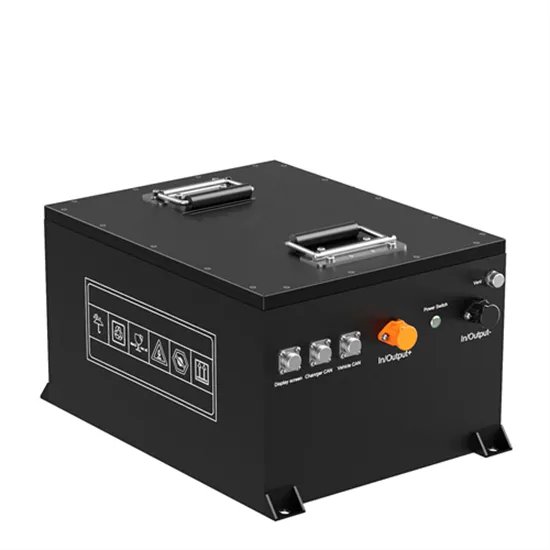
When choosing an inverter, what voltage ratings
Rated Voltage Rated voltage is the standard operating voltage that an inverter is designed to handle. It''s the voltage level that matches your grid or battery
Get a quote
Inverter Specifications and Data Sheet
The article provides an overview of inverter functions, key specifications, and common features found in inverter systems, along with an example of power calculations and inverter
Get a quote
What Size Inverter Do I Need?
Learning how to calculate inverter size for your needs can be a tricky task, especially if you''re unfamiliar with how an inverter works or how much power
Get a quote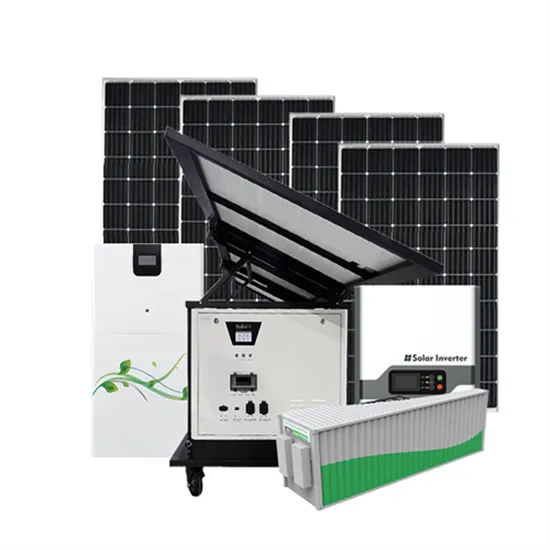
More volts or Amps for High voltage inverter?
Just basics - 450V x 100A says you''ve got a 45-kiloWatt MPPT input, which doesn''t sound right for a panel set of just 12x330W, or just under 4kW. You''re out by a factor of 10,
Get a quote
High-voltage VS Low-voltage Inverters: What''s the difference?
High-voltage inverters are designed to work with DC voltages typically ranging from 150V to 600V or even more. They are common in larger residential or commercial solar
Get a quote
What Size Inverter Do I Need?
Learning how to calculate inverter size for your needs can be a tricky task, especially if you''re unfamiliar with how an inverter works or how much power you need to produce.
Get a quote
What You Need To Know About a High Volt Inverter
High-voltage inverters are designed to handle large amounts of power, ranging from 10kW to several MW (megawatts). To choose the right inverter, you need to assess your energy needs
Get a quote
More volts or Amps for High voltage inverter?
What is better for best performance of a high voltage inverter, more volts or amps? i Have 12x330w panels, 38voc and 9A each. Do i arrange
Get a quote
Solar panel inverters & costs: the expert guide [UK, 2025]
Every inverter has a startup voltage – that is, the amount of power needed for it to turn on and start converting DC electricity from your solar panels. If your inverter is as big as
Get a quote
Interpreting inverter datasheet and main parameters | AE 868
Inverter and MPPT Depending on the topology, most modern inverters have built-in MPP trackers to insure maximum power is extracted from the PV array. Each inverter comes with a voltage
Get a quote
How much power does an Inverter use just sitting there idling?
