High Frequency vs Low Frequency Inverter: Which Has Higher
The two are similar, but the readers have noticed that the maximum PV voltage input of the high-frequency inverter is much higher than the maximum PV voltage input of the
Get a quote
Inverters, Types and Voltages
This blog post explores the key differences between low voltage and high voltage inverters as well as low frequency and high frequency inverters, helping you understand their
Get a quote
Advantages of High-Frequency Inverters in Modern
High-frequency inverters are known for their high efficiency, which is one of their most significant advantages. By operating at higher frequencies, typically in
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency
To sum up, variable frequency inverters and high frequency inverters each have their own advantages and disadvantages and are suitable
Get a quote
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave
The high frequency inverter can deliver the same power at higher frequency with a much smaller and lighter transformer, as a result, the HF
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why
The transformation of a high-frequency inverter steps up or down the voltage as needed, adjusting it to the desired level for the application. For
Get a quote
Harmonics and Inverters
Introduction Static UPS are almost perfect electric generators. They have high reliability and, by nature, ensure (within the battery operation limits) the uninterrupted power supply. Regarding
Get a quote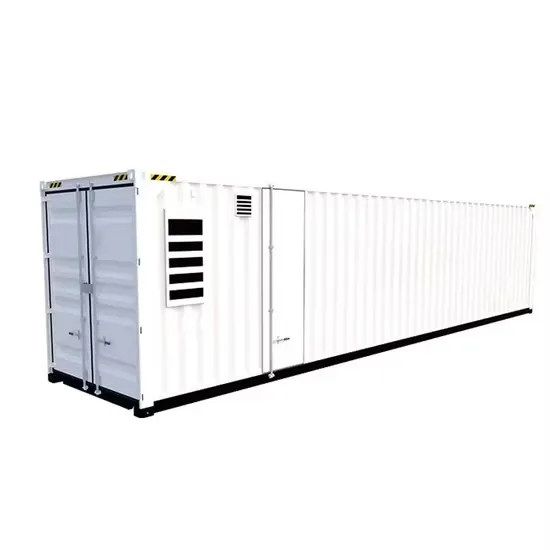
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
The output frequency of a high-frequency inverter is much higher than the power frequency, usually between a few kilohertz and ten kilohertz. With the use of high-frequency
Get a quote
High-Efficiency Inverter for Photovoltaic Applications
The topology is based on a series resonant inverter, a high frequency transformer, and a novel half-wave cycloconverter. Zero-voltage switching is used to achieve an average efficiency of
Get a quote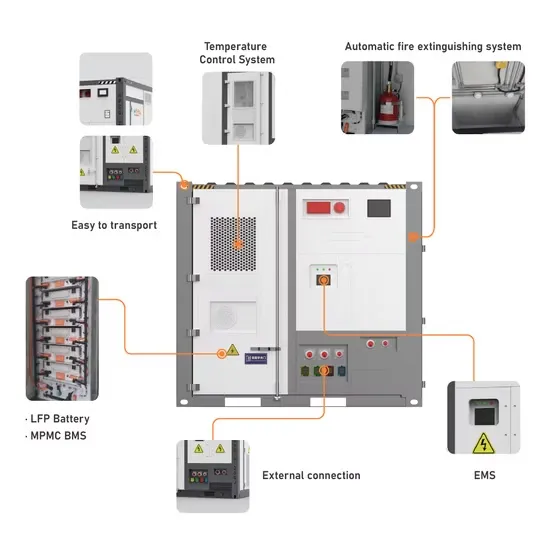
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High
This blog post explores the key differences between low voltage and high voltage inverters as well as low frequency and high frequency inverters, helping you understand their
Get a quote
CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
A high-frequency filter that is connected to the power supply side or load side of an inverter to absorb noise that is generated in an inverter when a power device switches.
