Understanding Inverter Input and Output: What is the
The output produced by the inverter is an alternating current (AC) that is usually used to power various kinds of electronic devices needed in
Get a quote
Definition of Inverter Specifications
Maximum Operating Current in DC (A). This indicates the maximum operating current on the DC side of the inverter. Maximum Input Voltage DC (V). This indicates the maximum voltage that
Get a quote
Understanding inverter voltage
In the realm of power electronics, the inverter voltage is a critical parameter that dictates its performance, compatibility, and safety. Understanding the intricacies of inverter
Get a quote
The Most Comprehensive Guide to Grid-Tied Inverter
Detailed Parameters of Grid-Tied Inverters Model and Naming Growatt grid-tied inverters are named based on their rated AC output power. For example, the
Get a quote
⚡ Never Stay Powerless Again! Introducing the 12V
Introducing the 12V 1000W Power Inverter – Convert 12V DC to 220V AC and power up your essentials anywhere, anytime! 🚗🔋 🔧 Specifications: Input Voltage: 12V DC (Car Battery / Solar
Get a quote
Inverter Basics: Classification and Applications
Inverter Basics: Resonant Inverters This is the class of inverters in which output voltage or current is passed though zero to minimize switching
Get a quote
Continuous power vs surge power for the fuse and the wire sizing?
Since inverter AC output voltage is regulated, the more DC input voltage slumps the greater the DC current draw will be to make the required AC output power. This
Get a quote
What is the definition of each of the terms (AC output rated
My impression is that "passthrough" means when the inverter is connected to the grid. It can "pass through" AC current, meaning that the inverter is not converting the DC
Get a quote
8. Technical Specifications
1) Minimum start-up voltage is 41 VDC. Over-voltage disconnect: 65,5 V. 3) Peak power capacity and duration depends on start temperature of heatsink. Mentioned times are with cold unit. 5)
Get a quote
What does the peak power of the power inverter mean and what
Rated power is also called continuous output power, which is a long-term, stable power that provides continuous power for your load to work normally. If the total energy
Get a quote
Enphase IQ 7 and IQ 7+ Microinverters
Complies with advanced grid support, voltage and frequency ride-through requirements Remotely updates to respond to changing grid requirements Configurable for varying grid profiles Meets
Get a quote
