Predictive Current Control of a Voltage Source Inverter
This paper presents a predictive current control method and its application to a voltage source inverter. The method uses a discrete-time model of the system to predict the future value of
Get a quote
Predictive Current Control Strategy for Voltage Source Inverter
This control scheme predicts the future load current behavior for each valid switching state of the converter, in terms of the measured load current and predicted load voltages.
Get a quote
Model-Free Predictive Current Control of a Voltage Source
The simulation and experimental results show that the proposed method is totally robust against parameters and model changes compared with the conventional model based solutions.
Get a quote
Optimal Structures for Voltage Controllers in Inverters
In this paper, we pose an optimal voltage control problem for ac inverter systems and study the structure of the resulting feedback laws.
Get a quote
Current Regulated Voltage Source Inverter | CLosed
Since the magnitude and waveforms of motor currents are independent of changes in motor impedance and source voltage, the inverter essentially
Get a quote
Voltage Source Inverter Reference Design (Rev. E)
Control design of such inverter is challenging because of the unknown nature of load that can be connected to the output of the inverter. This reference design uses devices from the C2000
Get a quote
Voltage Source Inverter : Construction, Phases & Its
The external commutation inverters, acquire sources externally from motors or power supply and the self-commutated inverters control the circuit with the
Get a quote
Current control techniques for three-phase voltage
The aim of this paper is to present a review of current control techniques for three-phase voltage-source pulsewidth modulated converters.
Get a quote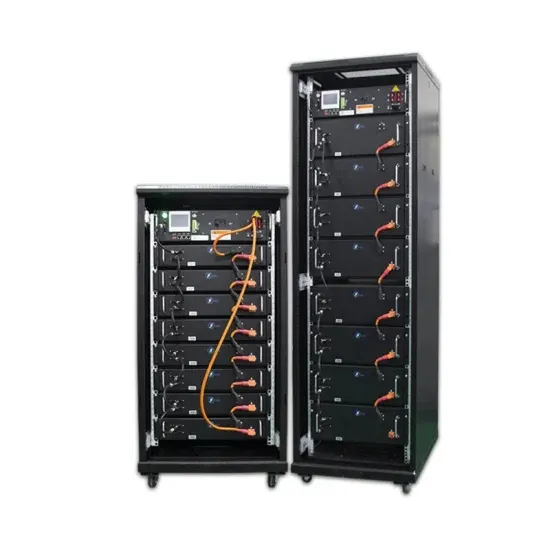
A Unified Control Design of Three Phase Inverters
The primary cascaded control loops and the phase-locked loop (PLL) can enable voltage source inverter operation in grid-forming and grid
Get a quote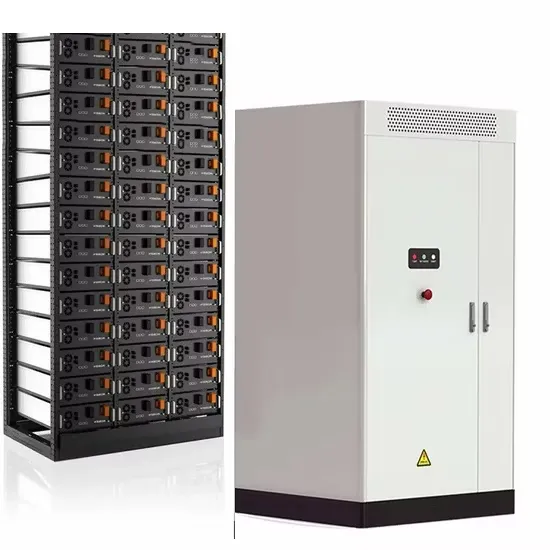
Model-Free Predictive Current Control of a Voltage Source Inverter
The simulation and experimental results show that the proposed method is totally robust against parameters and model changes compared with the conventional model based solutions.