Get a quote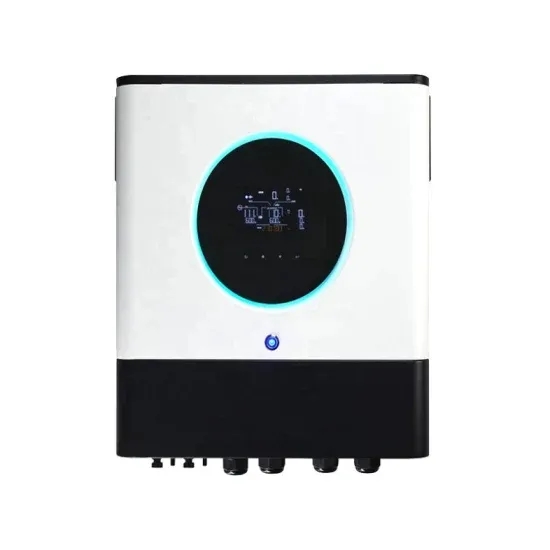
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency Inverters and High
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power efficiency, space saving, or suitability
Get a quote
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High Frequency
There are two types of inverters, low frequency and high frequency inverters. Inverters are used in solar power systems, wind turbines, and electric vehicles. In this article,
Get a quote
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get a quote
High Frequency vs Low Frequency Inverter: Which Has Higher MPPT PV Voltage?
The two are similar, but the readers have noticed that the maximum PV voltage input of the high-frequency inverter is much higher than the maximum PV voltage input of the
Get a quote
Understanding the Difference Between Frequency
Choosing between a frequency inverter and a high-frequency inverter depends on your specific needs—whether you''re looking for power
Get a quote
The current status and development of DC/AC inverter technology
The replacement of the industrial frequency transformer in the low-frequency link inverter process technology with a high-frequency transformer further optimizes and improves
Get a quote
High Frequency Inverter vs Low Frequency Inverter:
Discover the disparities between high frequency inverter vs low frequency inverter in this concise article, aiding your decision-making process.
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get a quote
Impact of high-frequency harmonics (0–9 kHz) generated by grid
The level of current harmonics circulating in a transformer winding can affect its operating temperature and lifetime. Although the existing standards mainly consider the impact
Get a quote
Evaluating the Effect of High Switching Frequency on the Performance
Evaluating the Effect of High Switching Frequency on the Performance of an Active Front End Converter This article features the benefits of operating at high frequencies and the
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs. High Frequency Inverter: Which is
To sum up, variable frequency inverters and high frequency inverters each have their own advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different application scenarios.
Get a quote
Multi-level Inverter Topologies for Electric Vehicles with Voltages
In this context, FEV has investigated various multi-level inverter topologies, evaluated them, and compared them with the current state of the art, a two-level voltage
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get a quote
High-Frequency Inverter: How They Work and Why They Matter
The transformation of a high-frequency inverter steps up or down the voltage as needed, adjusting it to the desired level for the application. For example, 12V DC can be converted from a solar
Get a quote
High frequency vs low frequency pure sine wave inverter
The high frequency inverter can deliver the same power at higher frequency with a much smaller and lighter transformer, as a result, the HF inverter is often called transformer
Get a quote
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
Operating Frequency Low-Frequency Inverter: Operates at a lower frequency, typically around 50Hz or 60Hz. Because its frequency is close to that of utility power, it is
Get a quote
ADDRESSING THE NEXT GENERATION SOLAR
By Mark Steinmetz, Field Applications Engineer Vincotech GmbH As the solar market matures, electronic power designers are faced with new challenges in inverter designs. The older less
Get a quote
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of inverter frequency, exploring its significance, factors affecting it, and its practical implications.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [The higher the voltage the higher the high frequency inverter]
What is the difference between low frequency and high frequency inverters?
Low frequency inverters generally have a longer lifespan than high frequency inverters due to their more durable components. In conclusion, low frequency and high frequency inverters have their unique features and benefits. Low frequency inverters are ideal for applications that require high power output and can handle heavy-duty appliances.
What is a high frequency inverter?
High frequency inverter: High frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology to chop DC power at high frequency through high-frequency switching tubes (such as IGBT, MOSFET, etc.), and then convert high-frequency pulses into stable alternating current through high-frequency transformers and filter circuits.
How do high frequency power inverters convert DC to AC?
High frequency power inverters typically convert the DC to AC by driving the transistors at a much higher frequency from 50 Kilo Hz to a few million Hz. Low frequency inverter circuit diagram
Why do high frequency inverters have distortion and harmonic content?
Due to factors such as the nonlinear characteristics of the high-frequency switching tube and the parasitic parameters of the high-frequency transformer, the output waveform of the high frequency inverter may have certain distortion and harmonic content.