Generally a 3 kW sinewave high freq inverter is 30 to 50 watts of full idle power. A high frequency inverter has two primary stages. First stage is high frequency DC to DC
Get a quote
Inverter Amp Draw Calculator
To calculate the amp draw for inverters at different voltages, you can use this formula. Maximum Amp Draw (in Amps) = ( Watts ÷ Inverter''s Efficiency (%)) ÷ Lowest Battery
Get a quote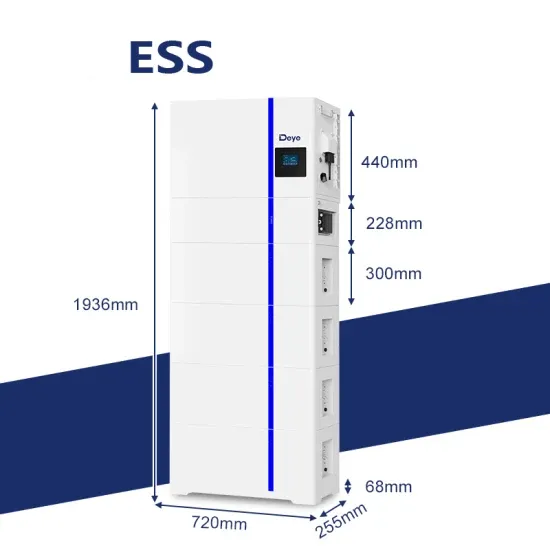
What You Need To Know About a High Volt Inverter
High-voltage inverters are designed to handle large amounts of power, ranging from 10kW to several MW (megawatts). To choose the right inverter, you need to assess your
Get a quote
Inverter Current Calculator, Formula, Inverter Calculation
Enter the values of inverter power, Pi(W), input voltage, Vi(V) and power factor, PF to determine the value of Inverter current, I(A).
Get a quote
Inverter Peak Power vs Rated Power: What it is and
Understand the key differences between inverter peak power and rated power. Discover the importance of both, how they affect your appliances.
Get a quote
High Voltage Inverter: What They Are, How They
A high voltage inverter can handle higher power output and quality, and can reduce the power losses and distortions that occur during the conversion and
Get a quote
How Does Input Voltage Affect a Grid-Tie Inverter?
Three-phase 400V inverter with the input rated voltage of 600V, equipping with 20 and 21 components will have the best effect. Three-phase
Get a quote
Inverter Basics and Selecting the Right Model
Watts - Or What Size Power Inverter do I Need? Peak Power vs Typical or Average An inverter needs to supply two needs - Peak, or surge power, and
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
What are high-frequency inverters? High-frequency inverters have a much higher internal switching frequency than conventional low-frequency
Get a quote
Whats is a High Voltage Hybrid inverter? What are
High voltage hybrid inverters are preferred in applications requiring greater efficiency and power capacity, making them suitable for larger
Get a quote
High Voltage Inverter: What They Are, How They Work, and
A high voltage inverter can handle higher power output and quality, and can reduce the power losses and distortions that occur during the conversion and transmission of electricity.
Get a quote
Understanding The Inner Workings Of Hybrid Car
How does the inverter control the flow of power in a hybrid car? In a hybrid car, the inverter plays a crucial role in controlling the flow of power
Get a quote
High Voltage Inverters: Understanding Its Benefits and Applications
A high-voltage inverter offers several benefits, from improved efficiency to cost-effective power transmission. Whether you''re considering it for a large solar installation or
Get a quote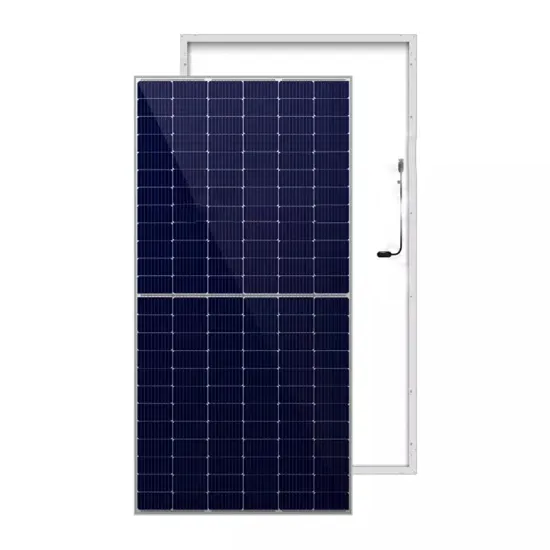
How Much Power Does An Inverter Draw With No Load?
