Technical comparison between Low Frequency Inverter VS high Frequency
Low-frequency inverters have much greater peak power capacity to handle large loads with power spikes than high-frequency inverters.
Get a quote
Low Vs High Frequency Inverters/UPS Comparison
In the world of renewable energy and uninterrupted power systems, inverters play a crucial role in converting direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), which is essential for powering most
Get a quote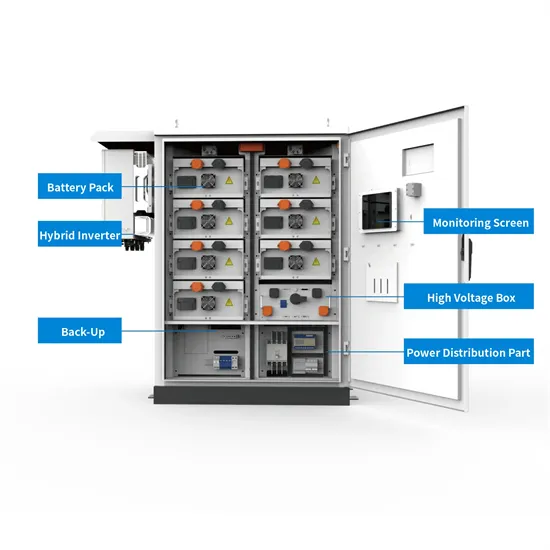
The difference between a high and low frequency inverter
High frequency inverters excel in energy efficiency, converting DC to AC power with minimal loss, which can lead to long-term cost savings. Low frequency inverters are better for off-grid
Get a quote
Comparing High Frequency UPS and Low Frequency UPS | Mingch
At MINGCH Electrical, we specialize in high-performance power solutions, including high-frequency UPS and low-frequency inverters. Our products are designed to meet
Get a quote
How Much Power Does An Inverter Draw With No Load?
After learning about how much power does an inverter draw with no load, it is time to know about the amount of power drawn from the batteries.
Get a quote
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get a quote
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get a quote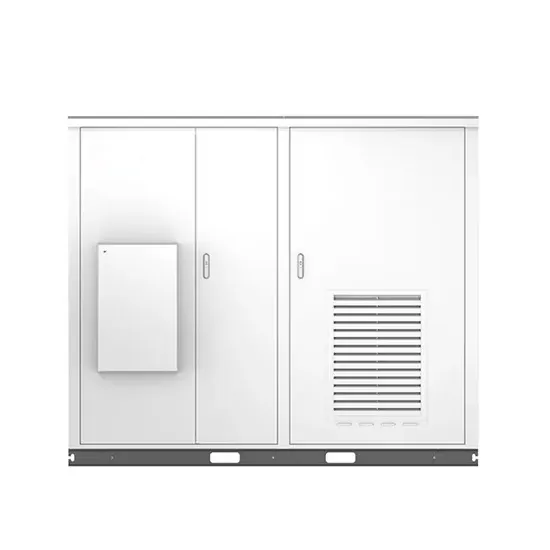