What are the advantages of high frequency inverters?
Volume and weight: Since high frequency inverters use high-frequency switching technology and compact circuit design, their size and weight are usually much smaller than power frequency inverters. This gives high frequency inverters significant advantages in mobile power supplies, aerospace, electric vehicles, and other fields.
Are high-frequency inverters a good choice?
Due to the use of high-frequency switching technology, high-frequency inverters have the advantages of small size, lightweight, and high efficiency, but they also have the problem of relatively poor output waveform quality.
Guess what you want to know
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
 High frequency inverter voltage can reach
High frequency inverter voltage can reach
-
 Characteristics of high frequency inverter
Characteristics of high frequency inverter
-
 High frequency inverter produces 1200v
High frequency inverter produces 1200v
-
 High frequency inverter 38kw
High frequency inverter 38kw
-
 510 000 arc high voltage inverter high power
510 000 arc high voltage inverter high power
-
 India high frequency inverter
India high frequency inverter
-
 High frequency inverter leaves a trace
High frequency inverter leaves a trace
-
 Amorphous machine inverter high voltage
Amorphous machine inverter high voltage
-
 1000kv high voltage pulse inverter price
1000kv high voltage pulse inverter price
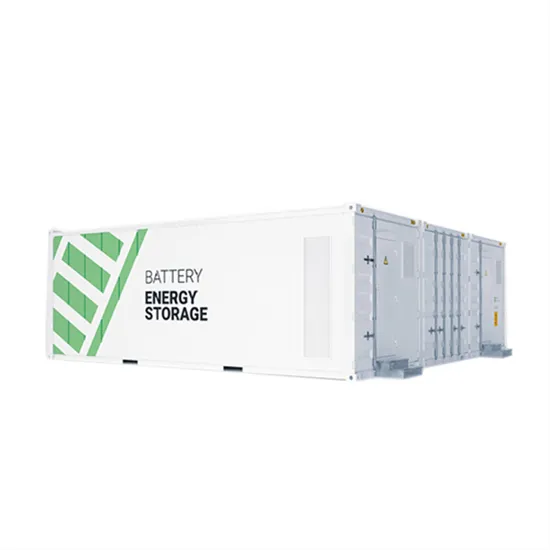
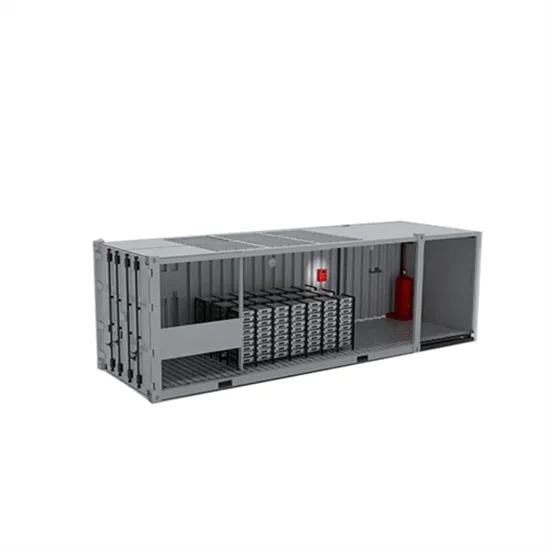
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
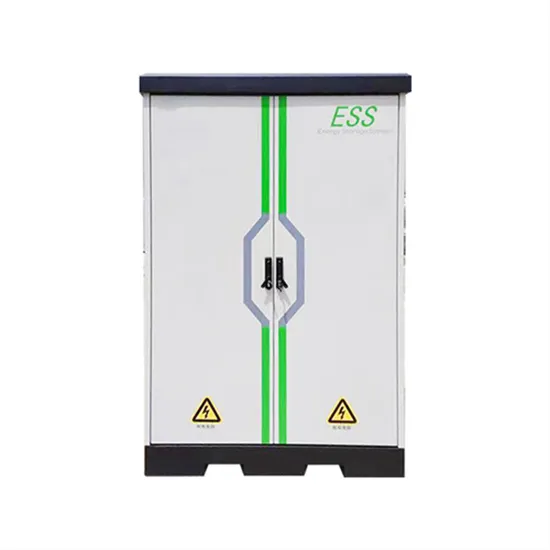
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