Get a quote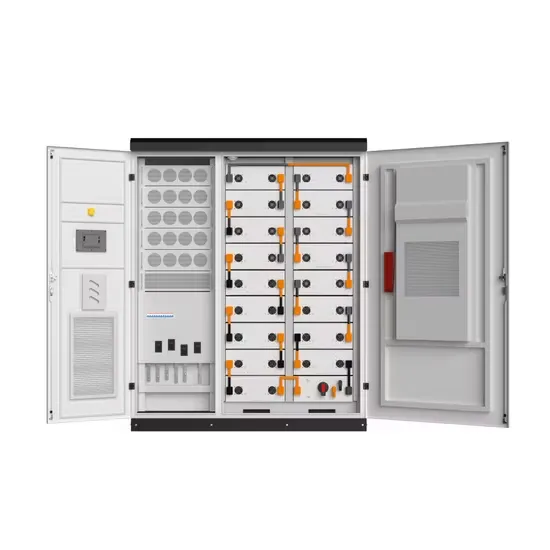
Comparison of Voltage Control and Current Control
This study is aimed at both summarizing the main implementation refinements which characterize the latest versions of the voltage source inverter controllers
Get a quote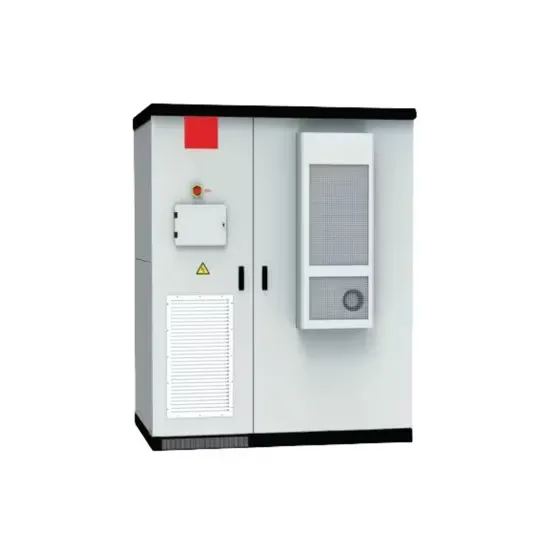
CURRENT CONTROL OF A MULTI-LEVEL VOLTAGE
ABSTRACT-In most high-performance applications of voltage source pulse-width modulation inverters, current control is an essential part of the overall control system. This paper propose
Get a quote
Current Control of a Voltage Source Inverter connected to
This paper proposes a simple current control scheme, based on the combination of deadbeat and PI control, for a three-phase voltage source inverter connected to the grid via an LCL filter.
Get a quote
Optimal Structures for Voltage Controllers in Inverters
Abstract—Output voltage regulation is a primary perfor-mance objective in power electronics systems which are not supported by a stiff voltage source. In this paper, we pose an optimal
Get a quote
Voltage Control Methods of Inverter – PWM Technique
In motor control applications, inverters handle the control of circuit voltage along with frequency so that the saturation of motor magnetic circuits
Get a quote
JETIR Research Journal
Voltage source inverters (VSIs) are indispensable components in power electronics, enabling the efficient conversion and control of power between direct current (DC) and alternating current
Get a quote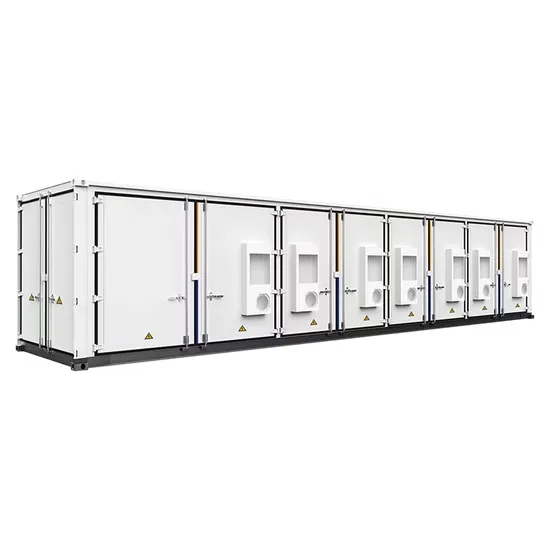
What is Current Source Inverter? Working, Diagram & Waveforms
Fig. 2: CSI using transistor The variable dc voltage source is converted into a variable current source by using inductance L. The current I L supplied to the single phase
Get a quote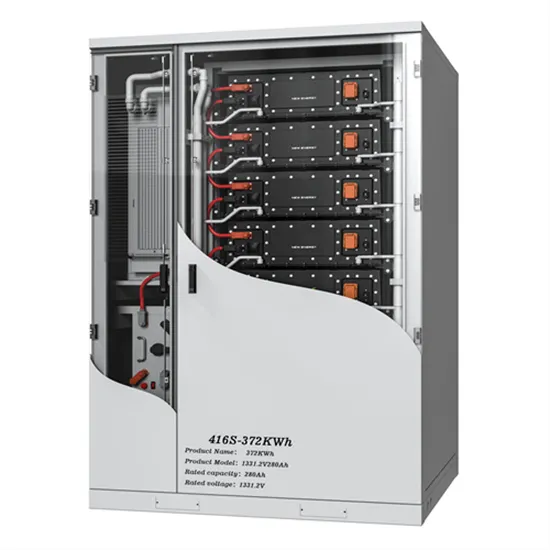
Current-Controlled Voltage Source Inverter
A current-controlled voltage source inverter (CCVSI) is defined as a type of inverter that operates as a current source, allowing for fast response in power flow control by adjusting the switching
