High Frequency vs. Low Frequency Inverter
A lot of the most popular AIO inverters are High Frequency Transformerless. How important is it to use the correct family of transformer (high vs. low freq) for to power devices
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
What is a High-Frequency Inverter? A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency, typically above
Get a quote
High Frequency Inverter Circuit
High frequency inverter circuits can be used in many applications where efficient power is needed. For instance, they can be used to power a wide variety of electrical devices,
Get a quote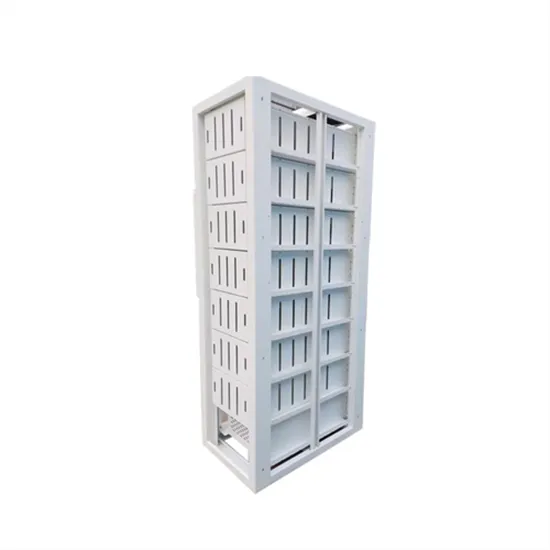
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency. They are typically less expensive, have smaller footprints, and have a lower tolerance for industrial loads.
Get a quote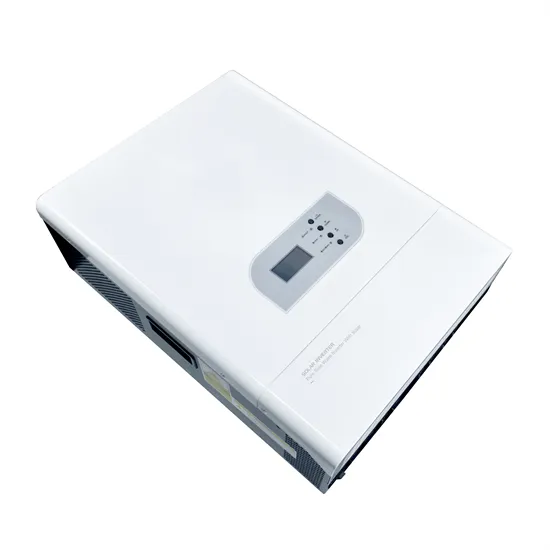
800VA Pure Sine Wave Inverter''s Reference Design
The pure Sine Wave inverter has various applications because of its key advantages such as operation with very low harmonic distortion and clean power like utility-supplied electricity,
Get a quote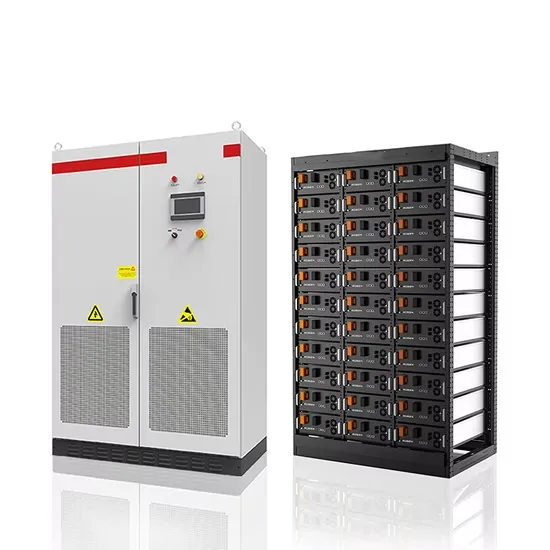
High Frequency Vs. Low Frequency Inverters... Which is better?
