How to Address Inverter Low Voltage Issues for
Inverters play a crucial role in industrial automation and energy management, ensuring seamless operation and efficiency. However, voltage
Get a quote
Switched pseudo-current mirror inverter for low-power, thermally stable
There are some improvement areas for a RO, encompassing low-power design and sensitivity reduction against variations, including the process variation, the temperature
Get a quote
Current limiting strategies for grid forming inverters under low
Despite sharing the same hardware, GFM inverters will behave as voltage sources, synchronizing with the grid through power balance. GFM inverters could replace SGs,
Get a quote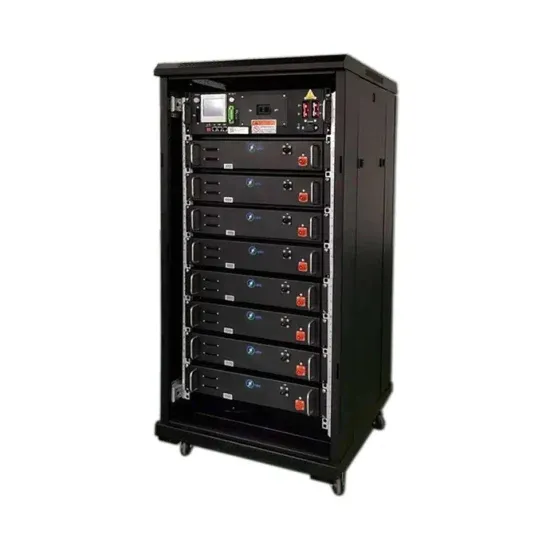
From 1000V to 1500V: A Comparison of High and Low Voltage
Through From 1000V to 1500V: A Comparison of High and Low Voltage Energy Storage Inverters news, you can learn more about the real practical applications and
Get a quote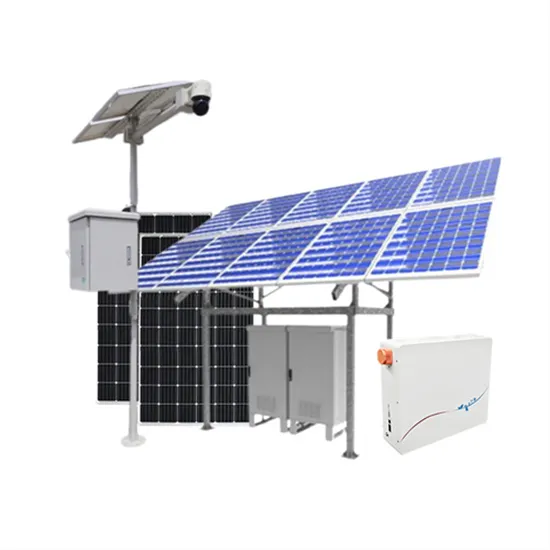
High Vs Low Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
There is a continuous fight between these two technologies as the Low-frequency battery inverter/UPS is very successful in countries with power
Get a quote
Low Power Inverter
The system to be presented is a low-power inverter system with the use of ULN2004 and HCF4047, to be used as an inverter that would efficiently change low-voltage DC power to a
Get a quote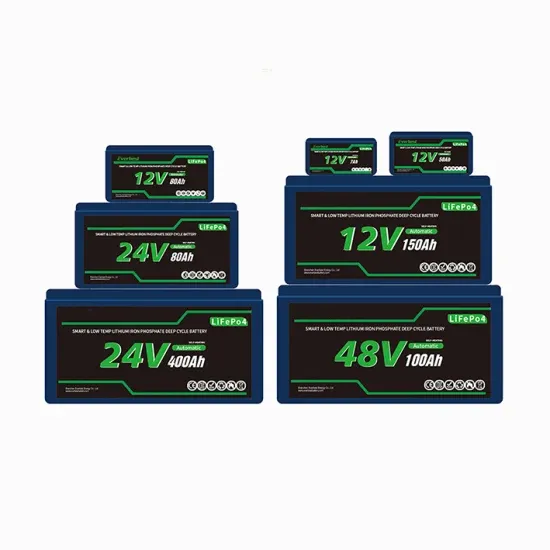
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
Insensitivity to Input Voltage Fluctuations: Low-frequency inverters are more tolerant of input voltage fluctuations and can operate stably over a
Get a quote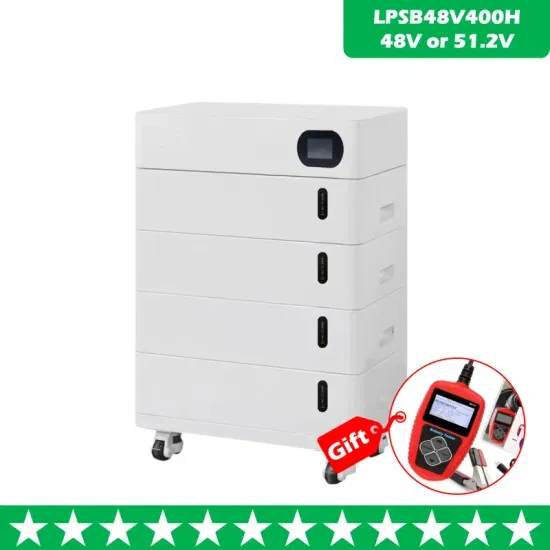
High Voltage Inverter: What They Are, How They
You need a solar inverter for your solar system. However, not all the inverter are same. There are high voltage and low voltage inverter, which differ from the
Get a quote
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Low-voltage inverters work with DC voltages ranging from 12V to 48V. These are often found in small systems like RVs, boats, cabins, and backup power for small homes. They
Get a quote
The Ups and Downs of Using Outdated Low-Voltage
While these older inverters can still be functional and useful, they come with inherent limitations. The market price for these units, often not
