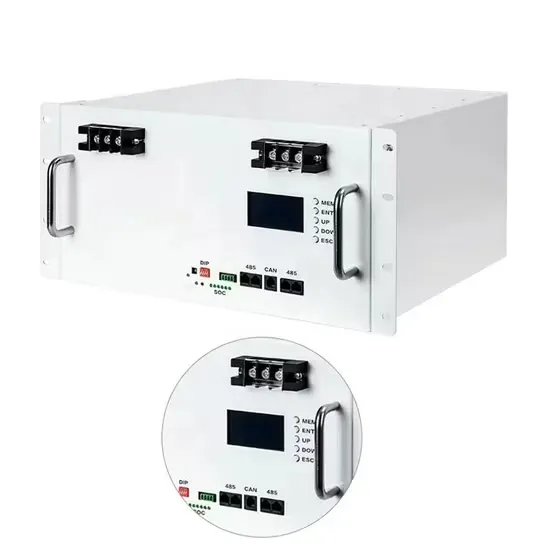
The highest frequency and basic frequency of the inverter
The maximum frequency is the maximum frequency that the inverter allows to output, expressed by fmax. Its specific meaning varies slightly depending on how the
Get a quote
CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
This setting enables the output of a constant torque based on the frequency, according to the V/f characteristics that represent the proportional relationship between the output frequency and
Get a quote
Mastering These 16 Frequency Inverter Parameter Settings Will
The typical maximum frequency for inverters is up to 60Hz, with some reaching 400Hz. High frequencies allow motors to operate at high speeds, which can strain the
Get a quote
Mastering These 16 Frequency Inverter Parameter
The typical maximum frequency for inverters is up to 60Hz, with some reaching 400Hz. High frequencies allow motors to operate at high
Get a quote
Essential Parameters for Frequency Converters: A
Frequency converters comprise a multitude of configurable parameters, each offering a distinct range of options. During operational use, instances may arise where improper configuration of
Get a quote
CM Inverter Maximum Output Current (V0
The document provides maximum current output specifications for Cascadia Motion inverters (CM200DX, CM200DZ, CM350DZ) under different operating
Get a quote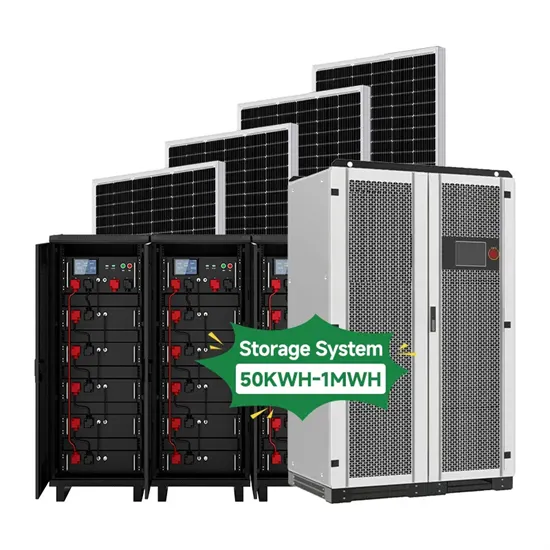
SolarEdge Inverters, Power Control Options — Application Note
The inverter de-rates power according to the defined graph, until the frequency reaches the trip value and the inverter disconnects (the trip point is preset per country therefore does not need
Get a quote
How to Optimize Your Low-Frequency Solar Inverter for Maximum
MPPT Functionality Maximum power point tracking (MPPT) is a critical feature in low-frequency solar inverters that ensures the system operates at optimal efficiency. MPPT algorithms
Get a quote
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
What is the maximum frequency of an inverter? The maximum inverter frequency depends on its design specifications, with most commercial models offering a maximum
Get a quote
FR-D700 catalog
When the motor is decelerated from the frequency higher than the base frequency, the average deceleration torque will reduce. Since the inverter does not contain a brake resistor, use the
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
You can set the frequency of an inverter by a number of different methods. It depends on what brand you use and also the number of available commands and
Get a quote
The highest frequency and basic frequency of the
The maximum frequency is the maximum frequency that the inverter allows to output, expressed by fmax. Its specific meaning varies
Get a quote
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used. These inverters use the pulse-width modification method: switching currents at high frequency, and for variable periods of time.