Get a quote
A Current-Control Strategy for Voltage-Source Inverters in Microgrids
In this paper, a current-control strategy is proposed for voltage-source inverters in microgrids. The main objective of the proposed controller is to inject a clean sinusoidal current
Get a quote
Voltage Source Inverters Control using PWM/SVPWM For
Similarly, these topologies can be found as current source inverters (CSIs), where the independently controlled ac output is a current waveform. These structures are still widely
Get a quote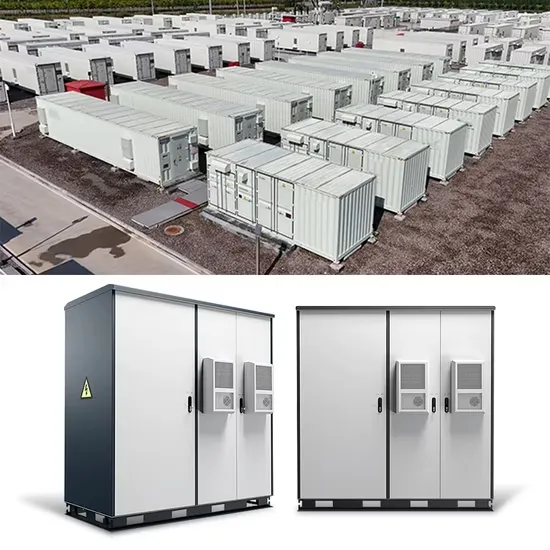
A review on current control techniques for inverter for three phase
Renewable based power generation system and their grid interconnection throughout the world. Due to large penetration of renewable sources into the grid, maintenance of power quality, grid
Get a quote
Comparison of Voltage Control and Current Control Methods in
This study is aimed at both summarizing the main implementation refinements which characterize the latest versions of the voltage source inverter controllers and comparing the different
Get a quote
Predictive Current Control of Voltage Source Inverters Using
hase Voltage Source Inverter (VSI) using a diode-based rectifier has been created. For general-purpose industrial motor drives that use three-phase Alternating Current (AC), the
Get a quote
Current Regulated Voltage Source Inverter | CLosed Loop Control
Since the magnitude and waveforms of motor currents are independent of changes in motor impedance and source voltage, the inverter essentially operates as a current source inverter.
Get a quote
(PDF) Hysteresis Current Controllers for Grid Connected Inverter
The purpose of this paper is to present a comparative study on basic hysteresis current controller techniques for grid connected inverters. Hysteresis current controllers are
Get a quote
Current Source Inverter (CSI) Power Converters in
In a CSI, the current source input implies that when an open circuit fault occurs, the inverter cannot inherently limit or control the output voltage.