Get a quote
The Ups and Downs of Using Outdated Low-Voltage Hybrid Inverters
While these older inverters can still be functional and useful, they come with inherent limitations. The market price for these units, often not reflective of their outdated
Get a quote
Very low mains voltage with hybrid inverter. Would it work to
A stabilizer can work off very low voltage to set up a stable 110V or 220V AC output at 50Hz or 60Hz. A 10kva unit would cost from US$250, lots available on Alibaba if you
Get a quote
How does an inverter help stabilize voltage fluctuations?
Whether addressing short-term transients or long-term voltage instability, inverters play a vital role in ensuring the reliability and stability of power systems.
Get a quote
Framework to assess the stable operation of commercially
Abstract. This paper presents a framework to assess the grid compatibility of single-phase inverters connected to public low voltage network, which is characterized by a stable operation
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
What are high-frequency inverters? High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency
Get a quote
How to make this inverter output voltage stable
The circuit diagram below is an inverter that has an output voltage ranging from 110 to 200 volt AC. My problem is anytime I turn it on the output voltage keeps going on and off
Get a quote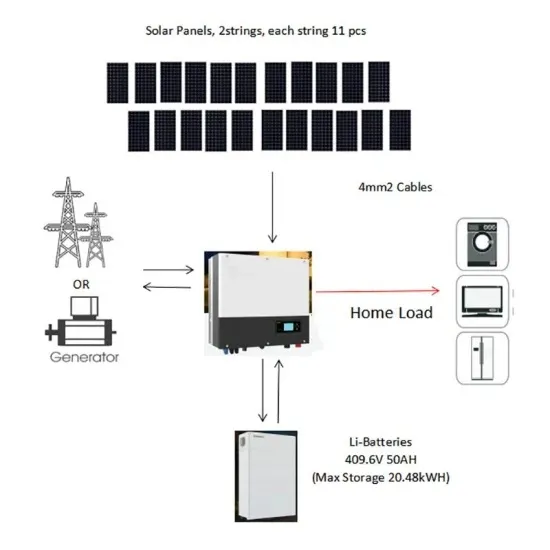
Why Should You Invest in a Low Voltage Inverter?
5. Off-Grid Power Solutions: Low voltage inverters are also valuable for off-grid power solutions. If you''re in a remote location or experiencing a power outage, a low voltage
Get a quote
High Vs Low Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
There is a continuous fight between these two technologies as the Low-frequency battery inverter/UPS is very successful in countries with power outage problems, and the High
Get a quote
Power decoupling strategy based on â virtual negative
The traditional P/w and Q/E droop method is effective for power control of the paralleled inverters if the system impedance is mainly inductive. However, in a low-voltage microgrid, the mainly
Get a quote
What is the optimal AC output voltage for inverter?
