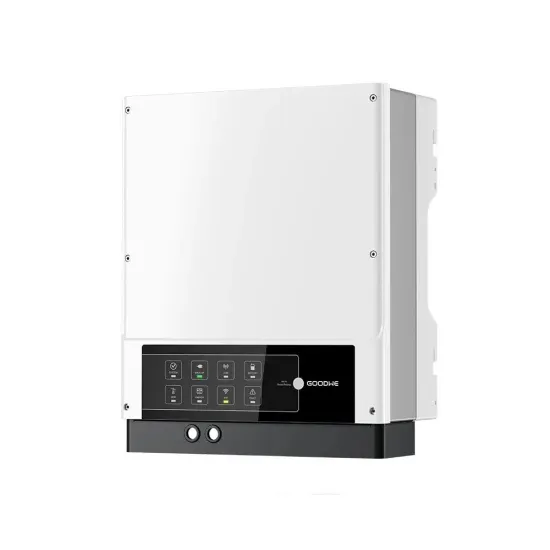
Power Base Station
Maximum base station power is limited to 24 dBm output power for Local Area base stations and to 20 dBm for Home base stations, counting the power over all antennas (up to four).
Get a quote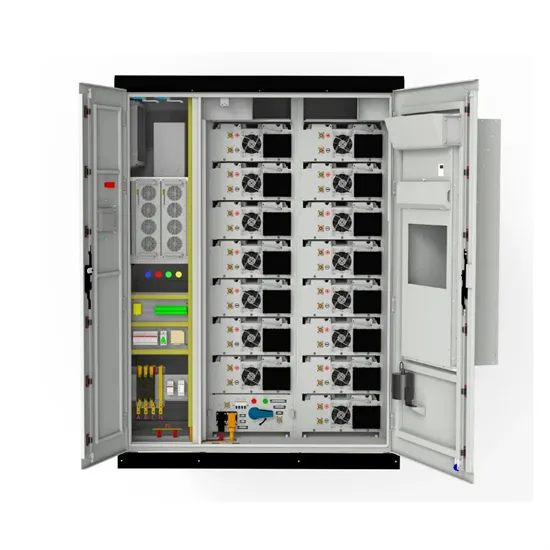
How to convert a mobile radio to a home base station? : r/gmrs
The mobile radios (and even most ham radio desktop models) use that same 12V DC voltage that you are going to need. The difference is how many amps the power supply
Get a quote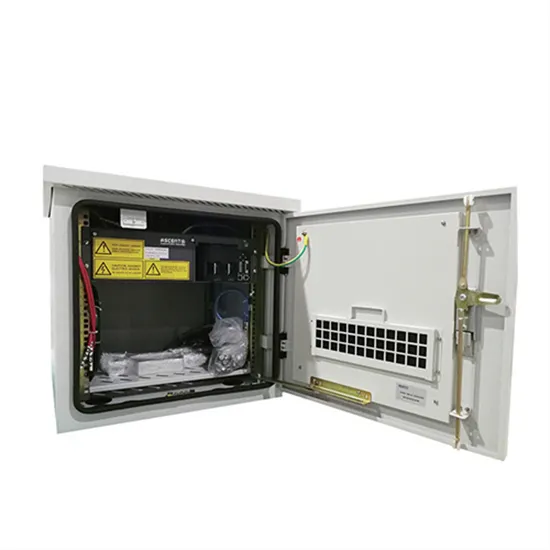
Mobile Substations | Mobile Transformers | Southern
Southern States designs, manufacturers, and can retrofit mobile substation and mobile transformer trailers for a wide range of utility applications.
