Zero-voltage-switching Three-phase T-type Inverter
A novel zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) three-phase T-type inverter and its control scheme are proposed, which can realize ZVS operation of all switches. The operation principle
Get a quote
(PDF) Single Phase T-Type Multilevel Inverters for
DC power sources. T his paper presents a review of the various topologies of single-phase T-Type MLIs (T-MLIs). These MLIs are used to
Get a quote
T-type Advanced 3-level Inverter Module Power dissipation
When T3 uses the FWD mode, please input the Vge = +15V of T3. This technical note contains the product specifications, characteristics, data, materials, and structures as of January2012.
Get a quote
Common-Mode Voltage Reduction and Neutral Point
The quasi-Z-source T-type inverter is a new type of three-level inverter. Compared with other three-level inverters, the quasi-z-source T-type
Get a quote
T-type Multilevel Inverters: A Comparative Performance
There are a few T-Type MLIs formulated based on requirements and applications. This work provides a comparative analysis of three different T-Type five-level MLIs with a five-level
Get a quote
3-level T-type inverter. | Download Scientific Diagram
Figure 3 illustrates the power circuit diagram of a three-level T-type converter, comprising four IGBT active switches labeled T1 to T4, forming the shape of a T.
Get a quote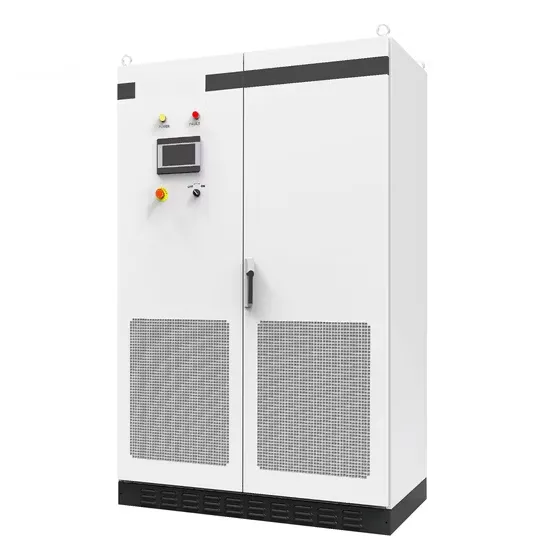
25 kW High Efficiency High Power Density Bi
The 25 kW bi-directional T-type inverter demonstrates the performance of Wolfspeed''s 650 V and 1200 V silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs within high
Get a quote
Common-Mode Voltage in Three-Level T-Type Inverter:
This paper investigates the origins of common-mode voltage (CMV) noises in SiC MOSFET-based three-level T-type inverters (3LT I), targeting adjustable speed drive (ASD) systems,
Get a quote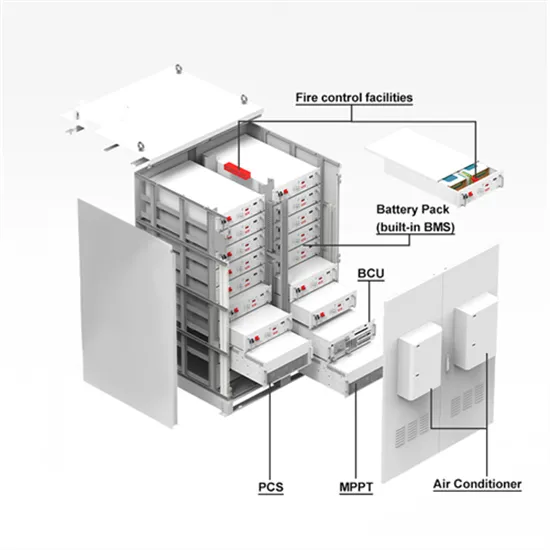
25 kW High Efficiency High Power Density Bi-directional T-type Inverter
The 25 kW bi-directional T-type inverter demonstrates the performance of Wolfspeed''s 650 V and 1200 V silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs within high power renewable energy systems such as
Get a quote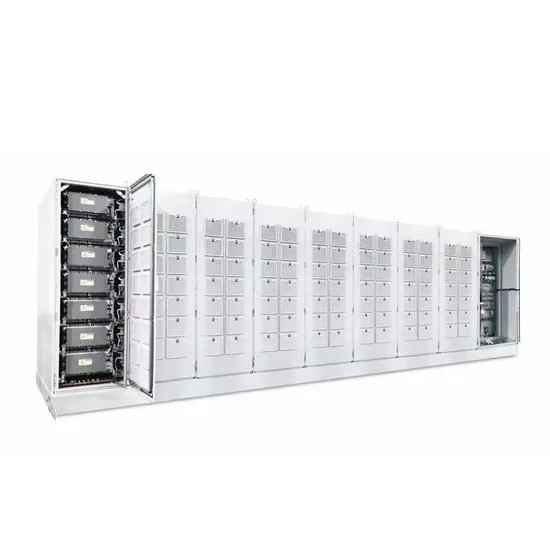
Paper Title [Font: Times New Roman, Size:20]
A 3-phase 3-level T-type inverter was implemented and multicarrier PWM technique is used for multilevel inverter strategies to generate 3-level output phase voltage.