Explore how inverters consume power at no load, understand no-load current, and discover tips to minimize power loss and improve inverter efficiency.
Get a quote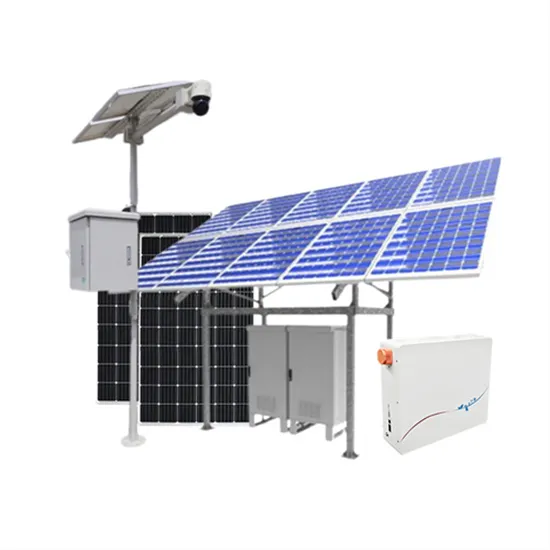
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters: Types, Uses, and
Unlock the potential of power supply with our comprehensive guide on all about inverters - discover types, benefits, and tips for the perfect choice.
Get a quote
Whats is a High Voltage Hybrid inverter? What are Key
High voltage hybrid inverters are preferred in applications requiring greater efficiency and power capacity, making them suitable for larger installations or those with space
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [How much power does a high voltage inverter have ]
How much power does a high frequency inverter use?
High frequency MOSFET drive switching is usually the dominate idle consumption but a poorly designed output PWM low pass filter can add to idle losses by having a high reactive power factor load. Generally a 3 kW sinewave high freq inverter is 30 to 50 watts of full idle power. A high frequency inverter has two primary stages.
How much power does an inverter need?
It’s important to note what this means: In order for an inverter to put out the rated amount of power, it will need to have a power input that exceeds the output. For example, an inverter with a rated output power of 5,000 W and a peak efficiency of 95% requires an input power of 5,263 W to operate at full power.
How does a high frequency inverter work?
A high frequency inverter has two primary stages. First stage is high frequency DC to DC converter that pumps battery voltage up to about 180-200vdc. Second stage is output MOSFET H-bridge that takes the high voltage DC and PWM chops it for sinewave synthesis, follow by low pass L-C filter.
What is an example of a power inverter?
Common examples are refrigerators, air-conditioning units, and pumps. AC output voltage This value indicates to which utility voltages the inverter can connect. For inverters designed for residential use, the output voltage is 120 V or 240 V at 60 Hz for North America. It is 230 V at 50 Hz for many other countries.
How much power does a 120V inverter use?
All inverters providing ready-to-use 120VAC have an idle consumption. There is a cost to running the circuitry that generates the 120VAC and 60Hz frequency. My 4kW Victron is about 30W as well.
What are inverter specifications?
Specifications provide the values of operating parameters for a given inverter. Common specifications are discussed below. Some or all of the specifications usually appear on the inverter data sheet. Maximum AC output power This is the maximum power the inverter can supply to a load on a steady basis at a specified output voltage.