Get a quote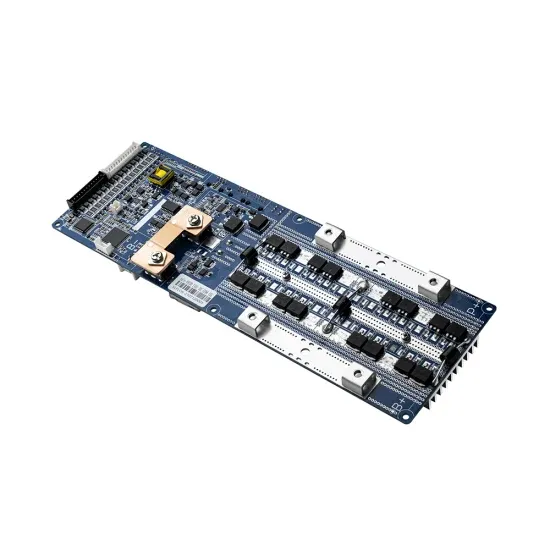
Mobile Ham Radio as a Base Station Power Supply
However, there are several important considerations to keep in mind when setting up a mobile radio as a base station. Power Supply Considerations: A mobile radio typically
Get a quote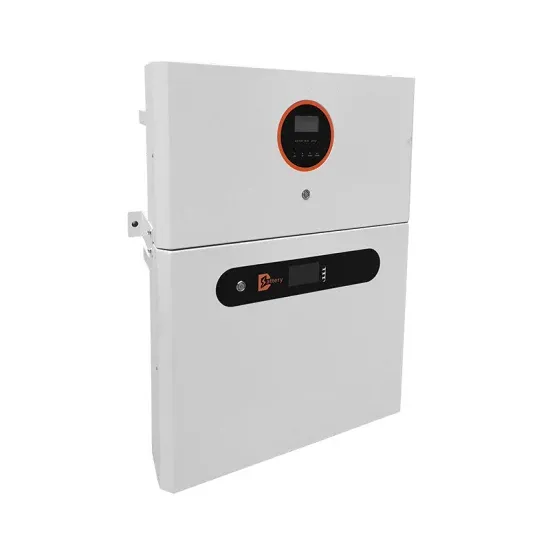
Mobile to Base Power Supply Question
Right now I am using one of the small computer server power supplies to power my radio. It''s rated at 85 amps, but only puts out 12.4 volts. It works great so far, no noise or
Get a quote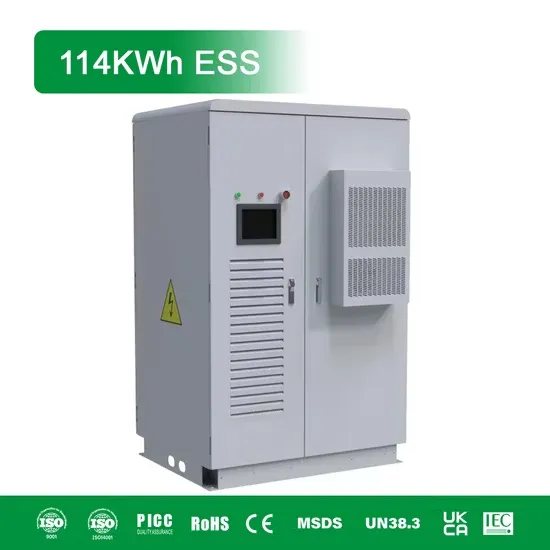
What''s enough power for a base station? : r/gmrs
What''s enough power for a base station? I''m looking at putting a small base station into the kitchen of our ranch home for communicating with the HTs outside. Distance is usually within a