Get a quote
A 5-level T-type inverter fed six-phase induction motor drive for
ABSTRACT This paper presents the performance analysis of a five-level T-type multilevel inverter (MLI) based six-phase induction motor drive (SPIMD) for high-power
Get a quote
T-type Multilevel Inverters: A Comparative Performance
The 5-level T-type inverter architecture was put forth in [13]–[15] to reduce the number of devices. It has become quite popular for applications like grid interfacing of renew-able energy sources.
Get a quote
Neutral-point-clamped and T-type multilevel inverters
The operating principles, switching states, switch fault analysis, influence of switching states on the dc capacitor voltages, and modulation of the NPC and T-type inverter
Get a quote
Full SiC Three‐Level T‐Type Quasi‐Z Source Inverter
As a relatively recent advanced inverter topology, the three-level T-type quasi-impedance source inverter (3L T-Type qZSI) offers the improved
Get a quote
Single Phase T-Type Multilevel Inverters for Renewable
It was determined that the DC voltage and current should be converted to AC voltage using an inverter [4,5]. A common type of single-phase inverter produces three levels of output voltage:
Get a quote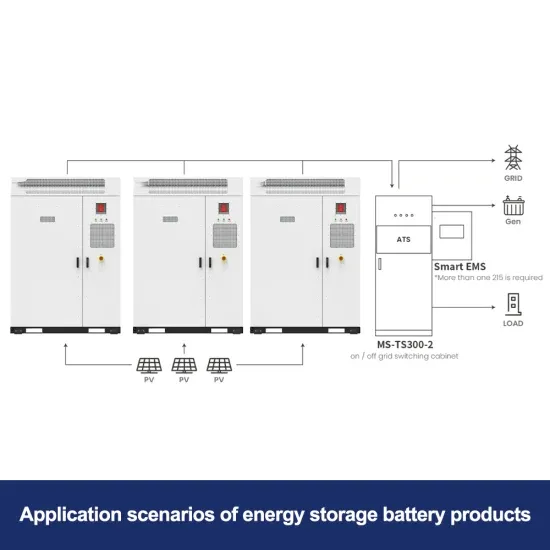
Design and Implementation of a Three-Phase Active T-Type
This paper presents the design and implementation of a 3 kVA three-phase active T-type neutral-point clamped (NPC) inverter with GaN power devices for low-voltage microgrids.
Get a quote
Choosing the Right 3-Level Inverter: T-Type vs. T-NPC
The decision between T-type and T-NPC is not about which is universally "better," but which is the best fit for your application''s specific priorities. Here''s a practical guide to help
Get a quote
Design and Implementation of a Highly Eficient Three-Level
In this paper, the alternative of using three-level converters for low-voltage applications is addressed. The performance and the com-petitiveness of the three-level T-type converter
Get a quote
A closer look at multilevel traction inverters
The main advantage of the T-type inverter is that it uses a standard triple half-bridge for driving the motor, but that also means the bridge switches must be rated to
Get a quote
Three-Phase T-Type Inverter
The T-type inverter is similar to the three-level neutral-point clamped (NPC) inverter in that it adds an additional output voltage level at 0 V, thereby offering improved harmonic performance over
Get a quote
Parameter Design of Current Double Closed Loop for T-Type
In this paper, a T-type three-level grid-connected inverter is used as the interface between the distributed power supply and the power grid, and the parameter design of the current double
Get a quote
11-kW, Bidirectional Three-Phase Three-Level (T-type)
This reference design provides an overview on how to implement a bidirectional three-level, three-phase, SiC-based active front end (AFE) inverter and power factor correction (PFC) stage.
Get a quote
Design and Implementation of a Three-Phase Active T
Discover the efficient design and implementation of a 3 kVA three-phase active T-type NPC inverter with GaN power devices for low-voltage microgrids.
Get a quote
Three-Phase T-Type Inverter
This video corresponds to the PLECS demo model of a three-level T-type inverter rated at 22 kVA that converts an 800 V DC-bus into a three-phase 480 V distribution for industrial grid-tied
Get a quote
What is a T-type inverter and how does it work?
In summary, the T-type inverter is a versatile and efficient solution for converting DC to AC power, particularly in applications requiring high efficiency and performance. Its
Get a quote
Guess what you want to know
-
 Which type of high voltage inverter is more than 500 yuan
Which type of high voltage inverter is more than 500 yuan
-
 Inverter rated voltage type
Inverter rated voltage type
-
 What is the voltage of Nordic inverter
What is the voltage of Nordic inverter
-
 AC voltage of single-phase inverter
AC voltage of single-phase inverter
-
 What voltage does the inverter change
What voltage does the inverter change
-
 Single voltage closed loop inverter
Single voltage closed loop inverter
-
 Influence of input voltage on inverter
Influence of input voltage on inverter
-
 Inverter high voltage side and low voltage side
Inverter high voltage side and low voltage side
-
 Ultra-high voltage DC inverter
Ultra-high voltage DC inverter
-
 Battery voltage reduction to inverter
Battery voltage reduction to inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