High Frequency Vs. Low Frequency? Which Inverter is better?00:00 - intro00:43 - low frequency inverters02:15 - High Frequency Inverters03:17 - Comparison
Get a quote
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get a quote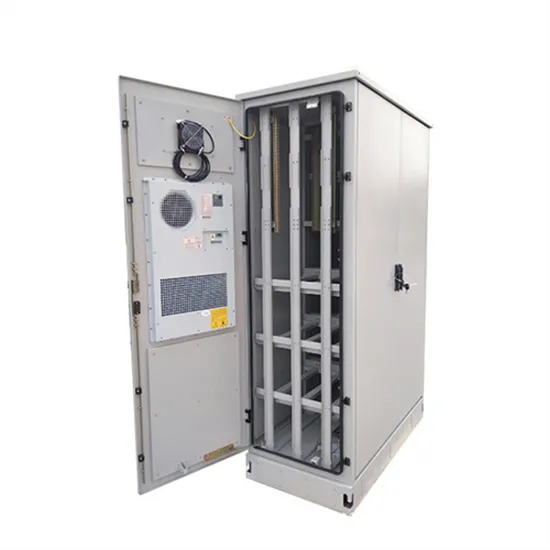
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical engineering. These can also be known as
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
What is a High-Frequency Inverter? A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC)
Get a quote
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
High frequency inverters are often used in applications that require smaller size, higher conversion efficiency and lower power, such as electronic
Get a quote
Ultimate Guide to the 3kW LF Inverter: Power, Battery Sizing,
3kW Power Inverter vs Other Types Picking the right inverter for your power system is not as easy as just looking at the numbers on the label. The type of inverter, especially
Get a quote
High frequency verses low frequency inverters
What is the difference between high, or low frequency inverters the pros and cons? I have seen a few posts someone said low was better for high surge load like AC units,
Get a quote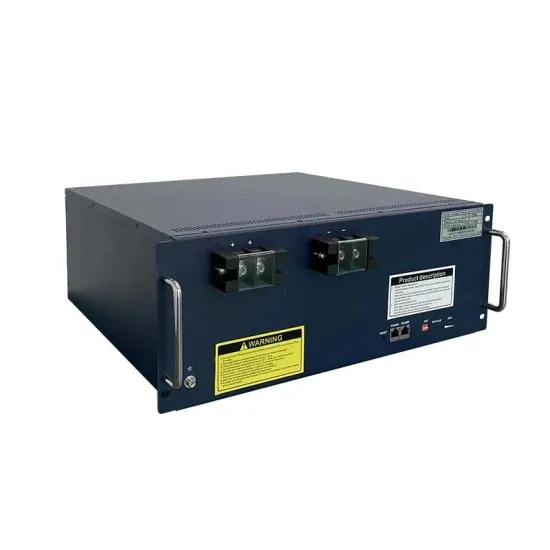
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency inverters - typically 20 kHz to 100
Get a quote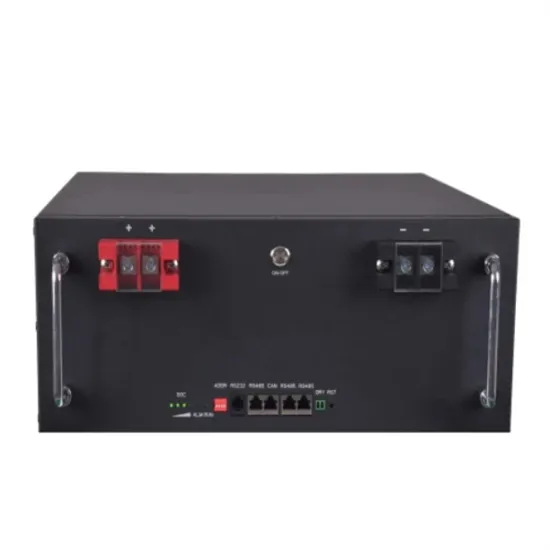
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few
Get a quote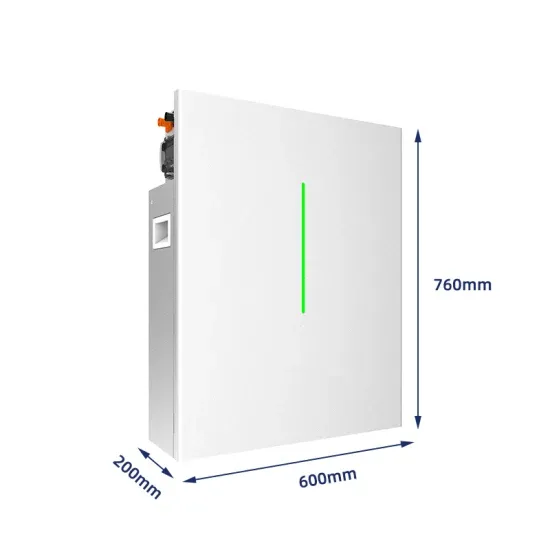
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency inverters - typically 20 kHz to 100 kHz. High-frequency inverters
