Inverters, Types and Voltages
This blog post explores the key differences between low voltage and high voltage inverters as well as low frequency and high frequency inverters, helping you understand their
Get a quote
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key
Low frequency inverters are larger and handle surges better, while high frequency inverters are compact and cost-effective. Which inverter is better for solar
Get a quote
What is the difference between high and low frequency inverter?
This article explores the key differences between low frequency inverter and high frequency inverter, including their working principles, performance characteristics, advantages and
Get a quote
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
Learn the key differences between high frequency inverters and low frequency inverters. Discover which one suits your power needs for efficiency and surge capacity.
Get a quote
Rotary compressor VS Inverter Compressor: A few
The differences between a rotary compressor and an inverter compressor There are several differences between a rotary compressor and an inverter
Get a quote
Difference Between Inverter and Non-Inverter AC
An inverter air conditioner is a type of AC that uses advanced technology to regulate the speed of the compressor motor. Unlike traditional units that switch the compressor on or
Get a quote
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HIGH AND LOW FREQUENCY INVERTERS
12 volt inverter high and low frequency Low-frequency inverters operate at a frequency of 50 or 60 Hz, which is the same frequency as the AC electricity grid. High-frequency inverters operate at
Get a quote
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
Understanding the differences in size, weight, and performance between high and low frequency inverters can help you make informed decisions for your power needs.
Get a quote
Difference Between High and Low Frequency Inverter
Why is the difference so big? Because it is determined by the orientation of their respective working principles: for high-frequency inverters, the inversion logic is inverted at
Get a quote
Solar Inverter Vs Normal Inverter
After learning about solar inverter Vs normal inverter efficiency, it is time to gather knowledge about their price differences. The price of a solar inverter differs from system to
Get a quote
HIGH VS LOW FREQUENCY INVERTERS
Low-frequency inverters have the advantage over high-frequency inverters in two fields: peak power capacity, and reliability. Low-frequency inverters are designed to deal with
Get a quote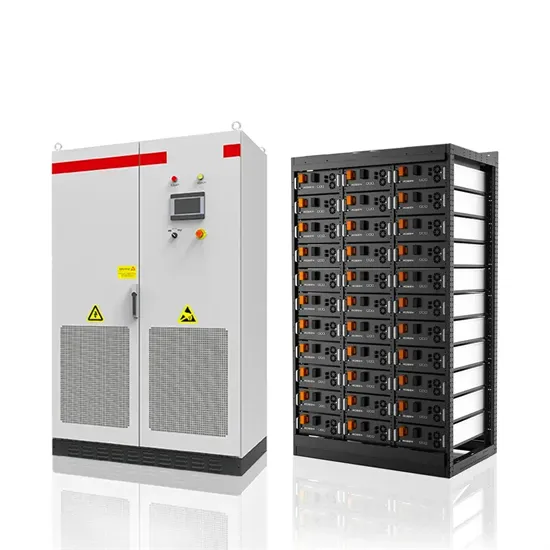
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get a quote
High Voltage Vs Low Voltage Batteries
Today we are going to look at the difference between high and low-voltage batteries. There are different applications for each of these systems and they both have very
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get a quote
Differences between Low Frequency (LF) Inverters
Differences between Low Frequency (LF) Inverters and High Frequency (HF) Inverters Nov 25, 2020. | By: José González Inverters can be
Get a quote
Low-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters: Which
Choosing the right inverter is key to maximizing your solar system''s efficiency. Explore the differences between high-frequency and low-frequency
Get a quote
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Key Differences
Low frequency inverters are larger and handle surges better, while high frequency inverters are compact and cost-effective. Which inverter is better for solar power systems? Are low
Get a quote
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar
Get a quote
Inverter vs Non-Inverter AC: The Ultimate Comparison
If you''re looking to buy a new air conditioner, you might be thinking about whether you should get the inverter or the non-inverter type. So, here is
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get a quote
Technical comparison between Low Frequency Inverter VS high
Low-frequency inverters have the advantage over high-frequency inverters in two fields: peak power capacity, and reliability. Low-frequency inverters are designed to deal with higher power
Get a quote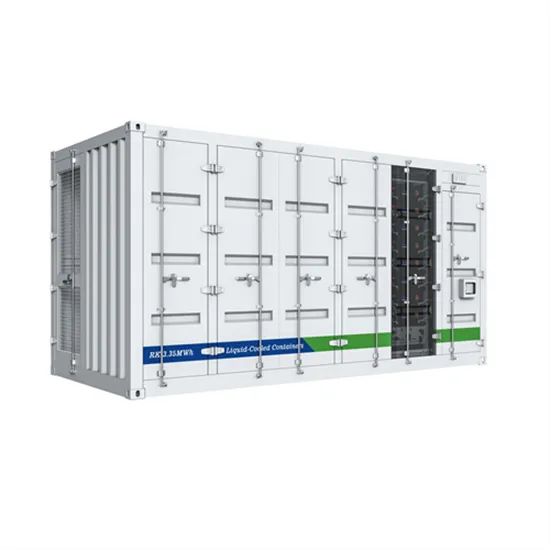
Technical comparison between Low Frequency
