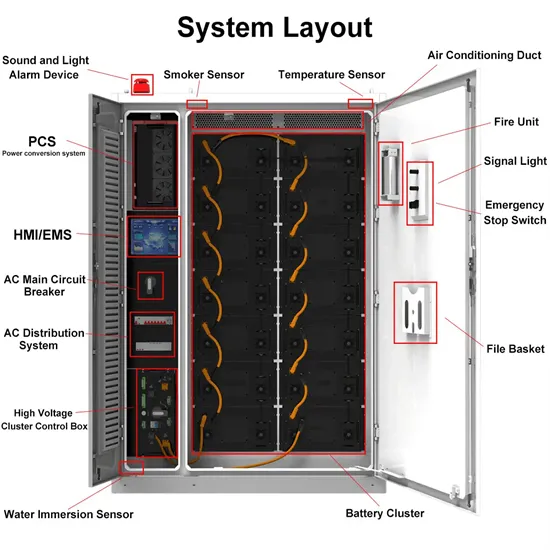
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
The low frequency inverters typically operate at ~60 Hz frequency. To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used. These inverters use the pulse-width modification
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency,
Get a quote
Voltage Fed Full Bridge DC-DC & DC-AC Converter High
The DC-DC section consists of 120 V boot, 4A peak high frequency high-side and low-side driver UCC27211 for driving the high-side and low-side FET''s of the Full Bridge converter.
Get a quote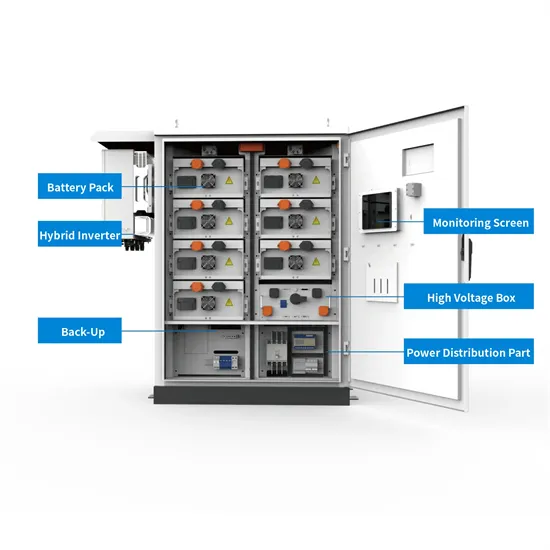
High-End Microwaves Include Inverters for Marketing,
The addition of MOSFET transistors in a high-frequency switching circuit allows for the generation of variable high-frequency AC power. This
Get a quote
A Variable Power Factor High Power Testbed for Traction
In this paper, a testing method using similar topology as open-end-winding motor drive is used for circulating high power test on the traction inverter with high power flow control accuracy and
Get a quote
Inverters PCB Manufacturing & Assembly Services
High-Frequency Inverters PCB Design Considerations Designing the PCB for high-frequency inverters requires careful attention to various factors to ensure
Get a quote
High frequency off-grid inverter control Integrated
This article delves into the intricacies of high-frequency off-grid inverter control systems, exploring their key components, operating principles,
Get a quote
A High Frequency Variable Load Inverter Architecture
This thesis presents the design, physical prototype, controller, and experimental results of a high-frequency variable load inverter architecture (referred to as HFVLI) that can directly drive
Get a quote
High frequency off-grid inverter control Integrated
This article delves into the intricacies of high-frequency off-grid inverter control systems, exploring their key components, operating principles, and advanced control strategies.