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
In a typical high-frequency design, the incoming DC voltage is first chopped by a high-frequency DC-DC converter. This stage uses fast-switching power semiconductors, such
Get a quote
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
High frequency inverters are often used in applications that require smaller size, higher conversion efficiency and lower power, such as electronic equipment, solar power
Get a quote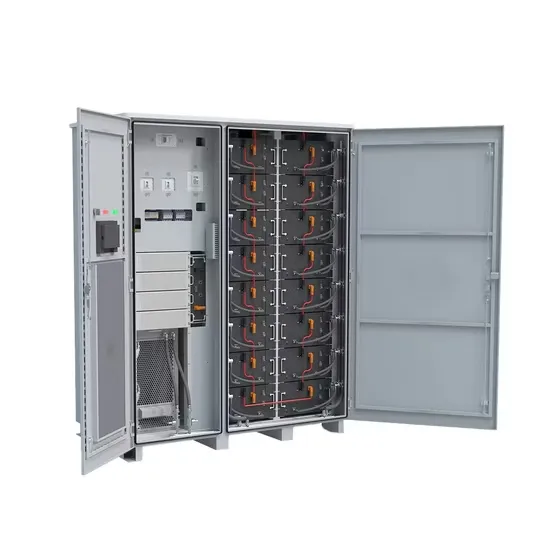
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency Inverters and High
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power efficiency, space saving, or suitability
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High
In a typical high-frequency design, the incoming DC voltage is first chopped by a high-frequency DC-DC converter. This stage uses fast-switching power semiconductors, such
Get a quote
A High-Frequency Inverter for Variable-Load Operation
This paper presents a new inverter architecture suitable for driving widely varying load impedances at high frequency (HF, 3-30 MHz) and above. We present the underlying
Get a quote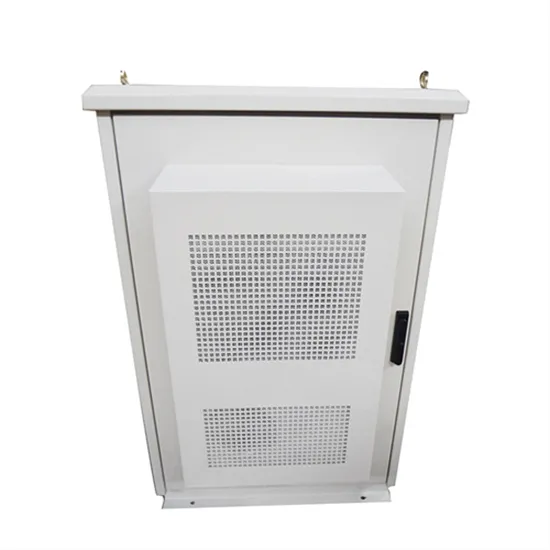
Low vs High frequency inverters | DIY Solar Power Forum
Small high frequency ferrite core transformers saturate quickly giving little time for any overload detection circuitry to react and shutdown inverter to save MOSFET drivers. Also
Get a quote
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Learn the key differences between high frequency inverters and low frequency inverters. Discover which one suits your power needs for efficiency and surge capacity.