Understanding Frequency Inverters: A Comprehensive Guide
A low-frequency inverter operates at a lower switching frequency, typically below 60 Hz. It is designed for applications requiring high power stability and minimal harmonic
Get a quote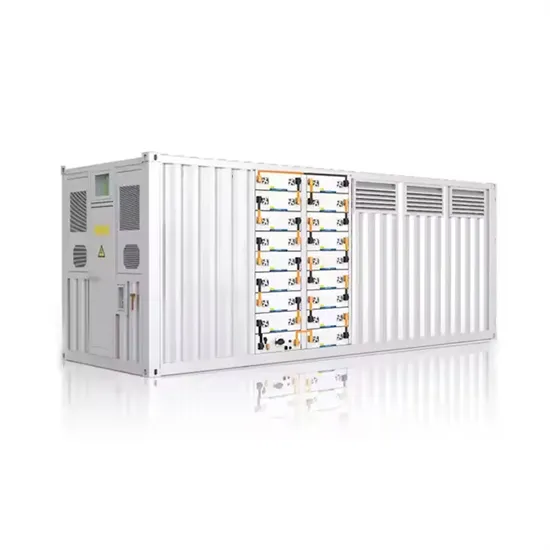
Understanding the Difference Between Low Frequency and High Frequency
In this article, we will examine the differences between low frequency or high frequency inverter. Both inverters have unique features and advantages and disadvantages,
Get a quote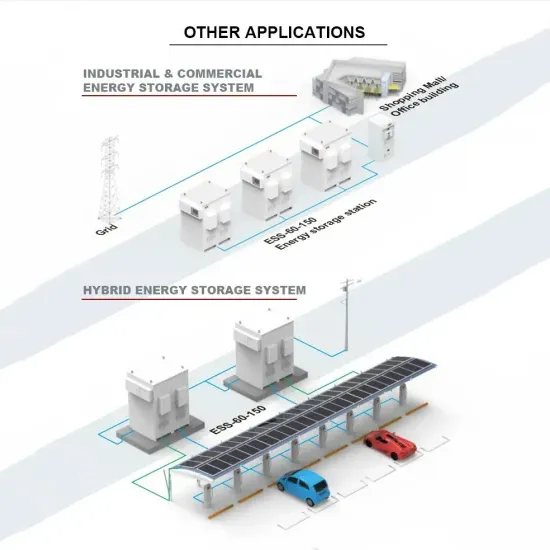
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Which One Is Best?
High-frequency inverters typically have 1.5-2 times their rated power, which limits their surge capacity. A low-frequency inverter is less efficient at lower loads due to energy losses in the
Get a quote
Which is Better Low Frequency or High-frequency Inverter?
This articles examines low frequency inverters operating near the AC line frequency versus high frequency inverters using much higher switching frequencies. The comparative advantages
Get a quote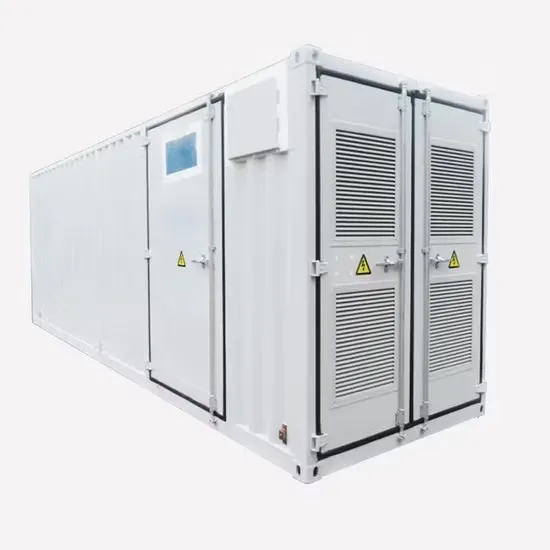
Low Frequency Inverter, High Frequency Inverter,
So what are the main differences between high-frequency inverters and industrial frequency inverters? 1. Low frequency inverter is superior to
Get a quote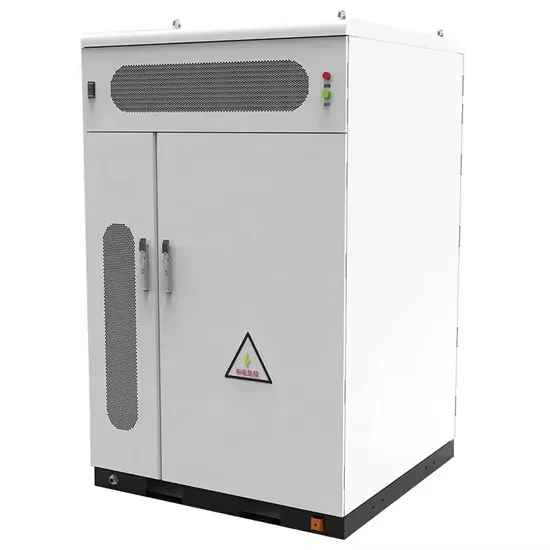
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency Inverters