Get a quote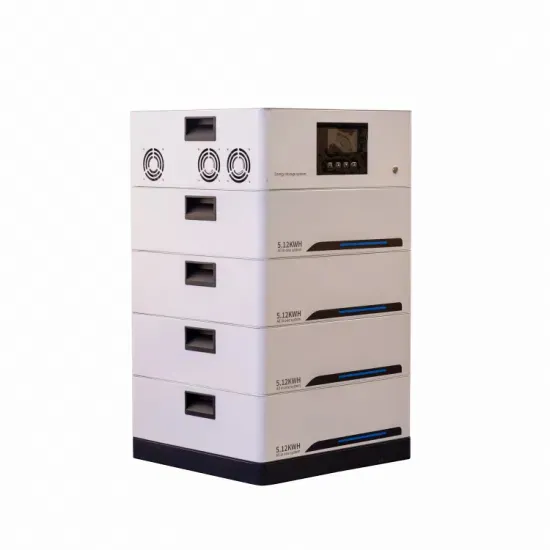
6 FAQs about [Voltage-source inverter current control]
What is a voltage source inverter?
Voltage source inverters (VSIs) are commonly used in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to generate a regulated AC voltage at the output. Control design of such inverter is challenging because of the unknown nature of load that can be connected to the output of the inverter.
How do I set up a voltage source inverter?
To get started: Confirm that no power source is connected to the design. Confirm that the output filter is correct for the mode that the device will run in. For example, voltage source inverter uses an LC filter. The L2 and L2N slot must be jumper wired as shown in Figure 11.
What is a voltage source inverter (VSI)?
An IMPORTANT NOTICE at the end of this TI reference design addresses authorized use, intellectual property matters and other important disclaimers and information. Voltage source inverters (VSIs) are commonly used in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to generate a regulated AC voltage at the output.
How to control the power flow of an inverter?
The first method is through the control of switching instance of inverter so as to produce a fundamental 50 Hz voltage in the output of inverter (Schauder, 1995; Mori, 1999). In this method, the power flow is controlled by adjusting the amplitude and phase of inverter output voltage relative to the line voltage.
How do you control an inverter?
