Frequency and Voltage Control Schemes for Three-Phase Grid
Grid-forming inverters play an important role in supporting power systems with low rotational inertia. Their frequency and voltage control policies must guarantee a synchronised
Get a quote
Voltage Control Using Inverter Reactive Power Control
In this post, we''ll look at four reactive power control modes that can be selected in modern smart inverters to control inverter reactive power
Get a quote
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters:
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters: It has already been mentioned that Inverter Control providing a variable frequency supply to three phase motors
Get a quote
Precise Power Sharing Among Parallel Inverters in an AC
This paper introduces an innovative method for enhanced power distribution in an AC microgrid (MG), utilizing parallel inverters with a decentralized droop control strategy. A
Get a quote
Voltage Control Methods of Inverter – PWM Technique
The output voltage of an inverter can be adjusted by employing the control technique within the inverter itself. This control technique can be accomplished by the
Get a quote
Control of Parallel Inverters for High Power Quality and
Abstract— This paper studies the control problem of using conventional droop method to achieve a highly power sharing accuracy/quality in a stand-alone microgrid that operates parallel
Get a quote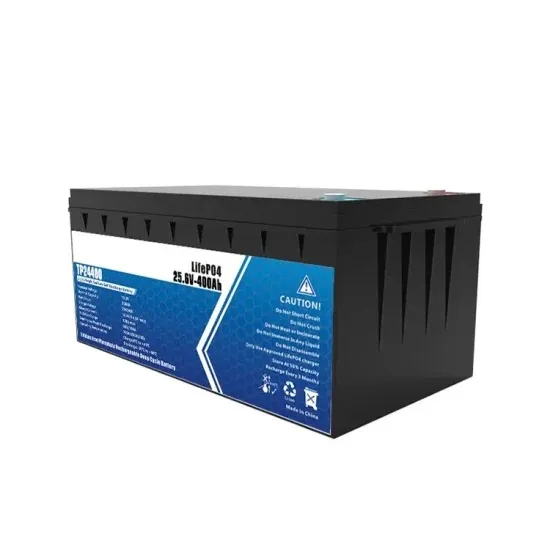
Feedforward control method for single‐phase inverters
Non-linear rectifier loads usually cause heavy distortion in the output voltage of single-phase inverters due to pulsating charging current of
Get a quote
Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes, topologies and
The latest and most innovative inverter topologies that help to enhance power quality are compared. Modern control approaches are evaluated in terms of robustness,
Get a quote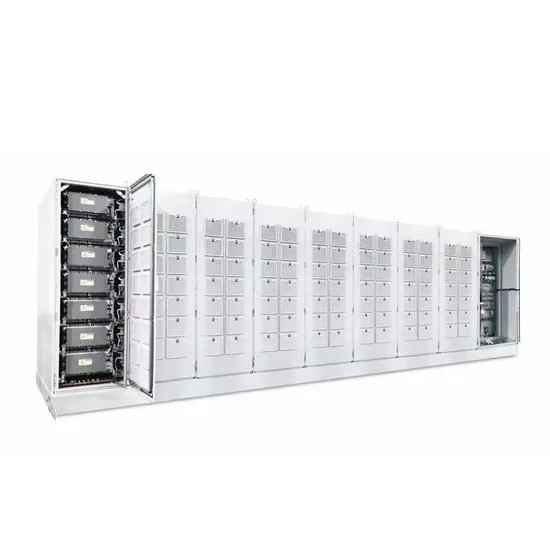
Voltage Control Using Inverter Reactive Power Control
In this post, we''ll look at four reactive power control modes that can be selected in modern smart inverters to control inverter reactive power production (or absorption) and
Get a quote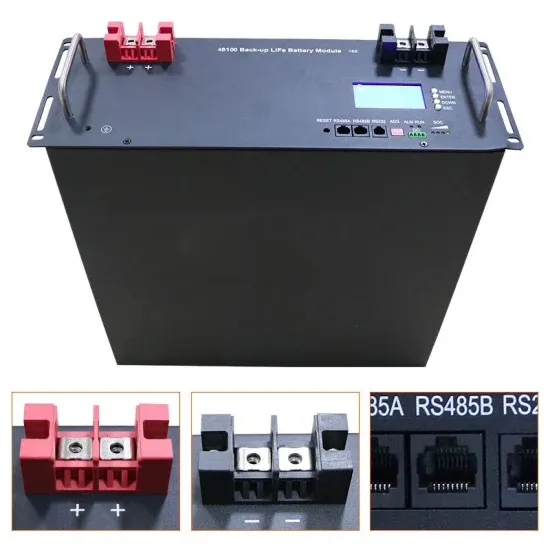
Voltage Source Inverter Reference Design (Rev. E)
Description This reference design implements single-phase inverter (DC/AC) control using a C2000TM microcontroller (MCU). The design supports two modes of operation for the inverter:
Get a quote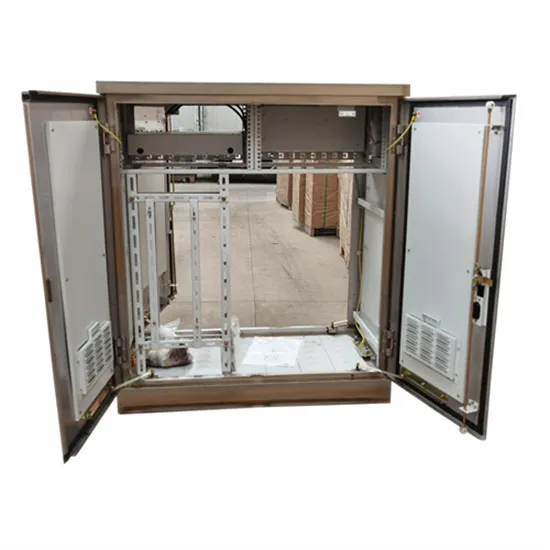