High-frequency inverters generally have higher efficiency than low-frequency inverters. This is because the higher operating frequency reduces the size of transformers, capacitors, and
Get a quote
Difference Between High-Frequency and Low
In Uninterruptible Power Supply systems, choosing high-frequency and low-frequency UPS depends on your specific power backup needs. High
Get a quote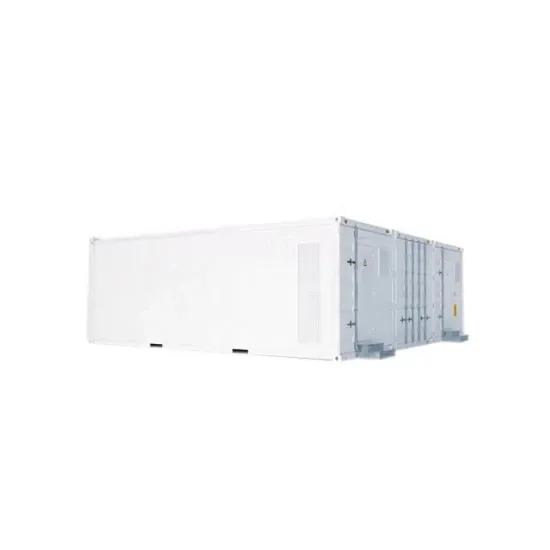
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
The choice between a low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) inverter depends on various factors, including the application requirements, load characteristics, and budget
Get a quote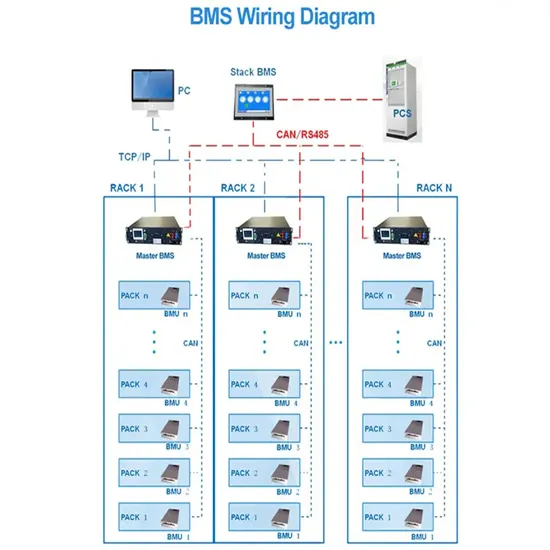
How Low Frequency Inverters Work and Their Benefits
A low frequency inverter converts DC to AC power using a transformer, offering high surge capacity, durability, and stable output for heavy-duty applications.
Get a quote
Low vs High frequency inverters | DIY Solar Power Forum
Low frequency core can absorb longer time period of peak core magnetic flux and enters core saturation less abruptly. On any transformer, saturate the core and MOSFET
Get a quote
High Frequency Inverter Board Assembly | Best Technology
What is high frequency inverter board? This guide covers its basics, how it works, function and application and differences from low-frequency ones.