Simple strategies focus on the direct control of a single variable, such as the output or inverter current (respectively at grid- or inverter-side of the filter) . A common approach comprises an outer control loop for capacitor voltage control and an inner control loop for the inverter current.
What is the difference between voltage and current controlled inverters?
Since in current controlled inverter, output current is directly controlled, there is inherent over current protection; but in voltage controlled inverters external hardware is needed for over current protection. According to Eq. 1, in voltage controlled inverters P is directly related to δ.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Battery inverter current limiting control
Battery inverter current limiting control
-
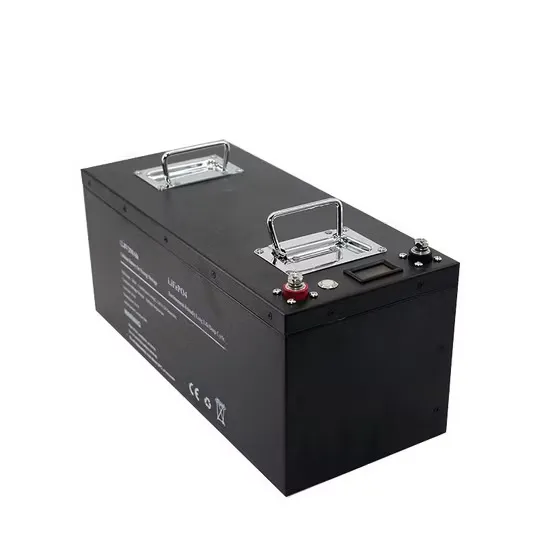 Battery cabinet and current output control
Battery cabinet and current output control
-
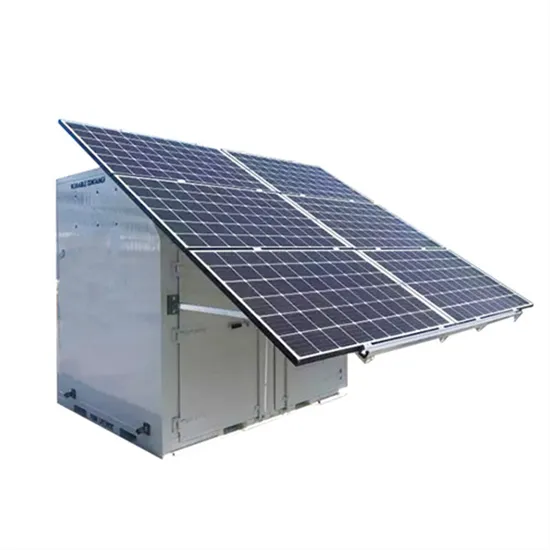
 Power frequency pure sine wave control inverter
Power frequency pure sine wave control inverter
-
 Current power of inverter
Current power of inverter
-
 Current inverter intermediate DC link
Current inverter intermediate DC link
-
 Power Control Unit and Inverter
Power Control Unit and Inverter
-
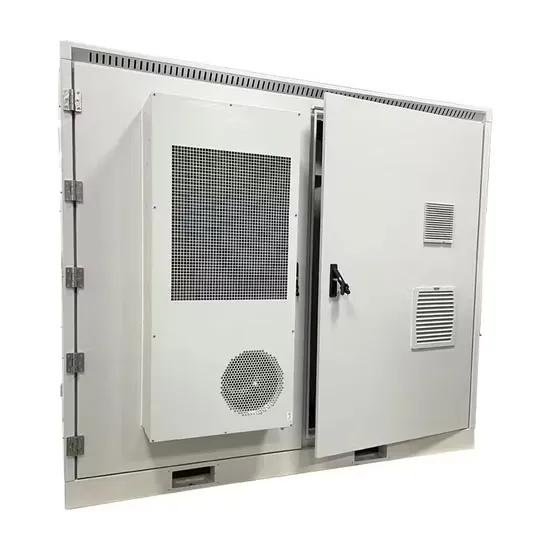 60kw inverter grid-connected current and voltage
60kw inverter grid-connected current and voltage
-
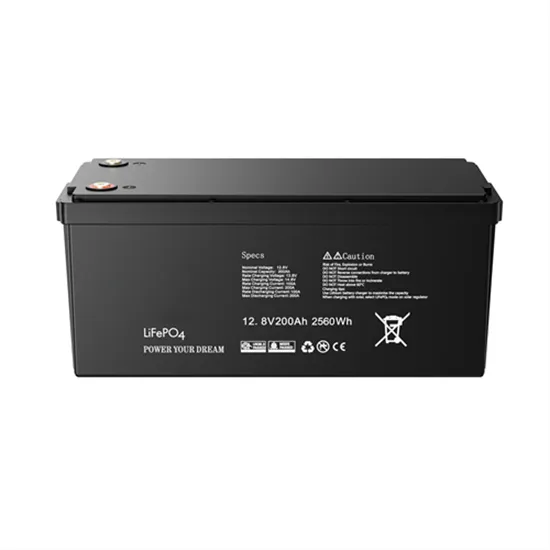 20A inverter current price
20A inverter current price
-
 Wattage Solar Control Inverter
Wattage Solar Control Inverter
-
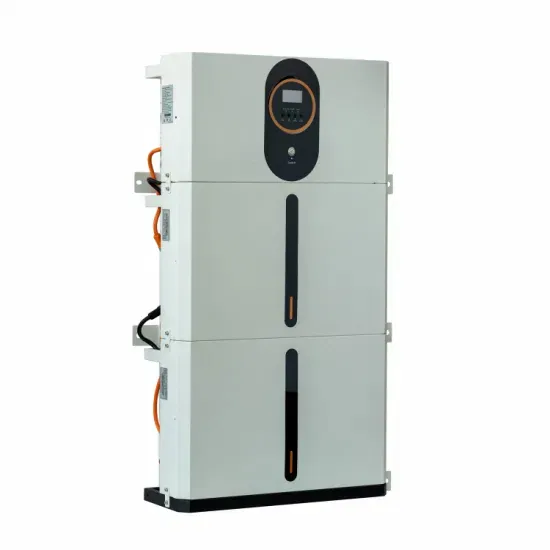 Three-phase grid-connected inverter repetitive control
Three-phase grid-connected inverter repetitive control
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