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
With the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the benefits of compact size, high efficiency, and lightweight but also have the
Get a quote
A High Performance High Frequency Inverter Architecture with
In this work, a high frequency inverter system that can work in a wide range of inductive or capacitive load is proposed, which includes Class D inverter, novel active impedance
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency, typically above 20 kHz (Kilohertz), to achieve
Get a quote
Three-phase inverter reference design for 200-480VAC
The three-phase inverter uses insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) switches which have advantages of high input impedance as the gate is insulated, has a rapid response ability,
Get a quote
HFL PV micro-inverter with front-end current-fed converter and
A series resonant circuit and high-frequency transformer are used to interface the front-end and the back-end converters. The operation of the proposed micro-inverter in grid
Get a quote
Advanced power inverter topologies and modulation techniques for
Such drive systems are usually fed by semiconductor switch-based inverters, which, unlike balanced pure sine-wave AC sources, produce large-amplitude, high-frequency
Get a quote
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get a quote
Design and Simulation of Back to Back Converter for
Back converter is a combination of Front end converter (FEC) and Back end converter (BEC). Front end converter maintains harmonic free input current ith unity power factor at supply end,
Get a quote
Estimation of voltage distribution on the inverter fed random
The high electrical stresses in the Electrical Insulation Systems of machines fed by pulse width modulation (PWM) inverters remain a limitation of the lifetime. The stress is caused by
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverters: From Photovoltaic, Wind, and
pave way for isolated high-power and HFL inverters. They have attained significant attention with regard to wide applications encompassing high-power renewable- and alternative-energy
Get a quote
TPEL2691668
Index Terms—Bus bar, stray inductance, stray capacitance, power electronics, three-phase inverter, SRM inverter, high-power inverter. I. INTRODUCTION Bus bars have been present in
Get a quote
Advanced power inverter topologies and modulation techniques
Such drive systems are usually fed by semiconductor switch-based inverters, which, unlike balanced pure sine-wave AC sources, produce large-amplitude, high-frequency
Get a quote
A Soft Switching Scheme for Multiphase DC/Pulsating-DC
Abstract—This paper outlines a switching scheme to improve the energy efficiency for an isolated high-frequency multiphase dc/pulsating-dc converter, which is the front end of a three-phase
Get a quote
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of inverter frequency, exploring its significance, factors affecting it, and its practical implications.
Get a quote
Understanding High-Frequency Inverters
Through a combination of lucid explanations, insightful illustrations, and practical examples, this guide empowers you to grasp the complexities of high-frequency inverters.
Get a quote
A High-Frequency Inverter for Variable-Load Operation
This paper presents a new inverter architecture suitable for driving widely varying load impedances at high frequency (HF, 3-30 MHz) and above. We present the underlying
Get a quote
RAYVERTER
Introducing the Luminous Rayverter—an advanced off-grid high-frequency inverter. With solar charging, battery backup, and pure sine wave output, it powers high-demand appliances
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [High-frequency inverter back-end]
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
Does victron use a high frequency inverter?
Victron combines both inverters, which they call Hybrid HF or Combined high frequency and line frequency technologies. What frequency inverter does growatt use? Growatt uses a high-frequency inverter. Which one is best? Low or high frequency? The best inverter is the low-frequency inverter.
What is the difference between a low frequency and high frequency inverter?
Low-frequency inverter: heavy and capable of surge power, lower efficiency, more reliable, expensive. High-frequency inverter: lightweight, not capable of surges, more efficient, less reliable, cheaper. I’m an off-grid enthusiast.
What is a high frequency variable load inverter architecture?
This thesis presents a high frequency variable load inverter architecture along with a physical prototype and e ciency optimizing controller. The inverter architecture consists of two constituent inverters, one connected directly through the load and the other connected through an immittance converter, which acts as a lossless power combiner.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of high frequency inverters?
Benefits of High-Frequency Inverters: Uncover the advantages offered by high-frequency operation, such as reduced size, improved efficiency, and noise suppression. Topologies of High-Frequency Inverters: Examine the different topologies used in high-frequency inverters, including half-bridge, full-bridge, and multilevel.
How do high-frequency inverters work?
These enigmatic devices possess the uncanny ability to transform direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at remarkably high frequencies, unlocking a world of boundless possibilities. This comprehensive guide embarks on a quest to unravel the intricacies of high-frequency inverters, peeling back their layers to reveal their inner workings.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Maximum operating frequency of high-frequency inverter
Maximum operating frequency of high-frequency inverter
-
 Which is better high-frequency or broadband inverter
Which is better high-frequency or broadband inverter
-
 The difference between high-frequency inverter and industrial frequency inverter
The difference between high-frequency inverter and industrial frequency inverter
-
 Swedish High-Frequency Inverter Device
Swedish High-Frequency Inverter Device
-
 High-frequency inverter voltage and frequency
High-frequency inverter voltage and frequency
-
 Yemen high-frequency inverter
Yemen high-frequency inverter
-
 How big is a high-frequency inverter
How big is a high-frequency inverter
-
 What frequency does a high-frequency inverter require
What frequency does a high-frequency inverter require
-
 High-frequency modular parallel inverter
High-frequency modular parallel inverter
-
 Single-stage high-frequency inverter
Single-stage high-frequency inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.