Guess what you want to know
-
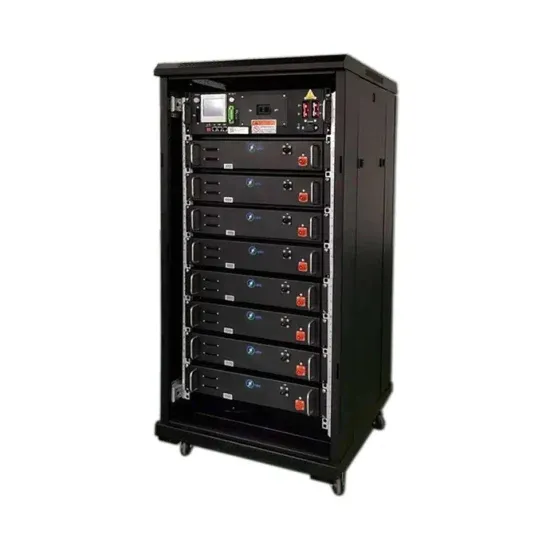 510 000 arc high voltage inverter high power
510 000 arc high voltage inverter high power
-
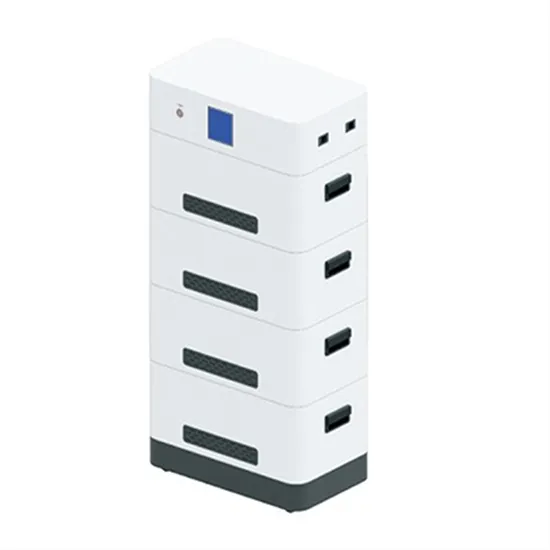 High power inverter equipment
High power inverter equipment
-
 How much voltage does the photovoltaic inverter change to
How much voltage does the photovoltaic inverter change to
-
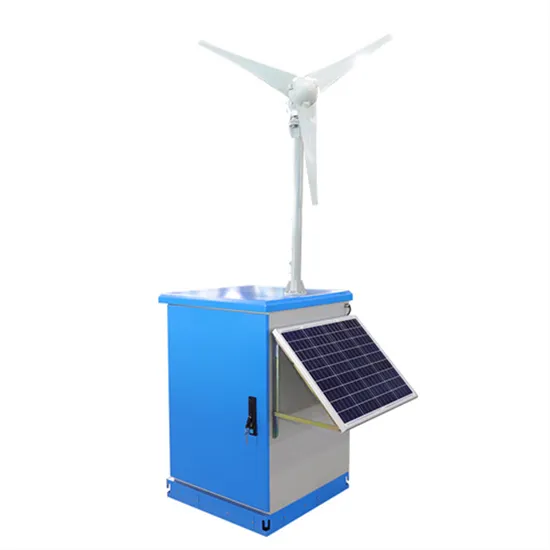
 French solar high power water pump inverter
French solar high power water pump inverter
-
 28V high power inverter
28V high power inverter
-
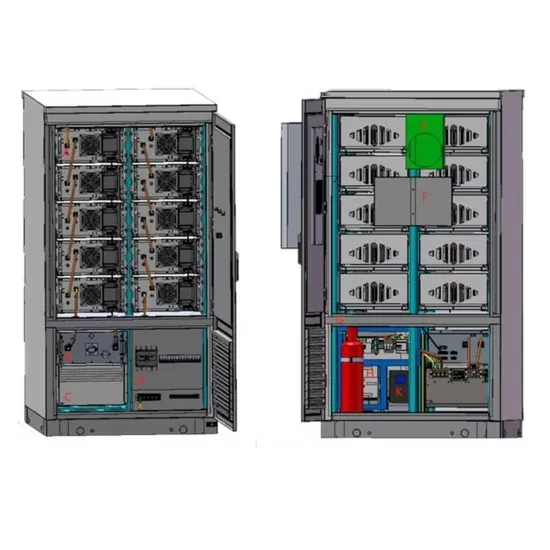
 Energy Storage Power Station High Voltage Direct Mounting