Get a quote
Mastering Inverter Switching Frequencies: A
Explore the intricate dance of inverter switching frequencies to optimize energy flow. Master the rhythms of power electronics with our
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used. These inverters use the pulse-width modification method: switching currents at high
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
This is also known as the surge power; it is the maximum power that an inverter can supply for a short time. For example, some appliances with electric motors require a much higher power on
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
What is a High-Frequency Inverter? A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high switching frequency, typically above
Get a quote
Siemens V20 Frequency Inverter Easy Start Guide
The Siemens V20 Frequency Inverter range is available to order from inverterdrive This guide is intended to compliment the user manual provided by the manufacturer. It is provided
Get a quote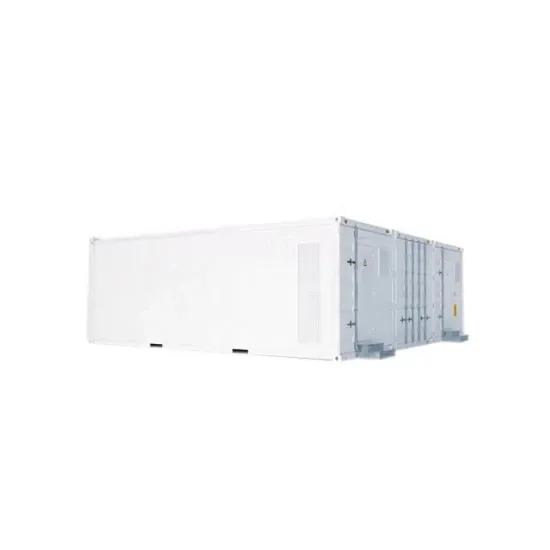
High Frequency vs Low Frequency Inverter: Which Has Higher
Why is the maximum PV input of the mppt of high-frequency inverter higher than the maximum PV input of the mppt of low-frequency inverter? For high-frequency inverter used
Get a quote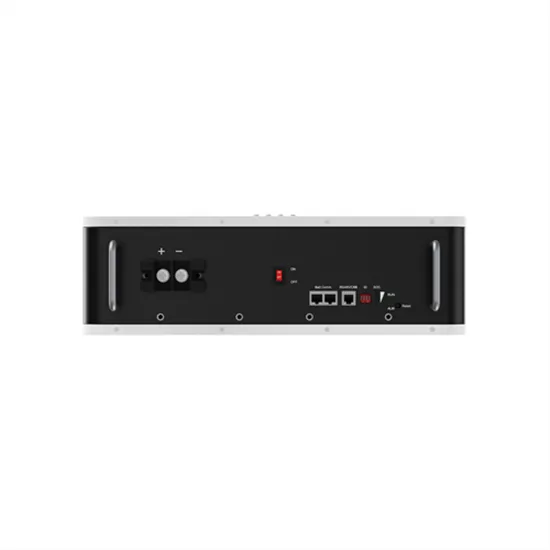
Mastering Inverter Switching Frequencies: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the intricate dance of inverter switching frequencies to optimize energy flow. Master the rhythms of power electronics with our comprehensive guide, your blueprint to
Get a quote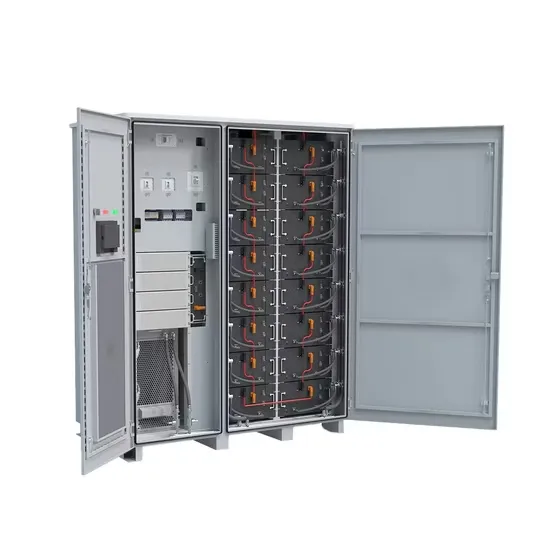
CHAPTER 2
generator. The filter capacitor across the input terminals of the inverter provides a constant dc link voltage. The inverter therefore is an adjustable-frequency voltage source. The configuration of
Get a quote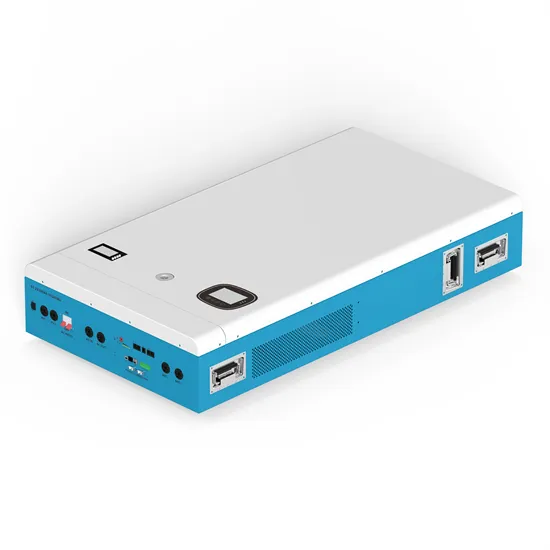
Understanding High-Frequency Inverters
In the realm of power electronics, the advent of high-frequency inverters has revolutionized the landscape. These enigmatic devices possess the uncanny ability to transform direct current
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency
You can set the frequency of an inverter by a number of different methods. It depends on what brand you use and also the number of available
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
What is a High-Frequency Inverter? A high-frequency inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) at a high
Get a quote
CHAPTER 2
2.2 Voltage Control in Single - Phase Inverters The schematic of inverter system is as shown in Figure 2.1, in which the battery or rectifier provides the dc supply to the inverter. The inverter is
Get a quote
How to set the parameters of Mitsubishi Electric inverter?