Low-frequency inverters have the advantage over high-frequency inverters in two fields: peak power capacity, and reliability. Low-frequency inverters are
Get a quote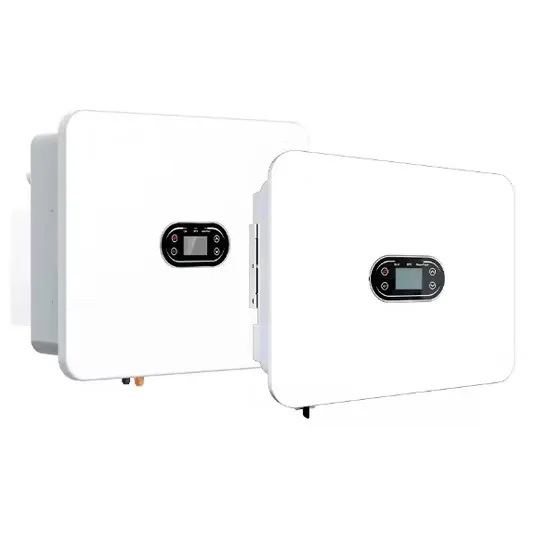
High frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter
This article compares high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter from the aspects of working frequency, components, efficiency, size
Get a quote
Low Frequency Vs. High Frequency Inverters
When choosing between a low-frequency and high-frequency inverter, consider your specific needs. For example, Victron combines both technologies in their Hybrid or Combined High
Get a quote
Low-Frequency vs. High-Frequency Inverters: Which One is
Choosing the right inverter is key to maximizing your solar system''s efficiency. Explore the differences between high-frequency and low-frequency inverters, and discover
Get a quote
Low vs High Voltage Home Energy Storage Systems: Pros, Cons
In this article, we''ll explore the technical differences between high and low voltage batteries, their respective benefits and trade-offs, and how to decide which option is right for
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Differences between high and low price inverters]
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
In the debate of high frequency vs low frequency inverters, both have their unique strengths and ideal use cases. High-frequency inverters offer efficiency and compactness, making them suitable for many modern applications, while low-frequency inverters provide robustness and are well-suited for heavy-duty tasks.
Is a low frequency inverter a good investment?
The price you would pay for a low frequency inverter over a high frequency inverter should be considered a long term investment, given how unlikely the low frequency inverter is to break down. They are indeed bigger, stronger, and tougher.
What is a low cost 1000w power inverter?
This power inverter, with a low cost, produces modified sine wave 1000w continuous and 2000w peak power, converting 24V DC to 110V/220V AC power. It is a low cost option that can be used for car, home, RV, or anywhere that AC power is needed. The inverter features durable housing, a built-in cooling fan, and multi-protections for safe and effective use.
How do I choose a high-frequency or low-frequency inverter?
Choosing between a high-frequency and low-frequency inverter depends on several factors, including efficiency, size, budget, and application needs. Here’s a quick guide: Residential Users: High-frequency inverters are ideal for home use, especially in solar systems, due to their efficiency and compact size.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Efficiency: Low-frequency inverters are known for their robustness and ability to handle high surge currents, making them suitable for powering heavy-duty appliances or equipment with high starting currents, such as motors and compressors.
Which solar inverter should I Choose?
Residential Users: High-frequency inverters are ideal for home use, especially in solar systems, due to their efficiency and compact size. Commercial Users: Businesses that require constant, reliable power may opt for low-frequency inverters, given their robustness.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Differences between industrial frequency and high frequency inverters
Differences between industrial frequency and high frequency inverters
-
 Inverter voltage high and low
Inverter voltage high and low
-
 Are low voltage inverters more stable
Are low voltage inverters more stable
-
 Is the voltage between the battery and the BMS high or low
Is the voltage between the battery and the BMS high or low
-
 Uganda high frequency inverter price
Uganda high frequency inverter price
-
 Zambia high frequency inverter price
Zambia high frequency inverter price
-
 52Hz low frequency high efficiency home inverter
52Hz low frequency high efficiency home inverter
-
 Price of high performance energy storage batteries in Kazakhstan
Price of high performance energy storage batteries in Kazakhstan
-
 Low voltage inverter high voltage grid connection
Low voltage inverter high voltage grid connection
-
 Price of low voltage energy storage integrated machine
Price of low voltage energy storage integrated machine
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