Energy Storage Power Station High Voltage Direct Mounting
-
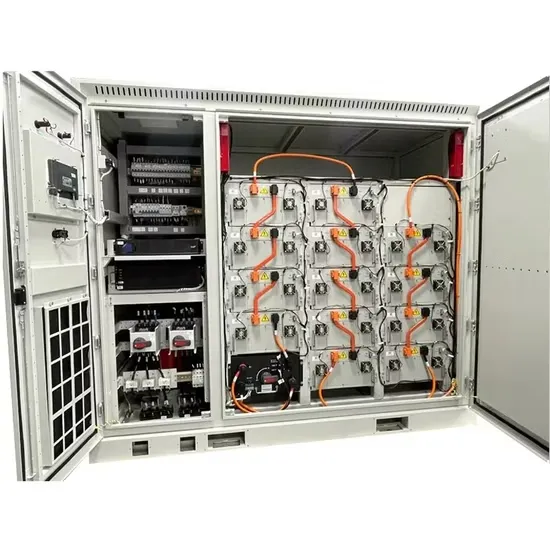
 Industrial frequency inverter high power solar energy
Industrial frequency inverter high power solar energy
-
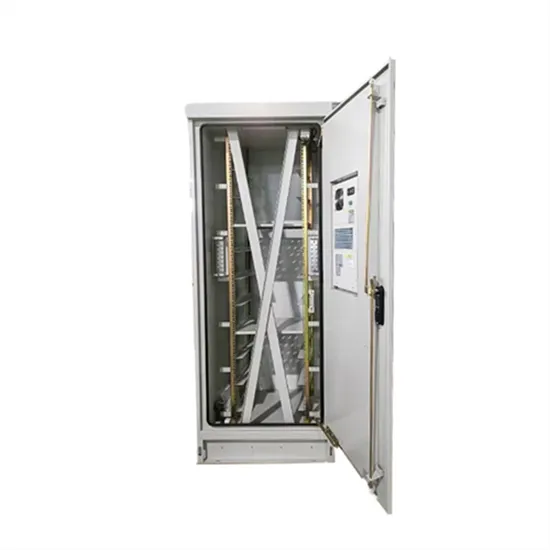
 Inverter high voltage side and low voltage side
Inverter high voltage side and low voltage side
-
 Does the inverter consume power at low frequency or high frequency
Does the inverter consume power at low frequency or high frequency
-
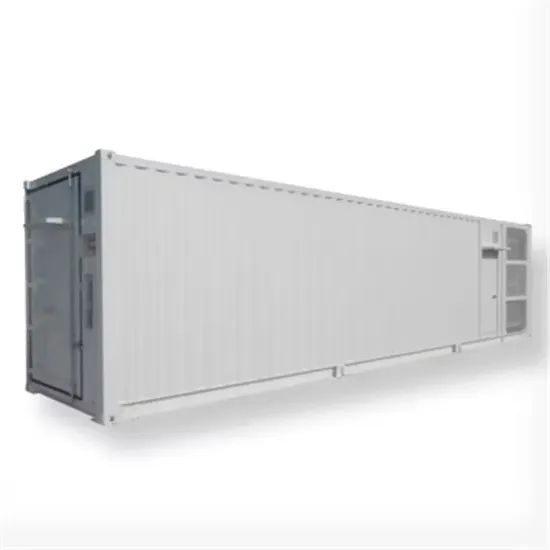 Huawei photovoltaic inverter high power
Huawei photovoltaic inverter high power
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


