Derivation and Analysis of a Secondary-Side LLC Resonant
Abstract—An isolated high step-up converter, which is derived from the reverse structure of a regular LLC resonant converter, is proposed in this paper. The proposed converter consists of
Get a quote
Low side vs. High side transistor switch
The low-side switch is switching ground while the high-side switch is connecting the voltage supply. Generally, you want to keep the ground connected in a circuit and switch the
Get a quote
FAQ on high-side vs. low-side load switching: part 1
The difference between high-side and low-side power switching is not apparent to many new designers, but it is a critical aspect of a viable circuit. Applying
Get a quote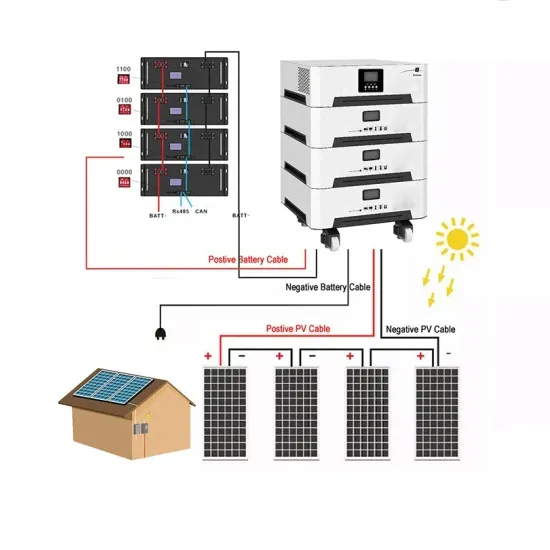
Inverter Protection and Ride-Through : RNWBL
The inverter voltage control characteristic can be combined with a plant controller to provide Point of Interconnection (POI) voltage controls that
Get a quote
The role and difference between high voltage inverter and low voltage
To summarize, high-voltage inverters are mainly used for high-power applications in industry, while low-voltage inverters are suitable for low-power applications in homes and
Get a quote
Quick Reference Guide Isolation in Electric Vehicle Systems
This high voltage to low voltage (HV-LV) dc-dc converter is often referred to as an auxiliary dc-dc, or Auxiliary Power Module (APM). These functions require galvanic isolation to separate
Get a quote
Reference design: 5kW Isolated Bidirectional DC-DC Converter
Total solution including low voltage side MOSFET (TK49N65W5) and gate driver (TLP5214A) This reference design uses silicon (Si) MOSFETs based on the assumption of 400V input-output on
Get a quote
Low-voltage VS High-voltage Inverters: What''s the Difference
The distinction between low-voltage (LV) and high-voltage (HV) inverters extends beyond nominal voltage thresholds, encompassing design architectures, efficiency trade-offs, and application
Get a quote
How to do high voltage high-side switching in a simple
Finally, it''s worth mentioning that I probably won''t be using these solutions for low voltage high side switching, as even a leakage power of
Get a quote
High Voltage vs Low Voltage
High frequency inverters run with fancier electronics doing high-speed switching to achieve a 230V output. This means they can be made lighter and cheaper, but any surge is
Get a quote
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
Low nominal voltages can be directly achieved by inverter using an internal transformer or buck-boost circuitry while for high nominal voltages, external step-up transformers are used.