Understand the parameters Before setting the inverter parameters, we need to first understand the main parameters of the inverter so that we can
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Inverter maximum frequency]
What is the maximum inverter frequency?
The maximum inverter frequency depends on its design specifications, with most commercial models offering a maximum frequency between 10 kilohertz to megahertz.
What is a high frequency inverter?
The typical maximum frequency for inverters is up to 60Hz, with some reaching 400Hz. High frequencies allow motors to operate at high speeds, which can strain the bearings and rotors of standard motors beyond their rated speed, challenging their ability to withstand the centrifugal forces.
What is the basic frequency of an inverter?
The frequency corresponding to the maximum output voltage of the inverter is called the basic frequency; b. When the output voltage of the frequency converter is equal to the rated voltage, the minimum output frequency is called the basic frequency. The fundamental frequency is represented by fBA.
What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency inverters?
The low frequency inverters typically operate at ~60 Hz frequency. To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used. These inverters use the pulse-width modification method: switching currents at high frequency, and for variable periods of time.
What is inverter switching frequency?
The inverter switching frequency refers to the rate at which power electronic switches, such as Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs) or Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs), cycle on and off.
What are inverter parameters?
Inverter parameters include motor power, current, voltage, speed, and maximum frequency, all of which can be directly obtained from the motor nameplate. Resonance might occur at certain frequency points, particularly with taller structures. When controlling compressors, it's crucial to avoid frequencies that could cause surge.
Guess what you want to know
-
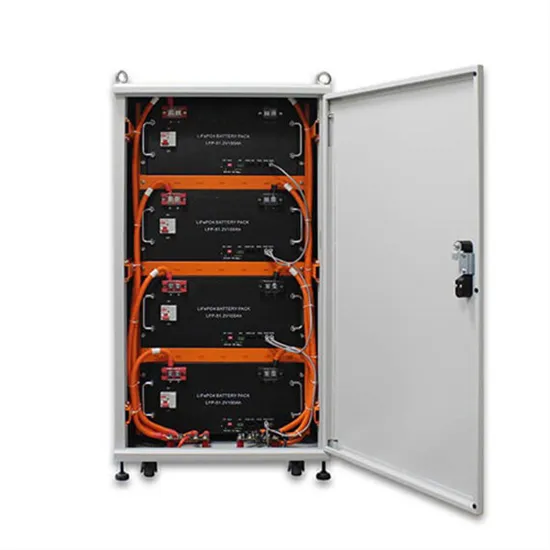 Inverter maximum frequency
Inverter maximum frequency
-
 What is the maximum wattage of a 48v industrial frequency inverter
What is the maximum wattage of a 48v industrial frequency inverter
-
 Columbia horizontal power frequency off-grid inverter
Columbia horizontal power frequency off-grid inverter
-
 Tuvalu power frequency inverter manufacturer
Tuvalu power frequency inverter manufacturer
-
 What is the maximum wattage of a solar water pump inverter
What is the maximum wattage of a solar water pump inverter
-
 Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
-
 High frequency inverter price in Pakistan
High frequency inverter price in Pakistan
-
 High frequency inverter quality
High frequency inverter quality
-
 Solar inverter chooses high frequency power supply
Solar inverter chooses high frequency power supply
-
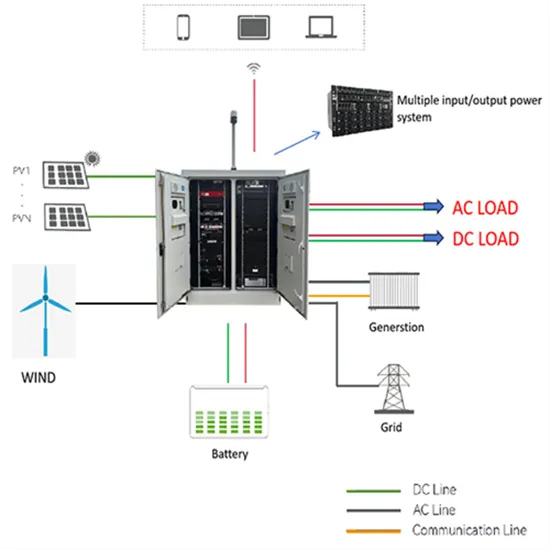
 Power frequency inverter efficiency and power
Power frequency inverter efficiency and power
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.