The Difference Between High Voltage Converters and Inverters
Various differences between high voltage converters and inverters influence modern electrical systems, offering distinct advantages and applications. Their ability to
Get a quote
Higher Voltage vs Higher Current Panels : r/solar
Looking at these 420W panels (using NOCT values as they''re more realistic): The Jinko has better warranty and lower degradation, but is a lower voltage and higher current output.
Get a quote
Whats is a High Voltage Hybrid inverter? What are
Explore the pivotal differences between high and low voltage hybrid inverters and how these variations can influence your choice in sustainable
Get a quote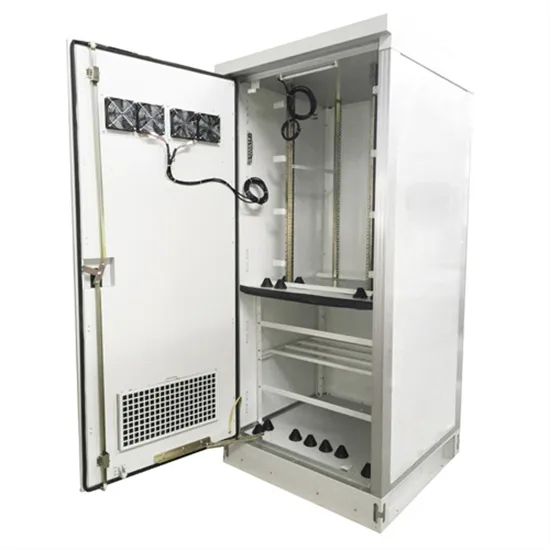
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Conclusion Choosing between a high-voltage and low-voltage inverter isn''t about which one is better overall—it''s about what''s better for your specific situation. Small, mobile, or
Get a quote
Solar Batteries in Cape Town | High vs Low Voltage batteries
Why? Certain inverters use low voltage (12, 24, or 48v) batteries and others use high voltage batteries (100v +). Low-voltage batteries are 60% efficient, whereas high-voltage
Get a quote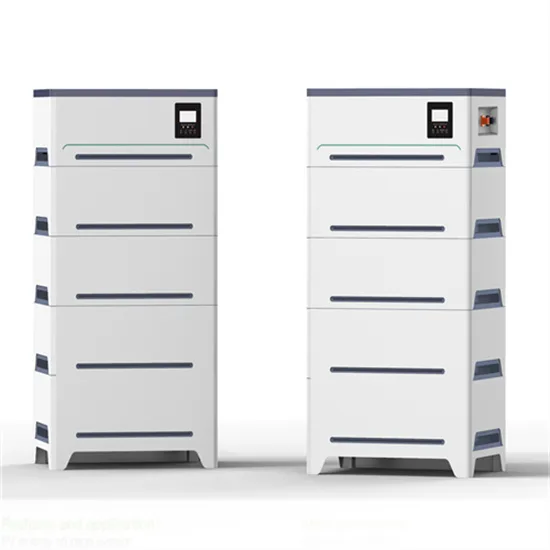
Curiosity: Why is higher voltage (~168-192V) not a standard?
When it comes to solar installations I get 12V systems for small installations, and 48V is useful for teleco standards reuse, but for home installations it seems like it would be better to use higher
Get a quote
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters: Types,
Unlock the potential of power supply with our comprehensive guide on all about inverters - discover types, benefits, and tips for the perfect
Get a quote
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter:
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) to meet the power needs of AC loads. According to topology, inverters can be
Get a quote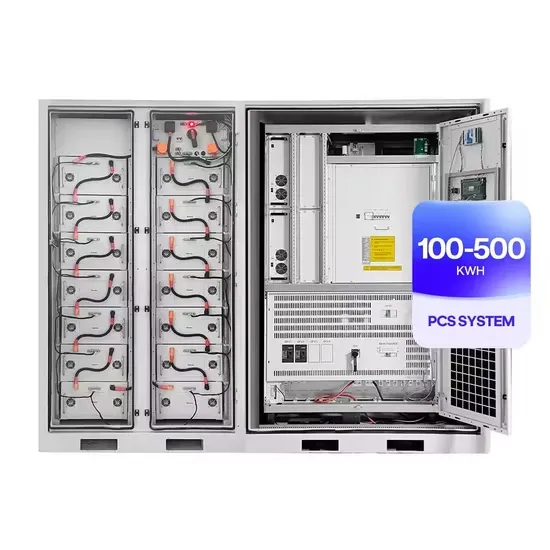
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency inverters - typically 20 kHz to 100 kHz. High-frequency inverters
Get a quote
Which is better using low DC voltage or high DC voltage for three
For the design of three phase inverter for three phase motor drive, which is better using low DC voltage (12 V or 24 V DC) for the inverter stage then step it up using three phase transformer,
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency inverters - typically 20 kHz to 100
Get a quote
High Voltage Inverter: Unlocking the Potential of High
This article will discuss the definition, working principles, characteristics, and benefits of using high voltage inverter in renewable energy
Get a quote
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
Confused about high-voltage vs low-voltage inverters? This easy-to-read guide explains the differences, pros, cons, and real-world uses—perfect for anyone exploring solar
Get a quote
Are higher voltage inverters inherently more reliable?