Inverter peak power and inrush current
Above this current draw at 2x the power output, the inverter can''t convert any more AC power. So, using Ohm''s law again, we can see that an increased current draw will result in a decreased
Get a quote
Understanding Inverter Input and Output: What is the Relationship
The output produced by the inverter is an alternating current (AC) that is usually used to power various kinds of electronic devices needed in everyday life such as lights, fans, televisions,
Get a quote
What is the Peak Output Power of a Power Inverter?
For the device, there is also the concept of continuous output power and peak output power. The continuous output power is the rated output power, and the peak output
Get a quote
A comprehensive guide to inverter voltage
What is an inverter''s output voltage? The output voltage of an inverter is the voltage produced when the inverter converts DC power to AC power. This AC power is then
Get a quote
How to Read Solar Inverter Specifications
The nominal AC output power refers to the peak power the inverter can continuously supply to the main grid under normal conditions. It is almost similar to the rated
Get a quote
What Is an Inverter: Inverter Ratings, Efficiency & More
The battery voltage of a solar or wind system can vary as much as 35 percent (with varying state of charge and activity). Through all of this, the inverter must regulate the quality of its output
Get a quote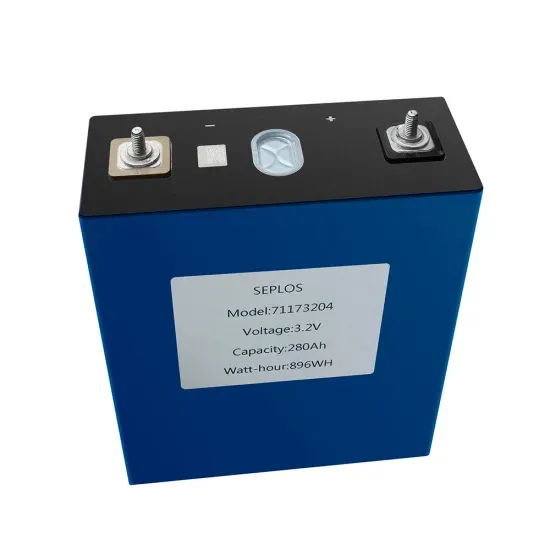
Inverter Basics and Selecting the Right Model
Battery based inverters use energy stored in a lead acid or lithium battery to generate AC output power that runs the loads. The low voltage DC battery
Get a quote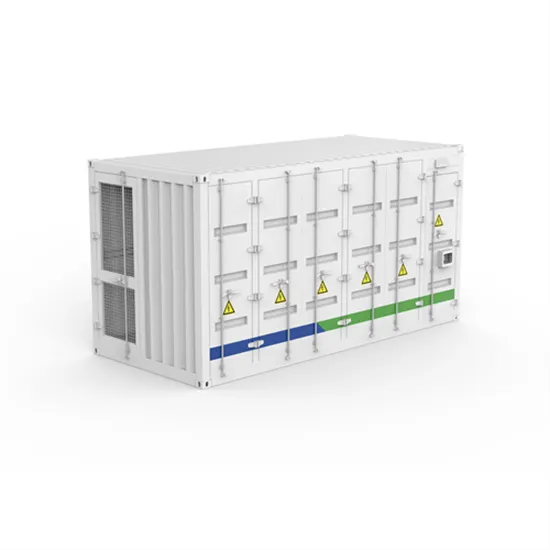
Understanding Inverters and How-to Select one that is
While actual output wattage of competitor''s inverters varies greatly, Wagan Tech inverters help consumers to understand and trust that the number printed on
Get a quote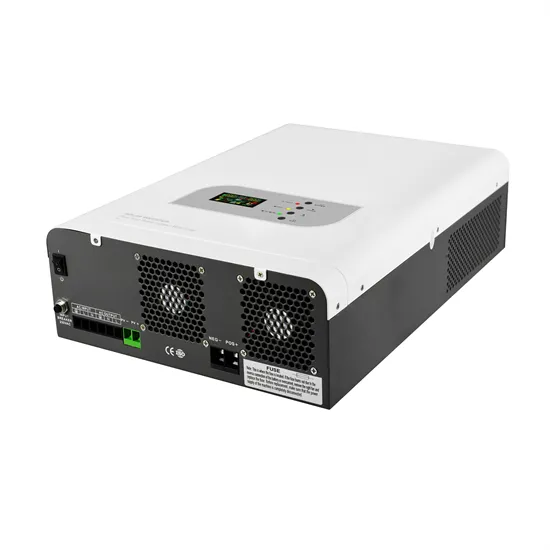
How To Read And Understand Solar Inverter
AC Output Voltage: This tells you the voltage the inverter will supply to your household or business, typically either 110V or 220V depending
Get a quote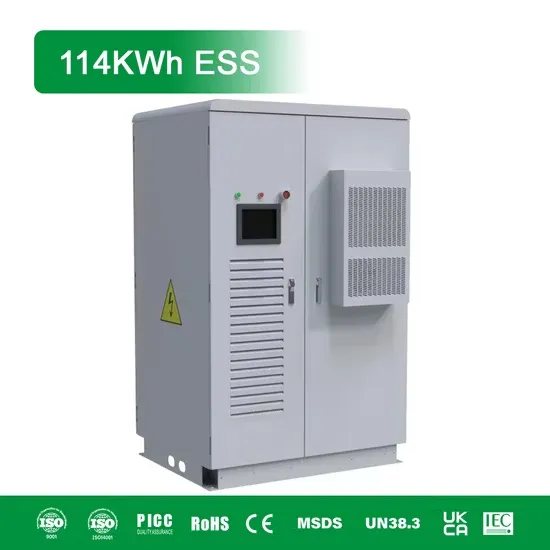
Understanding Inverters and How-to Select one that is right for you
While actual output wattage of competitor''s inverters varies greatly, Wagan Tech inverters help consumers to understand and trust that the number printed on the inverter is the actual
Get a quote
Solar Inverter Specifications