Get a quote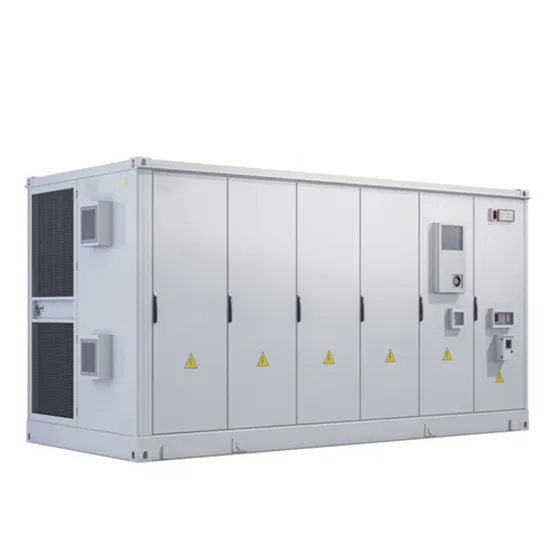
EMF
Mobile phones use the lowest possible power when in a good reception or coverage area. This is typically when close to a mobile base station as the phone only has to transmit over a short
Get a quote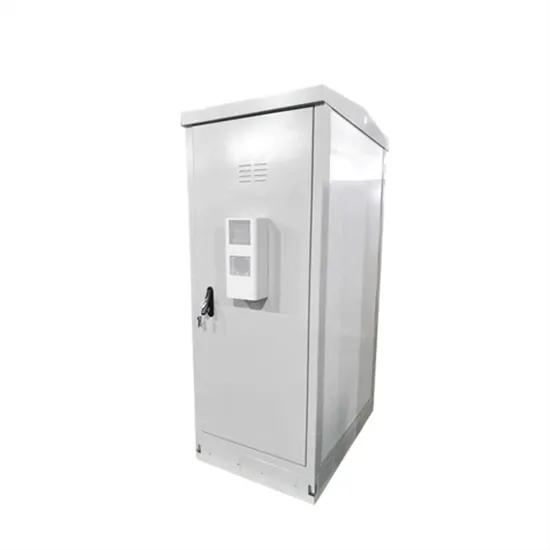
Mobile as base station--How do I power this thing? : r/gmrs
For an extra margin of error, and so the power supply isn''t running at 100% capacity, you''ll want to find something rated closer to 10 or 15 amps (what most lighter sockets are rated for).
Get a quote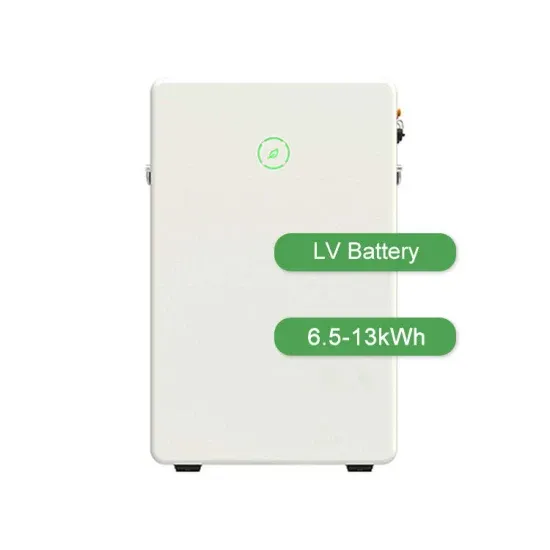
Measurements and Modelling of Base Station Power Consumption under Real
Abstract Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks significantly varies during a working or
Get a quote
Power supply for base station.