Optimal tracking for PV three-phase grid-connected inverter with
The paper presents a simple yet accurate tracking control strategy for a three-phase grid-connected inverter with an LC filter. Three-phase inverters are used to integrate
Get a quote
Cost Optimized, < 1% Accurate Current Sensing and
Description This reference design demonstrates a cost optimized three-phase inverter leg (low-side shunt) current sensing solution with high accuracy and faster response for sensorless 2
Get a quote
Regulating Voltage: Recommendations for Smart Inverters
This report from GridLab provides an introduction to voltage regulation concepts, including advantages and disadvantages of various control modes. The authors include
Get a quote
Model predictive control of 3L‐NPC inverter to
Three-level neutral-point clamped (3L-NPC) inverters have several advantages over two-level (2L) topologies, including reduced switching
Get a quote
REGULATING VOLTAGE: RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
Reactive power output is based on the distribution system voltage following a specified volt-var response "curve" which typically would have a deadband around the target voltage where no
Get a quote
Multiâ loop control of standâ alone inverters with minimum
Abstract: This study deals with the design of a load sensorless multi-loop control system for the stand-alone inverter. In the proposed strategy, only the inverter current is measured, which is
Get a quote
LADRC-based grid-connected control strategy for
Reference [22] addresses the issues of insufficient disturbance rejection performance and control accuracy in the traditional dual-loop PI
Get a quote
MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND ADVANCED CONTROL
This thesis explores the core advantages of grid-forming inverters comparing to conventional inverters, develops mathematical models for voltage and frequency control, and proposes
Get a quote
Integrated Synchronization Control of Grid-Forming Inverters
This paper develops an integrated synchronization control technique for a grid-forming inverter operating within a microgrid that can improve the microgrid''s transients during microgrid
Get a quote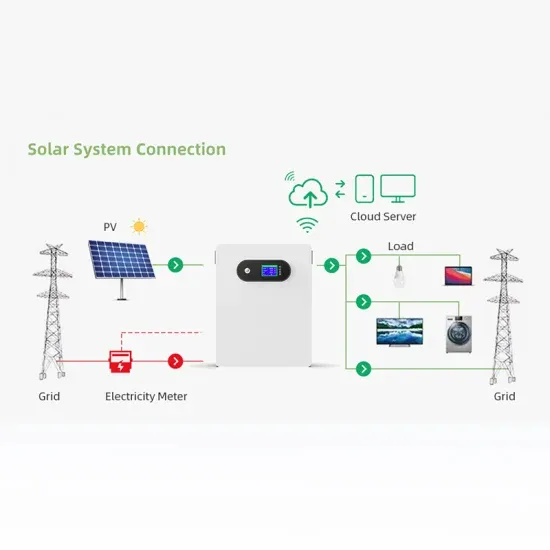
Grid-Forming Inverters: A Comparative Study
It ensures accurate power tracking in grid-connected mode with lower overshoots and shorter settling times compared to conventional VSG designs. In islanded mode, it
Get a quote
Inverter-Based Resource Performance Guideline