MOSFET similar, longer channel for higher voltage, resulting in higher resistance and more power dissipation for the same current. At higher temperature the breakdown
Get a quote
Demystifying high-voltage power electronics for solar inverters
One of the key subsystems in PV generation is the inverter. Advancements in high-voltage power electronics are resulting in more intelligent, more lossless and smaller PV inverters.
Get a quote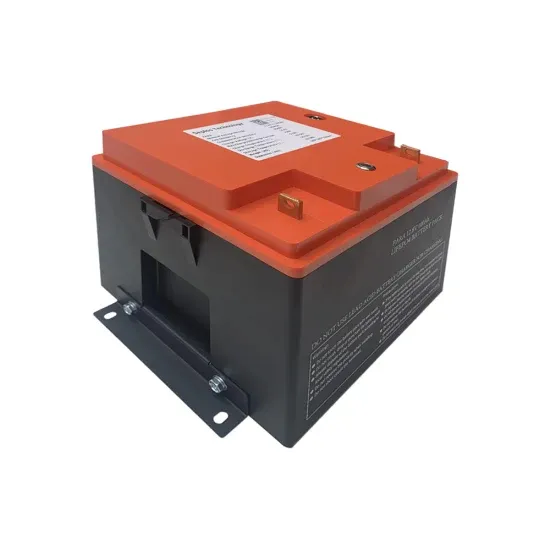
High Voltage Inverter: Unlocking the Potential of High-Power
This article will discuss the definition, working principles, characteristics, and benefits of using high voltage inverter in renewable energy systems.
Get a quote
A review on topology and control strategies of high-power inverters
Power electronic converters, bolstered by advancements in control and information technologies, play a pivotal role in facilitating large-scale power generation from solar energy.
Get a quote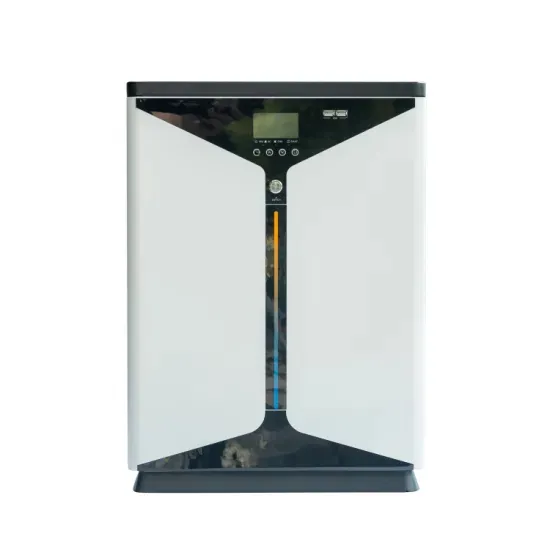
power supply
If you see the datasheet of the inverters with two input voltage options they are more efficient in converting higher input voltage to mains voltage than converting lower input
Get a quote
What Happens If the Inverter Is Too Big