Mobile radios are typically designed to operate on a 13.8 volt electrical system, which is what you have when the car''s alternator is charging the battery. The range is usually
Get a quote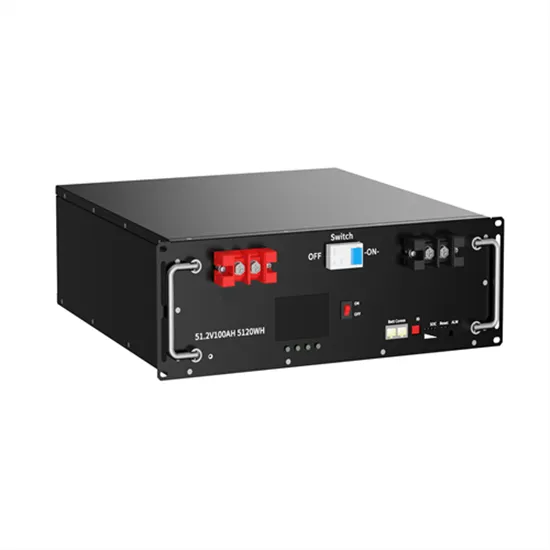
Choosing a Power Supply for Your Station
For this, you will need the operating specs of your radio. Since mobile radios are designed for use in a vehicle, they will typically need Direct
Get a quote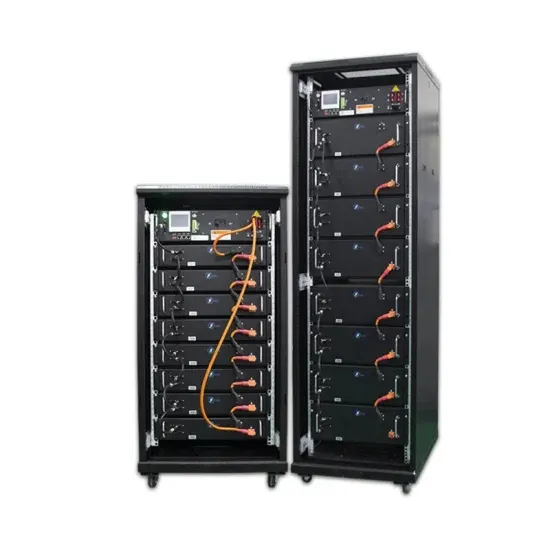
Choosing the right size power supply for your radio
For this, you will need the operating specs of your radio. Since mobile radios are designed for use in a vehicle, they will typically need Direct Current (DC) between 12VDC and
Get a quote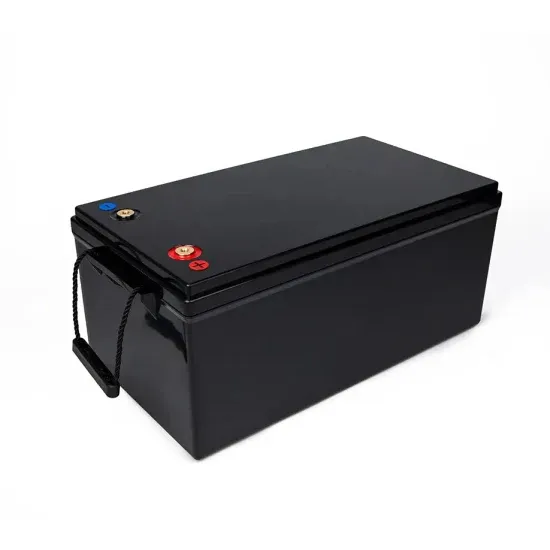
Power supply recommendations?
What is a good and not very expensive power supply that can handle the amp draw of a 40-50 watt GMRS mobile to be used as a base station? Turns out the power supply that I
Get a quote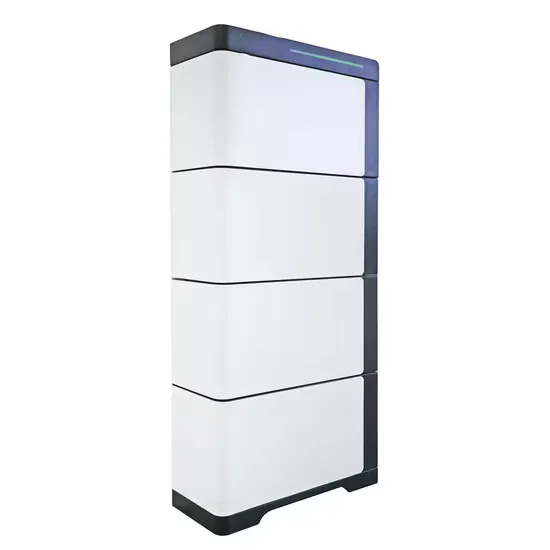
How to convert a mobile radio to a home base station? : r/gmrs
The mobile radios (and even most ham radio desktop models) use that same 12V DC voltage that you are going to need. The difference is how many amps the power supply needs to deliver.