With this information, and working closely with the electric industry, NERC has captured a set of recommended performance specifications for inverter-based resources in this Reliability
Get a quote
24TPEL12-YLi-2022828-x
The proposed power con-trol strategy contains a virtual inductor at the interfacing inverter output and an accurate power control and sharing algorithm with consideration of both impedance
Get a quote
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters:
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters: It has already been mentioned that Inverter Control providing a variable frequency supply to three phase motors should be capable of providing a
Get a quote
Voltage Control Methods of Inverter – PWM Technique
This report from GridLab provides an introduction to voltage regulation concepts, including advantages and disadvantages of various control modes. The authors include
Get a quote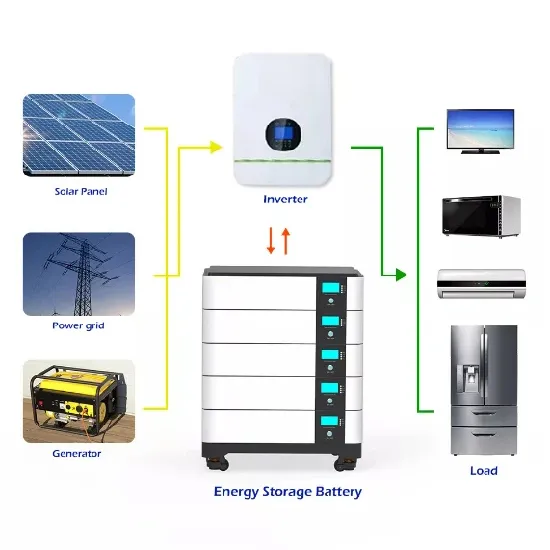
Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters:
The Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters can be done in two ways. by varying the dc link voltage by varying the ac voltage at the output using a variable ratio transformer (a) The
Get a quote
Voltage Regulation Strategy for Inverter Considering Data Quality
The simulation results have verified the accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed strategy, which can effectively support the operation of the inverter and guarantee the voltage quality of
Get a quote
Stability-improved repetitive control for inverters considering PLLs
This paper discusses the stability of a grid-tied inverter containing a phase-locked loop (PLL) and repetitive control (RC) under a weak grid. The application of RC significantly
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Inverter voltage control accuracy]
What are voltage control techniques for inverters?
This is required to avoid saturation and ensure operation at constant flux density. The Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters can be affected either external to the Inverter Control or within it. The Voltage Control Techniques for Inverters can be done in two ways. (a) The variation of dc link voltage can be achieved in many ways.
How to control AC voltage in an inverter?
Basically, there are three techniques by which the voltage can be controlled in an inverter. They are, Internal control of Inverter. In this method of control, an ac voltage controller is connected at the output of the inverter to obtain the required (controlled) output ac voltage.