Get a quote
Whats is a High Voltage Hybrid inverter? What are
Explore the pivotal differences between high and low voltage hybrid inverters and how these variations can influence your choice in sustainable
Get a quote
Differences and similarities between low-voltage inverters and
Both low-voltage and high-voltage inverters have their place in the electrical and energy systems, and understanding their differences is key to making informed decisions about energy
Get a quote
High Side vs Low Side Mosfet Drivers? | Electronics Forum
A high side driver is a boot-strapped supply driver of an output N-ch MOSFET with a level shifter on the driver''s input. One typical useage is for an H-bridge MOSFET output
Get a quote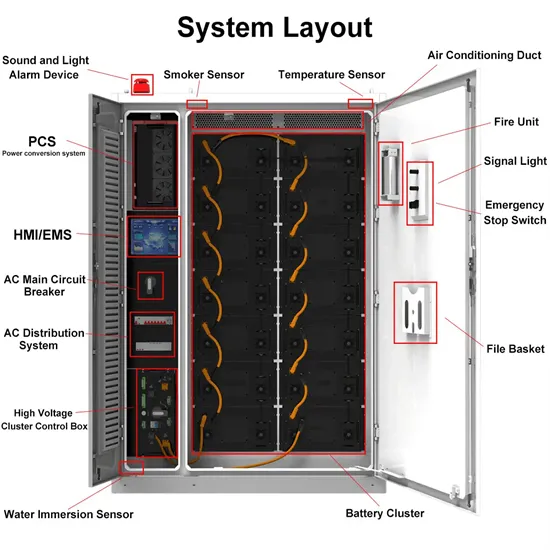
Tackling Low-Voltage Signaling in Inverter Design: Part 2
Discover practical strategies for managing noise in high-power inverter designs. From component selection and PCB stack-up to routing
Get a quote
The role and difference between high voltage inverter
To summarize, high-voltage inverters are mainly used for high-power applications in industry, while low-voltage inverters are suitable for low
Get a quote
Is there a difference between a high voltage inverter and a low voltage
The choice between low-voltage and high-voltage hybrid inverters depends on system size, power requirements, and availability and investment opportunities. Low voltage is
Get a quote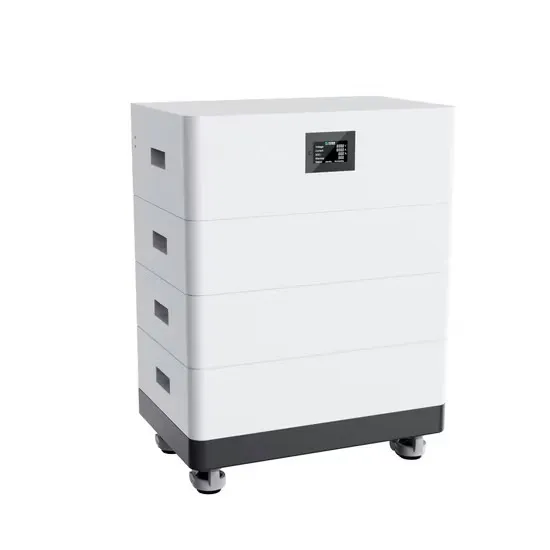
Differences and similarities between low-voltage inverters and high
Both low-voltage and high-voltage inverters have their place in the electrical and energy systems, and understanding their differences is key to making informed decisions about energy
Get a quote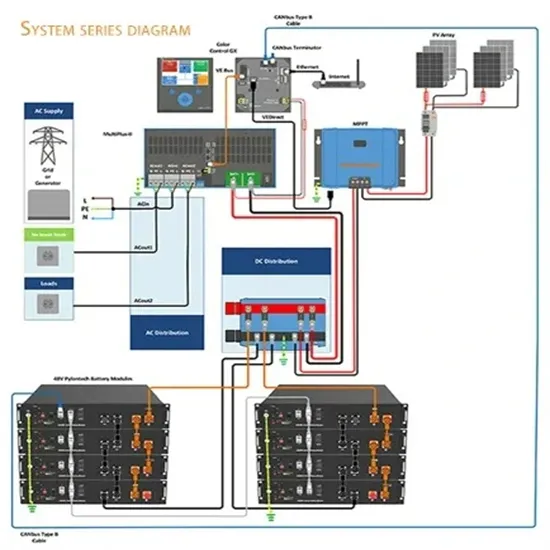
High Voltage High Side/ Low Side N-Channel MOSFET Driver
The LTC4446''s high side driver is capable of driving a 1nF load with 8ns rise and 5ns fall times using a bootstrapped supply voltage VBOOST-TS of 12V while its low side driver is capable of
Get a quote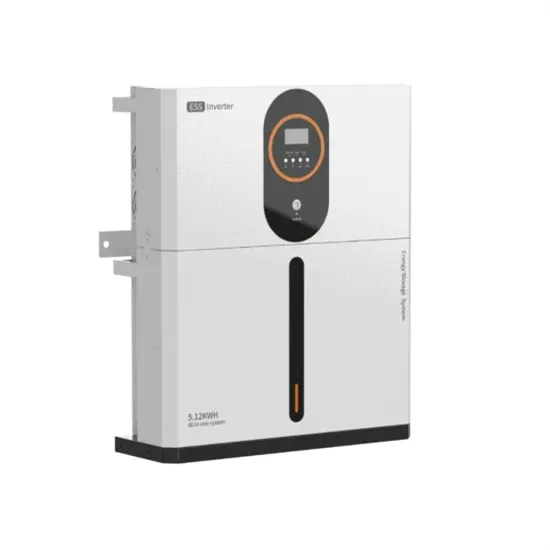
Whats is a High Voltage Hybrid inverter? What are Key
Explore the pivotal differences between high and low voltage hybrid inverters and how these variations can influence your choice in sustainable energy solutions.