Get a quote
Low Frequency vs High Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters typically have 1.5-2 times their rated power, which limits their surge capacity. A low-frequency inverter is less
Get a quote
What are the Types of Frequency Inverter? | inverter
These frequency converters are typically used in low-power applications and high-frequency applications. Frequency inverters are
Get a quote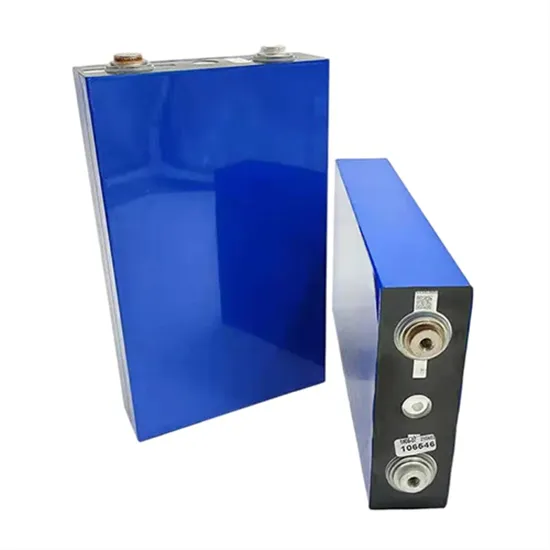
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical engineering. These can also be known as
Get a quote
How Does a Frequency Inverter Work? | inverter
Frequency inverters can be used in home appliances. Among the home appliances that use a frequency inverter are not only motors (e.g., air
Get a quote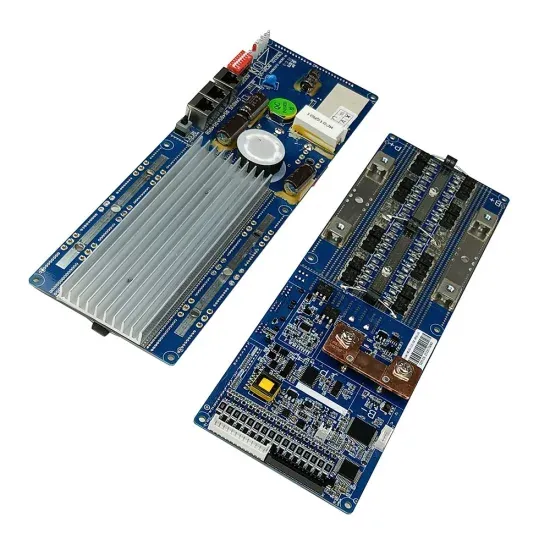
Comparing High-Frequency vs. Low-Frequency
High-frequency inverters generally have higher efficiency than low-frequency inverters. This is because the higher operating frequency reduces the size of
Get a quote
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a high
The primary distinctions between low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters lie in their operating frequencies, design structures, and performance characteristics
Get a quote
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used. These inverters use the pulse-width modification method: switching currents at high frequency, and for variable periods of
Get a quote
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and
The choice between a low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) inverter depends on various factors, including the application requirements,
Get a quote
Frequency Inverter Basic: Introduction, Functions and Advantages
According to the use classification, it can be divided into general-purpose inverter, high-performance special inverter, high-frequency inverter, single-phase inverter three-phase
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get a quote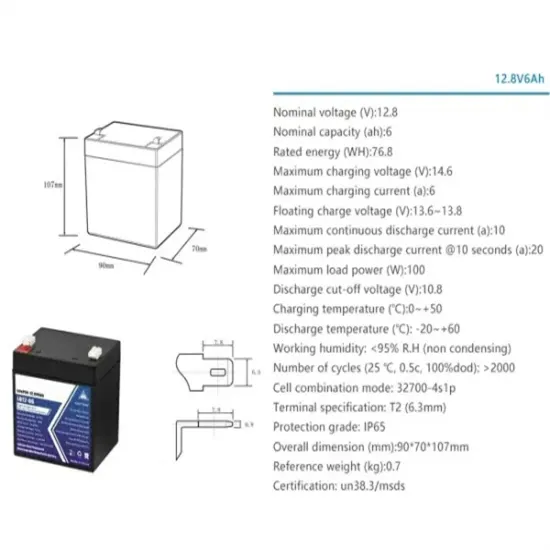
Which is Better Low Frequency or High-frequency
This articles examines low frequency inverters operating near the AC line frequency versus high frequency inverters using much higher switching
Get a quote
What is the difference between a low frequency inverter and a
The primary distinctions between low-frequency inverters and high-frequency inverters lie in their operating frequencies, design structures, and performance characteristics
Get a quote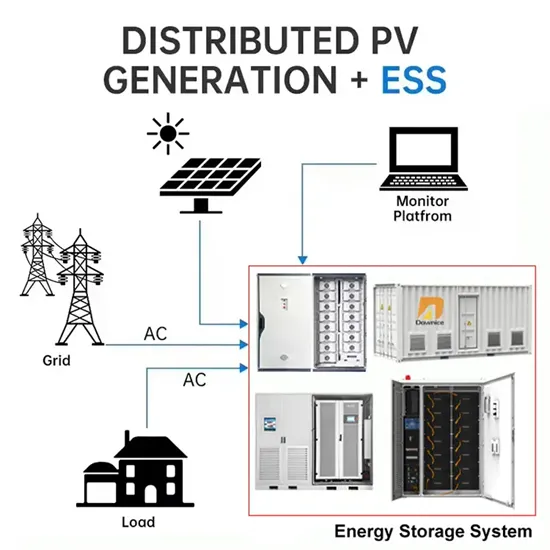
6 FAQs about [Does the inverter consume power at low frequency or high frequency ]
What is the difference between high frequency and low frequency inverters?