Get a quote
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
Inverters are essential components of many electrical systems, converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to power various devices and applications. When selecting an inverter,
Get a quote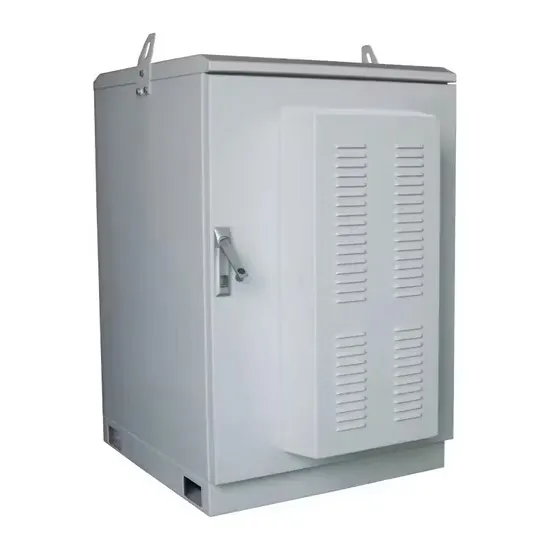
How to size an inverter that can run your air conditioner?
While high-frequency inverters can supply 200% of their Cont. power for a couple of seconds, low-frequency inverters can supply 300% of
Get a quote
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power
Get a quote
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz.
Get a quote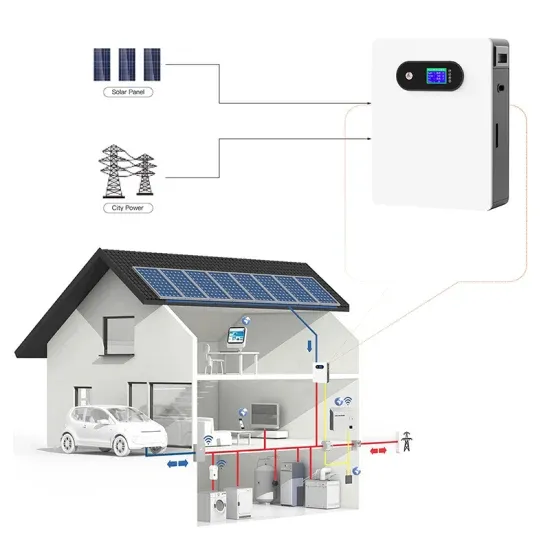
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
A high frequency inverter operates at several kilohertz, making it ideal for applications requiring compact size and high efficiency, such as solar power systems and electronic equipment.
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
For example, a high-frequency 3000W inverter would equal 3000V, but a power-frequency 3000VA inverter would equal 2400W. Power frequency inverters are typically
Get a quote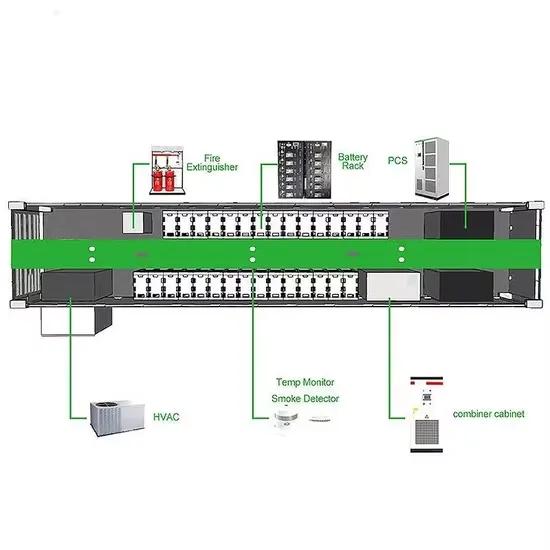
6 FAQs about [How big is a high-frequency inverter ]
How do high frequency power inverters convert DC to AC?
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz. Low frequency inverter circuit diagram
Which is better low frequency or high frequency inverter?