Get a quote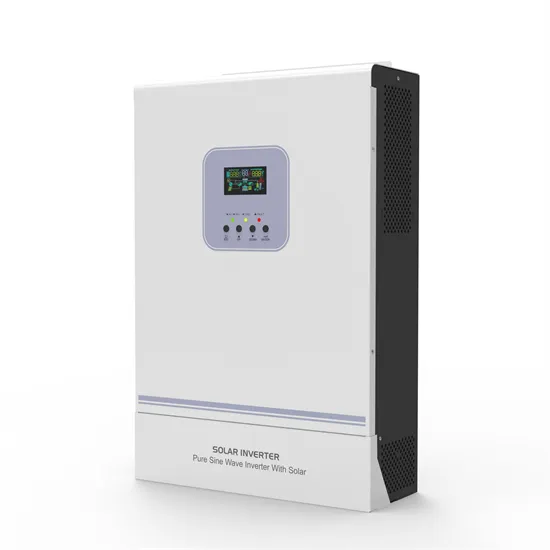
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
High frequency inverters run with fancier electronics doing high-speed switching to achieve a 230V output. This means they can be made lighter and cheaper, but any surge is
Get a quote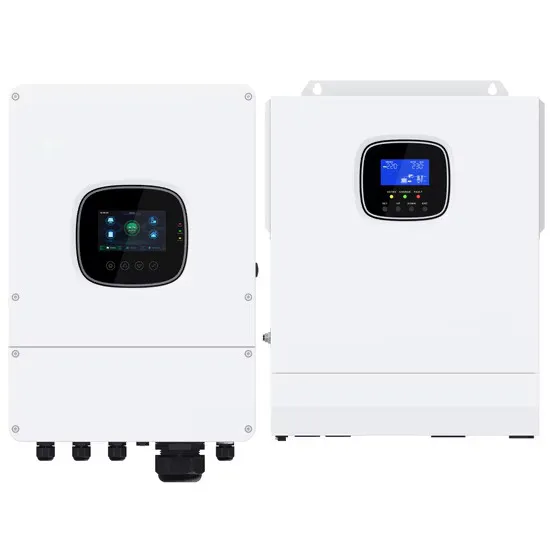
Is there a difference between a high voltage inverter and a low
The choice between low-voltage and high-voltage hybrid inverters depends on system size, power requirements, and availability and investment opportunities. Low voltage is
Get a quote
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar
Get a quote
Inverters, Types and Voltages
This blog post explores the key differences between low voltage and high voltage inverters as well as low frequency and high frequency inverters, helping you understand their
Get a quote
Guess what you want to know
-
 Low voltage inverter high voltage grid connection
Low voltage inverter high voltage grid connection