Inverters play a crucial role in converting DC power to AC power, but choosing the right size is essential for optimal performance. In this article,
Get a quote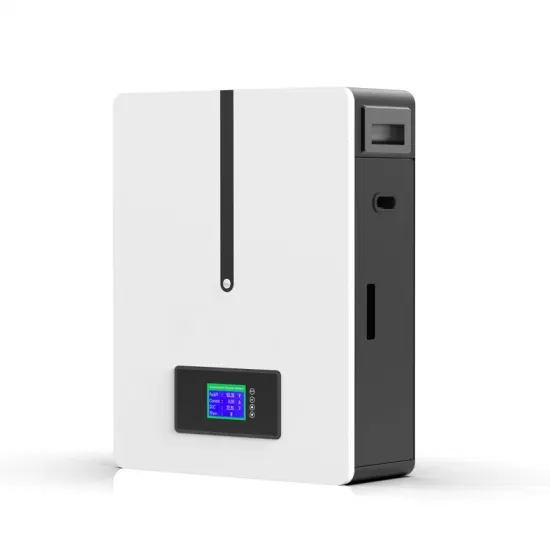
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
An inverter is a key component that converts DC power into AC power for household appliances and is commonly used in solar energy systems or with batteries as a
Get a quote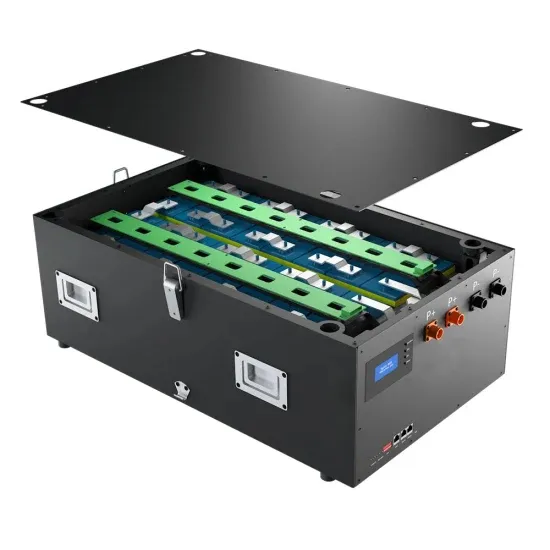
Setting aside wiring efficiency, what are the
Set aside wiring cost and efficiency, what are the advantages and disadvantages of a high differential between PV array and battery voltage. In what specific situations or
Get a quote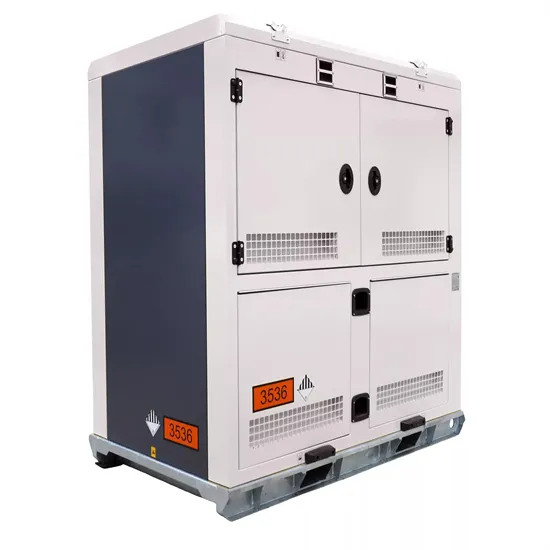
High Voltage vs Low Voltage Solar Battery: Which to Choose?
Discover the key differences between high voltage and low voltage solar batteries to choose the best energy storage solution for your solar PV system.
Get a quote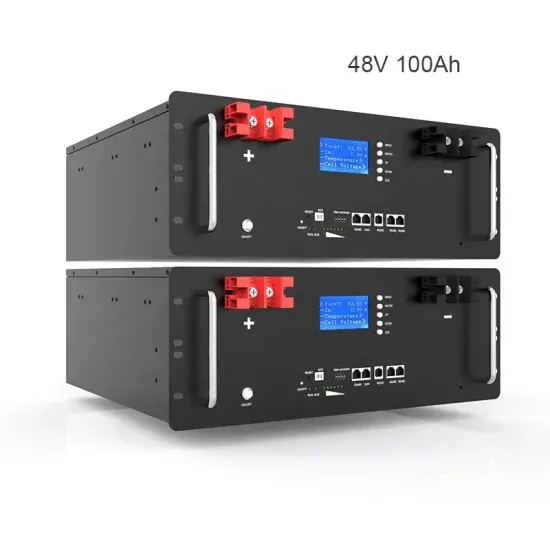
Whats is a High Voltage Hybrid inverter? What are Key
Explore the pivotal differences between high and low voltage hybrid inverters and how these variations can influence your choice in sustainable energy solutions.