④ Low frequency inverters have higher reliability than high frequency inverters and are less likely to break down. ⑤ The load capacity of low frequency inverters, especially impact load capacity, is better than that of high frequency inverters, and it can suppress high-order harmonic components in the waveform.
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
What determines a high or low frequency inverter?
Size and tolerances of the transistors used in the inversion process, and the speed at which they operate determines the classification of high or low frequency. The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency.
Does victron use a high frequency inverter?
Victron combines both inverters, which they call Hybrid HF or Combined high frequency and line frequency technologies. What frequency inverter does growatt use? Growatt uses a high-frequency inverter. Which one is best? Low or high frequency? The best inverter is the low-frequency inverter.
How does a low frequency inverter work?
The low frequency inverter first inverts the DC power into low-frequency low-voltage AC power, and then boosts it through the low frequency transformer into 220V, 50Hz AC power for the load. Features of low frequency inverter:
Guess what you want to know
-
 How big an inverter should I use for 60v 40a
How big an inverter should I use for 60v 40a
-
 How big of an inverter can a 24v power supply be installed on
How big of an inverter can a 24v power supply be installed on
-
 How big an inverter should I use for a 7kw photovoltaic system
How big an inverter should I use for a 7kw photovoltaic system
-
 How big a water pump inverter should I buy for solar power
How big a water pump inverter should I buy for solar power
-
 How big an inverter should I use for 220v 1800w
How big an inverter should I use for 220v 1800w
-
 How big a battery should I buy for a 5500w inverter
How big a battery should I buy for a 5500w inverter
-
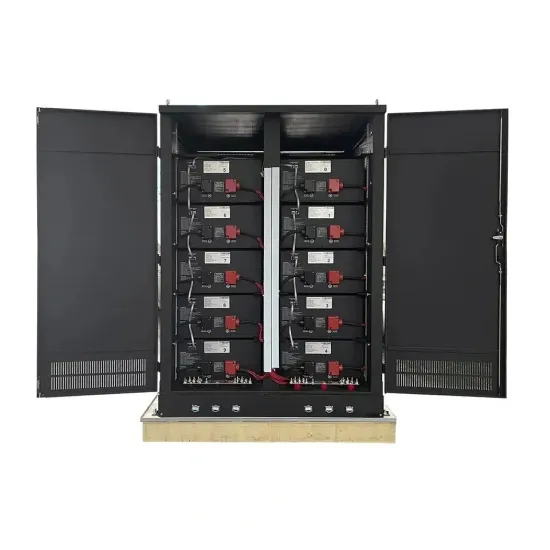 How big of an inverter should I use for my home
How big of an inverter should I use for my home
-
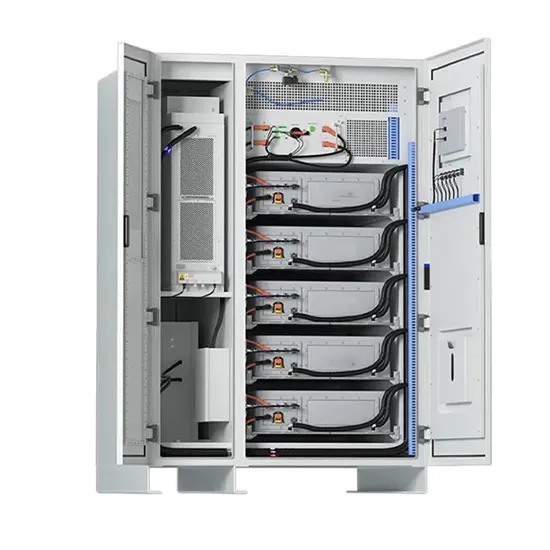 How big an inverter should I use for a 60 volt battery
How big an inverter should I use for a 60 volt battery
-
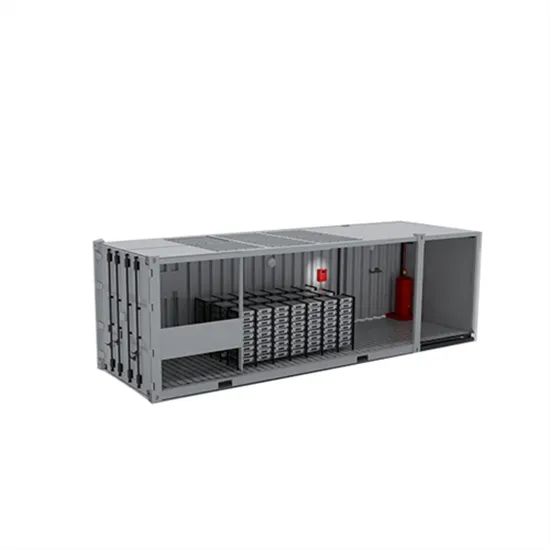 How big of an appliance can a 12v 600w inverter power
How big of an appliance can a 12v 600w inverter power
-
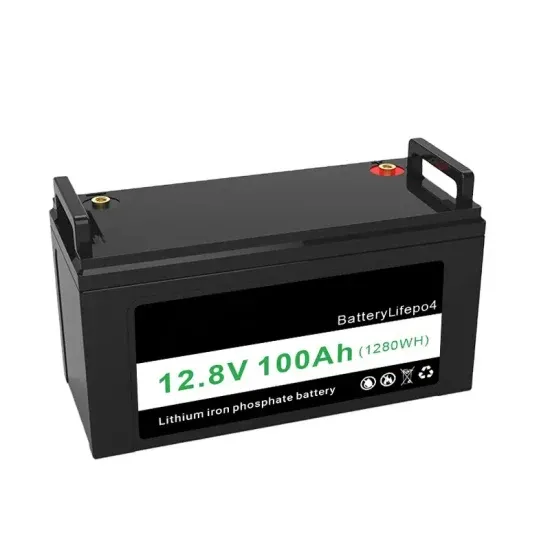 How big an inverter can a 42w solar panel support
How big an inverter can a 42w solar panel support
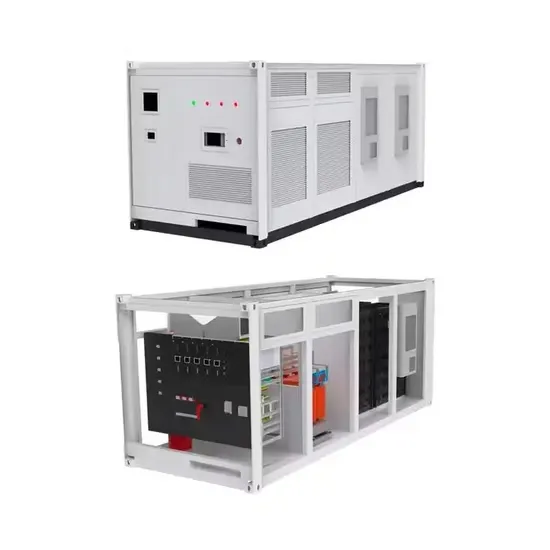
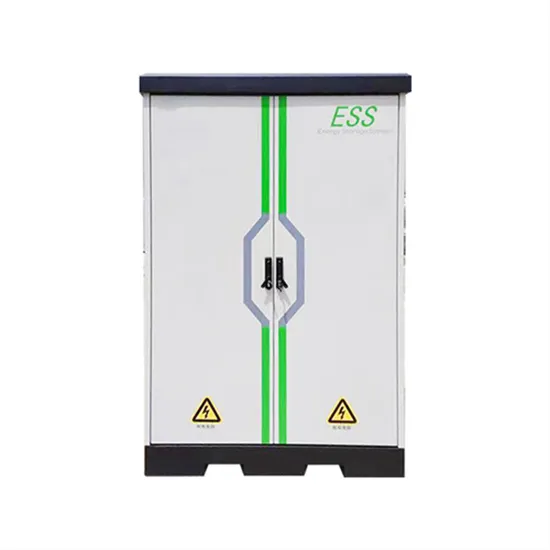
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