I''m running my inverter on 230v. What I''m noticing is that the City Power voltage is around 220v when loadshedding is over, sometimes as low
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
Insensitivity to Input Voltage Fluctuations: Low-frequency inverters are more tolerant of input voltage fluctuations and can operate stably over a wide range of input
Get a quote
A Stable and Ultrafast Control for Multiparallel Grid-Tied SiC
SiC device-based grid-tied inverters can achieve advantages such as higher efficiency, reduced size of interface filters, and fast dynamics; however, they can exacerbate
Get a quote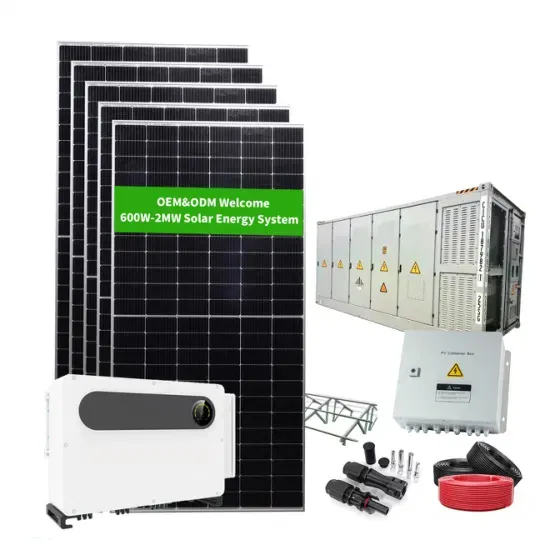
How to Address Inverter Low Voltage Issues for Reliable
Inverters play a crucial role in industrial automation and energy management, ensuring seamless operation and efficiency. However, voltage instability, particularly low
Get a quote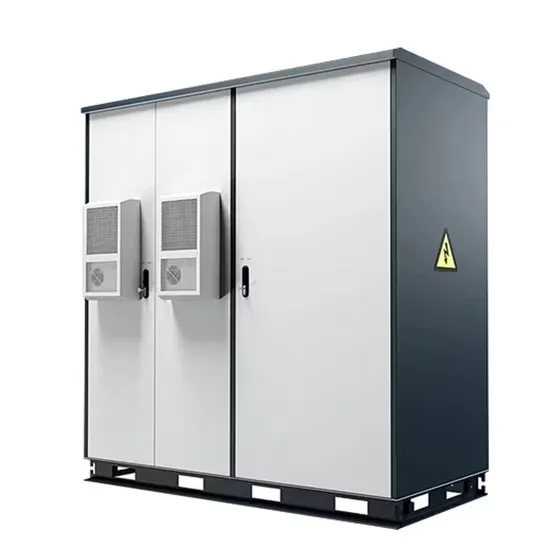
Understanding Inverter Input And Output: What Is The
Input Current: determines the amount of electric current required by the inverter based on the load and input voltage. Input Stability: if the input voltage and
Get a quote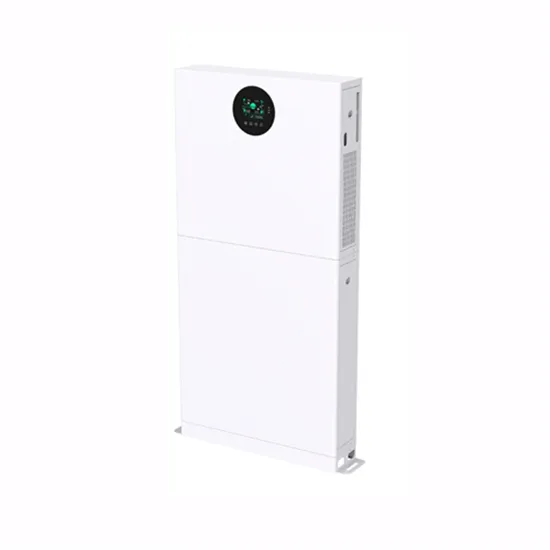
Get To Know What Is Low Frequency Inverter
Here are some of the advantages of low frequency inverters in their application. The structure of the low frequency inverter is simpler. Better electrical isolation, where the transformer will
Get a quote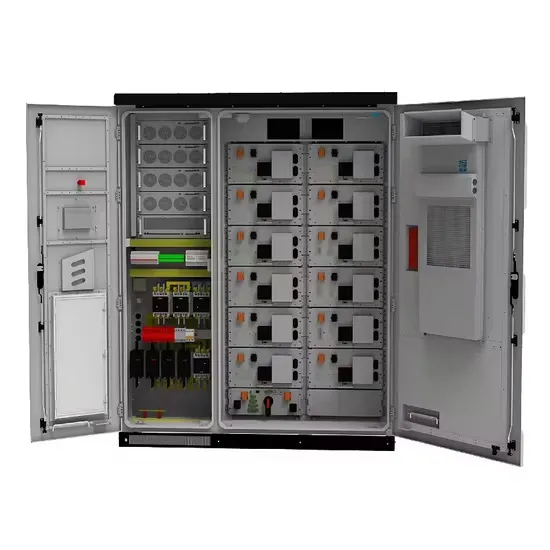
Frequency Stability Analysis for Inverters in Low Voltage
For practical purposes, we will not design new inverters, instead, we will analyze existing inverter designs. We would like to analyze whether a gridtie inverter or a droop inverter will be stable
Get a quote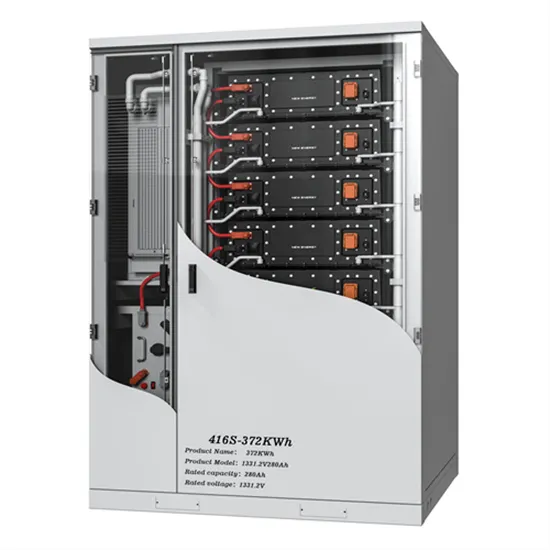
6 FAQs about [Are low voltage inverters more stable ]
Should I buy a high voltage or low voltage inverter?