Get a quote
12V VS. 24V Off-Grid Systems: Pros and Cons
Another drawback is that a 12V system is limited to powering an inverter that is rated 3000VA or less. It is possible to power inverters with
Get a quote
IGBT, MOSFET and GaN: An Overview of Efficiency,
The applications like Solar Inverters and Traction Inverters where it is vital to have lower losses and increased efficiency it is better to use the
Get a quote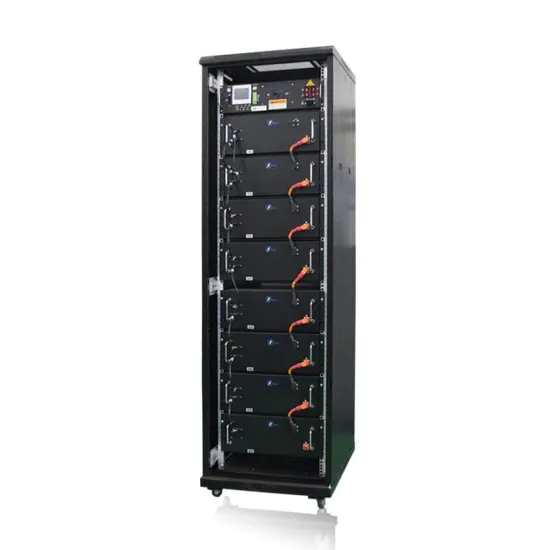
6 FAQs about [Is it better to use a higher voltage inverter ]
Should I buy a high voltage or low voltage inverter?
Low voltage and high current means you need to spend more on copper/cables. Going for a higher voltage saves money on copper up until you reach issues with cable insulation and/or max input voltage to the inverter. The "problem" is not so much on the inverter side as it is on the supply side.
Is there a difference between a commercial inverter and a high voltage?
For 'reasonable' voltages, in the several 10s to several 100s range, there's not a lot of difference between the efficiency of commercial inverters. Comparably higher voltage is more preferable when given choice between different voltages.
Can a high voltage inverter hook up more than one panel?
Higher voltage does not mean that you could go as high as you want or you could hook as many panels as you have in series. You should look at the max input voltage rating of the inverter you are going to use and the max series voltage of the panels.
Why do inverters have two input voltage options?
The third and most distinctive advantage is the higher efficiency of inverters at higher input voltages. If you see the datasheet of the inverters with two input voltage options they are more efficient in converting higher input voltage to mains voltage than converting lower input voltage to the same mains voltage.
Why is it important to have a good solar inverter?
It is important to have a good inverter. In grid-connect systems, an inverter failure means your solar panels are doing nothing until the inverter is repaired or replaced. Still, it’s worth remembering that even the best inverter is unlikely to last as long as the rest of your system.
Should I use a higher voltage if I have a copper inverter?
Going for a higher voltage saves money on copper up until you reach issues with cable insulation and/or max input voltage to the inverter. The "problem" is not so much on the inverter side as it is on the supply side. (Generally speaking, each inverter may have their own issues)
Guess what you want to know
-
 The higher the voltage of energy storage inverter the better
The higher the voltage of energy storage inverter the better
-
 Use the inverter voltage to drive the servo
Use the inverter voltage to drive the servo
-
 The higher the voltage the higher the high frequency inverter
The higher the voltage the higher the high frequency inverter
-
 Can I use an inverter if the battery voltage is low
Can I use an inverter if the battery voltage is low
-
 Romania voltage stabilizer inverter price
Romania voltage stabilizer inverter price
-
 Middle East low voltage inverter manufacturer
Middle East low voltage inverter manufacturer
-
 What voltage does the inverter output
What voltage does the inverter output
-
 Armenia high voltage inverter
Armenia high voltage inverter
-
 Photovoltaic Power Generation Voltage Inverter Price
Photovoltaic Power Generation Voltage Inverter Price
-
 What is the voltage of a 19kw inverter
What is the voltage of a 19kw inverter
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.