-
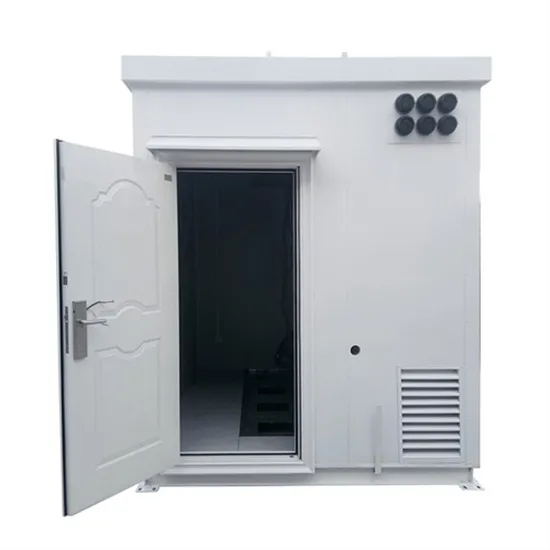 Inverter voltage high and low
Inverter voltage high and low
-
 Can the inverter convert low voltage into high voltage
Can the inverter convert low voltage into high voltage
-
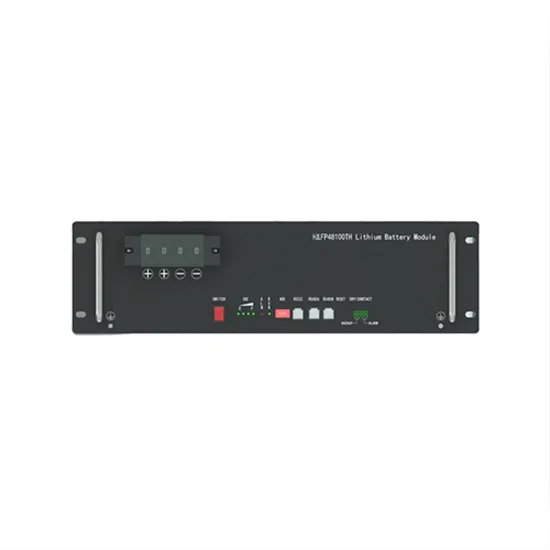 Inverter high voltage side and low voltage side
Inverter high voltage side and low voltage side
-
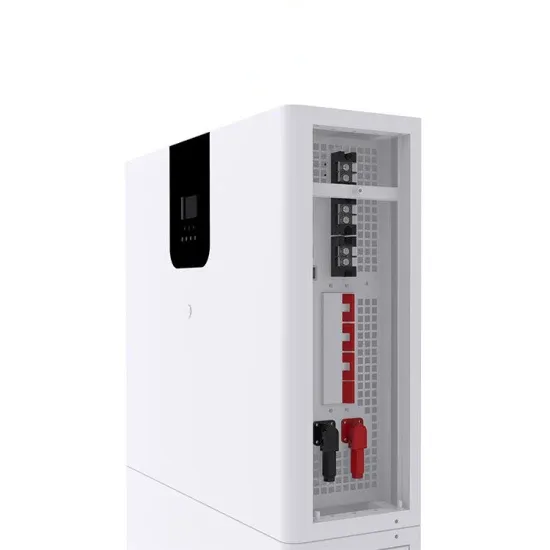 Single-phase high and low voltage inverter
Single-phase high and low voltage inverter
-
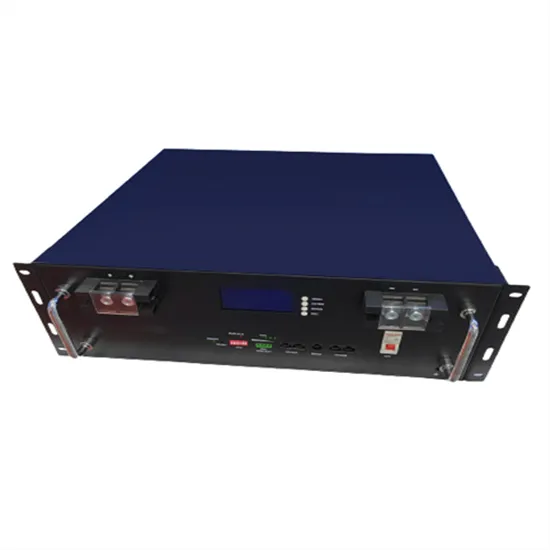 ASEAN high voltage inverter 220v
ASEAN high voltage inverter 220v
-
 High voltage inverter model
High voltage inverter model
-
 Amorphous machine inverter high voltage
Amorphous machine inverter high voltage
-
 Inverter for converting low voltage to 220V
Inverter for converting low voltage to 220V
-
 Middle East low voltage inverter manufacturer
Middle East low voltage inverter manufacturer
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