High-frequency inverters generally have higher efficiency than low-frequency inverters. This is because the higher operating frequency reduces the size of transformers, capacitors, and other components, leading to lower power losses. Low-frequency inverters have lower efficiency due to higher losses in magnetic components and switching devices.
What internal frequency do inverters operate at?
What internal frequency the inverter circuits operate at – low frequency or high frequency (not to be confused with AC power output frequency which is a standard 50Hz for our inverters). Low-frequency inverters have the advantage over high-frequency inverters in two fields: peak power capacity, and reliability.
Should you buy a low-frequency inverter?
If you need to power appliances with high surge requirements, like refrigerators, compressors, or industrial machinery, a low-frequency inverter is a better choice due to its ability to handle high starting currents.
What is a low frequency inverter?
Efficiency: Low-frequency inverters are known for their robustness and ability to handle high surge currents, making them suitable for powering heavy-duty appliances or equipment with high starting currents, such as motors and compressors.
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
How do I choose a low frequency or high frequency inverter?
When deciding between a low frequency or high frequency inverter, it is important to consider the power requirements of the appliances and devices that you wish to power. Heavy-duty items, such as air conditioners and refrigerators, may require a low frequency inverter with high surge capacity.
Guess what you want to know
-
 5kva high frequency power inverter
5kva high frequency power inverter
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
 Cambodia high frequency power inverter
Cambodia high frequency power inverter
-
 Industrial frequency inverter high power solar energy
Industrial frequency inverter high power solar energy
-
 52Hz low frequency high efficiency home inverter
52Hz low frequency high efficiency home inverter
-
 Which energy storage inverter is better power frequency or high frequency
Which energy storage inverter is better power frequency or high frequency
-
 Which is better for off-grid inverters power frequency or high frequency
Which is better for off-grid inverters power frequency or high frequency
-
 Power frequency inverter connected to solar panels
Power frequency inverter connected to solar panels
-
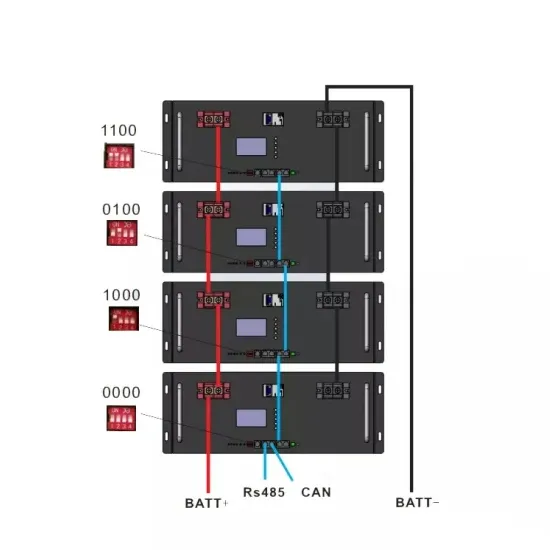 Spain high frequency inverter installation
Spain high frequency inverter installation
-
 High inverter power
High inverter power
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