Get a quote
Actual Base Station CB or use a Mobile as a base station
What some may not know is that a typical mobile transceiver will generally hear better than a base radio. Most base radio operates with AC current through a transformer
Get a quote
G78 Mobile Phone Base Stations
Insulated Shaft Units (ISU) are a form of electrical isolation between the high voltage electrical systems associated with the pylon and the DNO Low Voltage supply providing power to the
Get a quote
Telecom Base Station Backup Power Solution: Design
Discover the 48V 100Ah LiFePO4 battery pack for telecom base stations: safe, long-lasting, and eco-friendly. Optimize reliability with our
Get a quote
Choosing a Power Supply for Your Station
Basic models just change 125VAC to 13VDC. Typical add-on features include volt/amp meters, multiple power outputs, noise offset controls to minimize RFI, variable
Get a quote
Energy Management of Base Station in 5G and B5G: Revisited
Since mmWave base stations (gNodeB) are typically capable of radiating up to 200-400 meters in urban locality. Therefore, high density of these stations is required for actual 5G deployment,
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What is the voltage of the mobile base station power]
How many volts does a base radio use?
Most base radio operates with AC current through a transformer down to unregulated 13.8 DC volts. Most electronic operate more efficiently on DC current. With a quality power supply with a variable output, a mobile radio can operate safely at 14 to 14.5 volts. My base CB is a Uniden PC-122 mobile.
How many volts does a mobile radio use?
Most electronic operate more efficiently on DC current. With a quality power supply with a variable output, a mobile radio can operate safely at 14 to 14.5 volts. My base CB is a Uniden PC-122 mobile. No frills, other than USB and LSB, but it does what I want it to.
How much power does a cellular base station use?
This problem exists particularly among the mobile telephony towers in rural areas, that lack quality grid power supply. A cellular base station can use anywhere from 1 to 5 kW power per hour depending upon the number of transceivers attached to the base station, the age of cell towers, and energy needed for air conditioning.
Is a mobile radio better than a base station Radio?
I currently am using a Galaxy DX 88HL mobile for my base station radio on a power supply. What some may not know is that a typical mobile transceiver will generally hear better than a base radio. Most base radio operates with AC current through a transformer down to unregulated 13.8 DC volts. Most electronic operate more efficiently on DC current.
How much power does a mobile radio need?
For starters, let's discuss how much power you will need for safe and stable operation. For this, you will need the operating specs of your radio. Since mobile radios are designed for use in a vehicle, they will typically need Direct Current (DC) between 12VDC and 13.8VDC operate.
How do I convert my mobile radio into a base station?
Simply put, to convert your mobile two way radio into a base station, we recommend that you buy a higher amp power supply than is absolutely needed. When it comes to power, you can't over buy. If in doubt, go bigger. At the end of the day, you'll be glad you did.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Peru Mobile Base Station Power Box
Peru Mobile Base Station Power Box
-
 Wind power principle of mobile base station power supply
Wind power principle of mobile base station power supply
-
 Slovenia Mobile 5G base station power consumption
Slovenia Mobile 5G base station power consumption
-
 Mobile base station inverter communication power supply
Mobile base station inverter communication power supply
-
 Power issue of a mobile base station
Power issue of a mobile base station
-
 What does the base station power supply include
What does the base station power supply include
-
 What are the solar energy standards for China Mobile s base station equipment
What are the solar energy standards for China Mobile s base station equipment
-
 What are the photovoltaic power generation of base station communication equipment
What are the photovoltaic power generation of base station communication equipment
-
 What is the voltage of an industrial and commercial energy storage power station
What is the voltage of an industrial and commercial energy storage power station
-
 What equipment does the energy storage system of a mobile communication base station have
What equipment does the energy storage system of a mobile communication base station have
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.