Low voltage and high current means you need to spend more on copper/cables. Going for a higher voltage saves money on copper up until you reach issues with cable insulation and/or max input voltage to the inverter. The "problem" is not so much on the inverter side as it is on the supply side.
Why do inverters have a stable operation point?
Depending on the voltage sag depth and current capabilities of the inverter, a stable operation point can be achieved. Moreover, it has probed to be effective against other voltage perturbations, such as phase jumps or frequency excursions .
Should I use a higher voltage if I have a copper inverter?
Going for a higher voltage saves money on copper up until you reach issues with cable insulation and/or max input voltage to the inverter. The "problem" is not so much on the inverter side as it is on the supply side. (Generally speaking, each inverter may have their own issues)
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
High-frequency inverters/UPS operate at 20,000 to 100,000 Hz frequencies, while transformer-based Low-frequency inverters/UPS operate at 50 or 60 Hz frequencies. Transformer-based Inverters are more expensive and bulkier compared to High-Frequency Inverters/UPS. They are also more tolerant of higher and lower voltage fluctuations.
How stable are GFL inverters?
The stability of GFL inverters is limited under deep voltage sags and weak grid conditions . One method to evaluate their stability is through | v g | γ curves, where γ is the phase shift between the PLL output and the grid voltage , .
Why do inverters have two input voltage options?
The third and most distinctive advantage is the higher efficiency of inverters at higher input voltages. If you see the datasheet of the inverters with two input voltage options they are more efficient in converting higher input voltage to mains voltage than converting lower input voltage to the same mains voltage.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Energy storage high voltage battery and low voltage battery
Energy storage high voltage battery and low voltage battery
-
 How many watts does a low voltage 12v solar integrated machine have
How many watts does a low voltage 12v solar integrated machine have
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
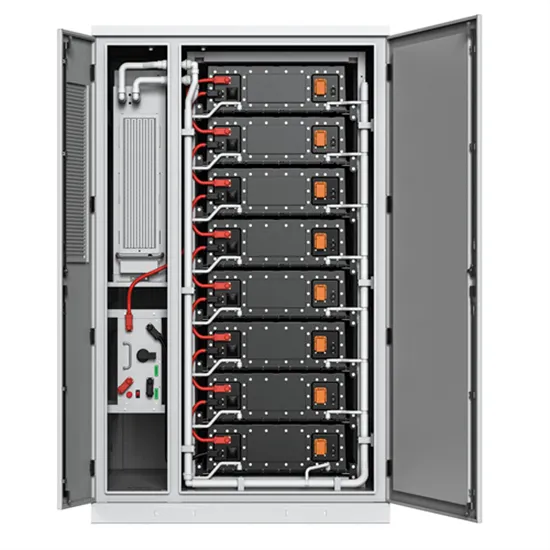 15kw three-phase low voltage hybrid inverter
15kw three-phase low voltage hybrid inverter
-
 Low voltage mobile power box
Low voltage mobile power box
-
 Moldova low voltage inverter price
Moldova low voltage inverter price
-
 Inverter high voltage side and low voltage side
Inverter high voltage side and low voltage side
-
 The voltage of one of the lithium battery strings is low
The voltage of one of the lithium battery strings is low
-
 Inverter for converting low voltage to 220V
Inverter for converting low voltage to 220V
-
 Is the inverter voltage output high or low
Is the inverter voltage output high or low
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