The following specifications reflect Tesla Solar Inverter with Site Controller (Tesla P/N 1538000-45-y). For specifications on Tesla Solar Inverter without Site Controller, see Tesla Solar
Get a quote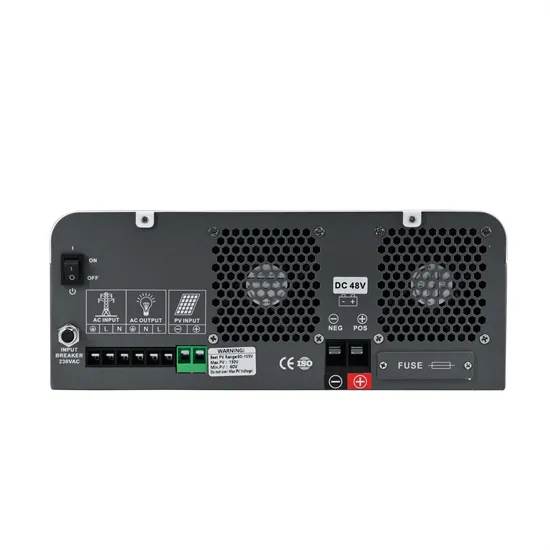
How does an inverter work?
At this time, the inverter circuit changes only the frequency, so it is called "CVVF (Constant Voltage Variable Frequency)". Last but not least, the inverter circuit
Get a quote
What Is an Inverter: Inverter Ratings, Efficiency & More
The battery voltage of a solar or wind system can vary as much as 35 percent (with varying state of charge and activity). Through all of this, the inverter must
Get a quote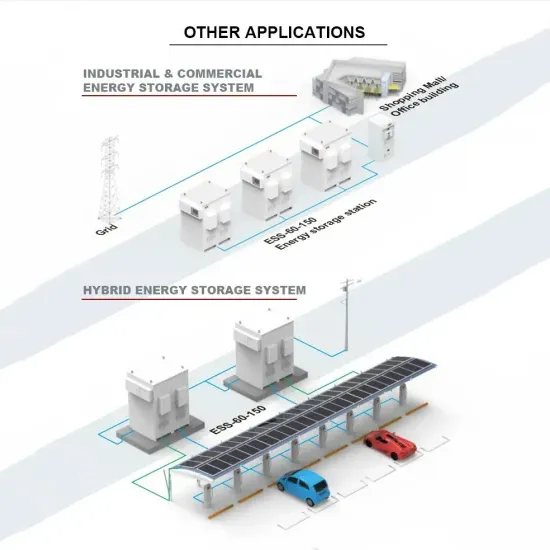
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power calculations and inverter
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What is the inverter s continuous output voltage ]
What does AC mean in a power inverter?
Nominal Voltage (AC). This indicates the nominal voltage that is output from the inverter. Rated AC Power Output (VA). This indicates the maximum AC power output from the inverter. Maximum Continuous Current Out AC (A). The indicates that maximum continuous AC current that may be output from the inverter. Peak Efficiency (%).
How do you classify an inverter based on its power output?
Using the CEC efficiency, the input power to the inverter must be PIN=POUT/CEC Efficiency=3,300 W/0.945=3,492 W Inverters can be classed according to their power output. The following information is not set in stone, but it gives you an idea of the classifications and general power ranges associated with them.
What is inverter output?
The inverter output is the electrical power generated by the inverter from the process of converting the DC input source into alternating current (AC).
How much power does an inverter need?
It’s important to note what this means: In order for an inverter to put out the rated amount of power, it will need to have a power input that exceeds the output. For example, an inverter with a rated output power of 5,000 W and a peak efficiency of 95% requires an input power of 5,263 W to operate at full power.
What do you need to know about input power inverters?
Here are some important specifications that you need to know about input power inverters. Input Voltage: The input voltage supplied from the DC source to the inverter follows the inverter voltage specifications, which start from 12V, 24V, or 48V.
What is the input voltage of an inverter?