Should inverters be able to control voltage?
There may be benefits to enabling this capability in inverters, such as less expensive zero or slightly negative active power voltage support (compared with synchronous machines) and more dispersed resources supporting automatic voltage control.
Can an inverter provide more reactive power?
The ability to provide additional reactive power while not operating at maximum active power capability is part of automatic voltage control and an ERS. If the inverter-based resource can provide more reactive current within its limitations to maintain scheduled voltage pre- or postcontingency, the inverter should be programmed to do so.
How much power can an Inverter Supply?
At nominal voltage, the inverter-based resource can supply 1.0 pu apparent power continuously to the grid.38 Each inverter has a capability curve similar to a synchronous machine, which is affected by terminal voltage of the inverter. At higher and lower voltage, the reactive capability is restricted at leading and lagging output, respectively.
What is the minimum angular frequency of inverter output?
Based on the power quality requirement that the grid voltage frequency variation should not be greater than 1 % and the voltage amplitude variation should not be greater than 5 %, the minimum permissible angular frequency of the inverter output is 310.86 rad/s and the minimum voltage amplitude is 295.45 V.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Inverter voltage space vector control
Inverter voltage space vector control
-
 Voltage closed loop control of inverter
Voltage closed loop control of inverter
-
 Low voltage inverter control cabinet implementation standards
Low voltage inverter control cabinet implementation standards
-
 Single voltage closed loop inverter
Single voltage closed loop inverter
-
 Inverter power voltage range
Inverter power voltage range
-
 1v input voltage inverter
1v input voltage inverter
-
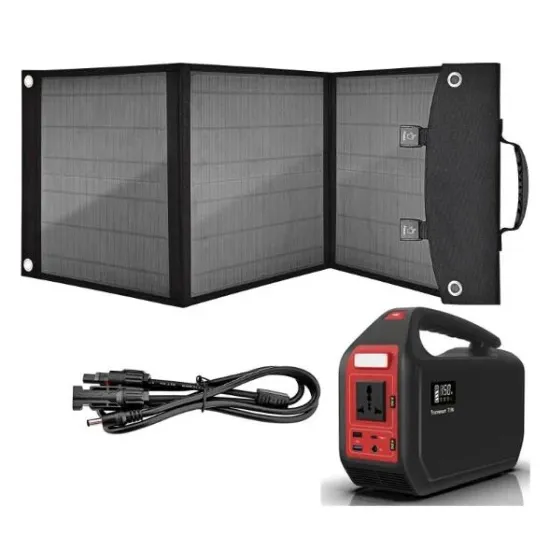 Inverter 24v flash charging wide voltage
Inverter 24v flash charging wide voltage
-
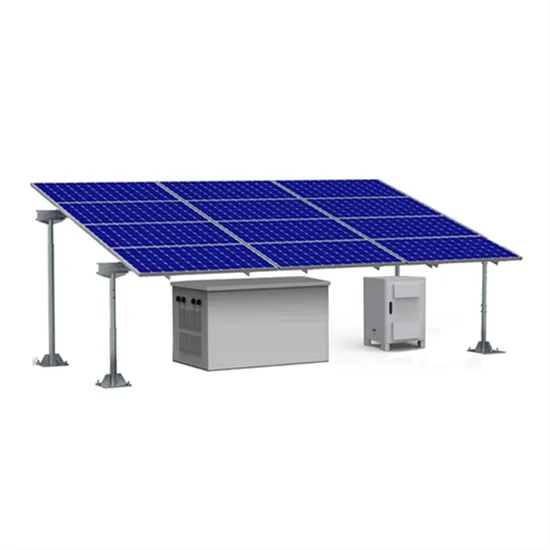 Off-grid photovoltaic inverter voltage and frequency
Off-grid photovoltaic inverter voltage and frequency
-
 Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter reverse voltage
Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter reverse voltage
-
 Influence of input voltage on inverter
Influence of input voltage on inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