Understanding the inverter voltage is crucial for selecting the right equipment for your power system. Inverter voltage typically falls into three main categories: 12V, 24V, and 48V. These values signify the nominal direct current (DC) input voltage required for the inverter to function optimally. What is the rated input voltage of an inverter?
Guess what you want to know
-
 What voltage does the inverter output
What voltage does the inverter output
-
 What is the tracking voltage of the inverter
What is the tracking voltage of the inverter
-
 What is the output voltage of a 295w photovoltaic panel
What is the output voltage of a 295w photovoltaic panel
-
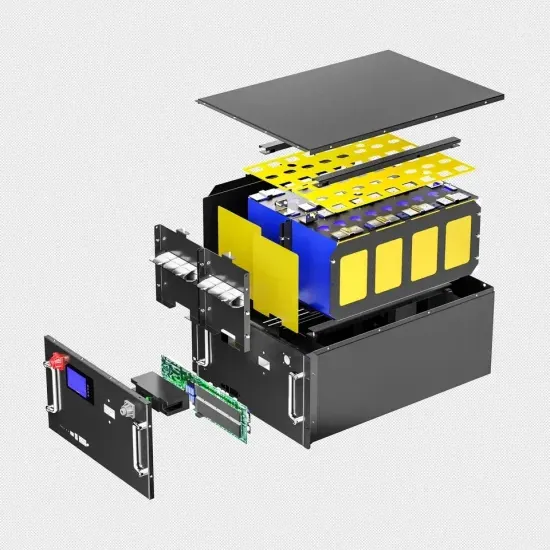 What is the output voltage of a 12V solar panel
What is the output voltage of a 12V solar panel
-
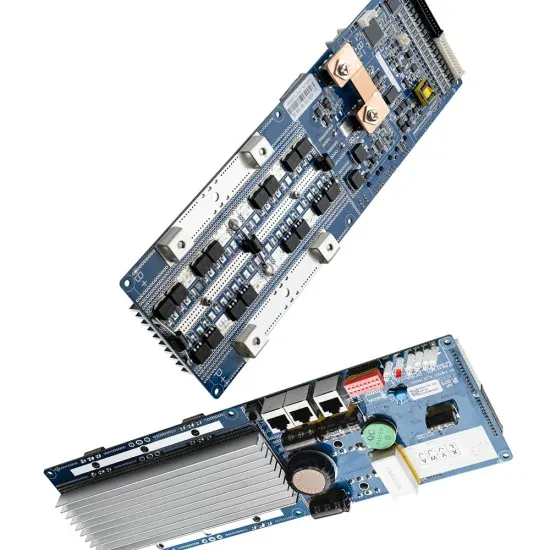 What is the maximum voltage of a 5kw inverter
What is the maximum voltage of a 5kw inverter
-
 What is the normal inverter voltage in Bosnia and Herzegovina
What is the normal inverter voltage in Bosnia and Herzegovina
-
 What is the maximum voltage of a 72V inverter
What is the maximum voltage of a 72V inverter
-
 Inverter voltage output is too low
Inverter voltage output is too low
-
 Is the inverter output voltage 233v normal
Is the inverter output voltage 233v normal
-
 What voltage does the inverter change
What voltage does the inverter change
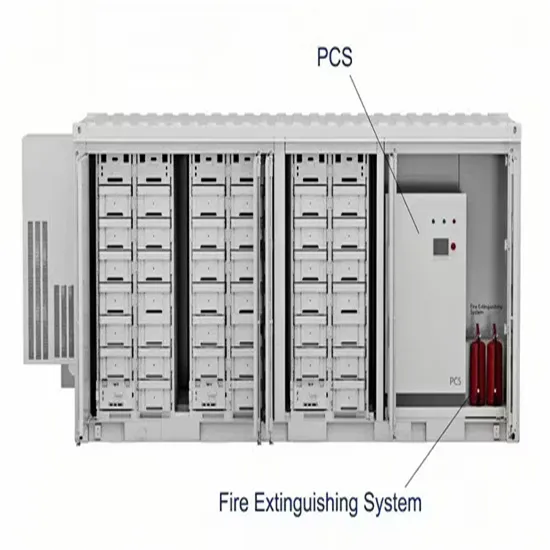
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


