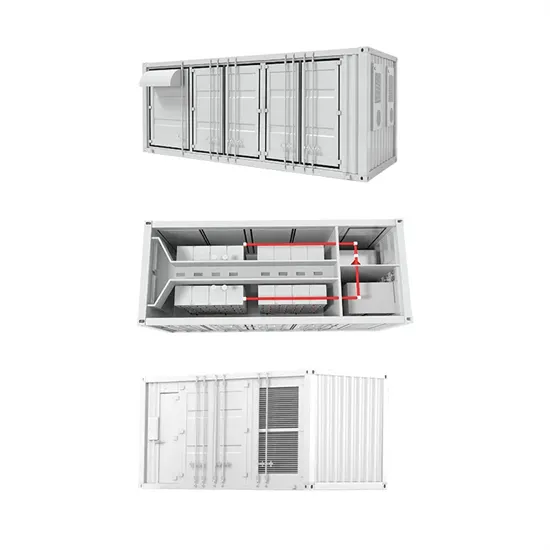
Five major integration technologies for energy storage
This article mainly introduces five major energy storage integration technologies and the comparison of different energy storage integration
Get a quote
Distributed or Centralized? Choosing the Best System
Discover the key differences between distributed and centralized energy storage systems and learn which is best for your unique needs.
Get a quote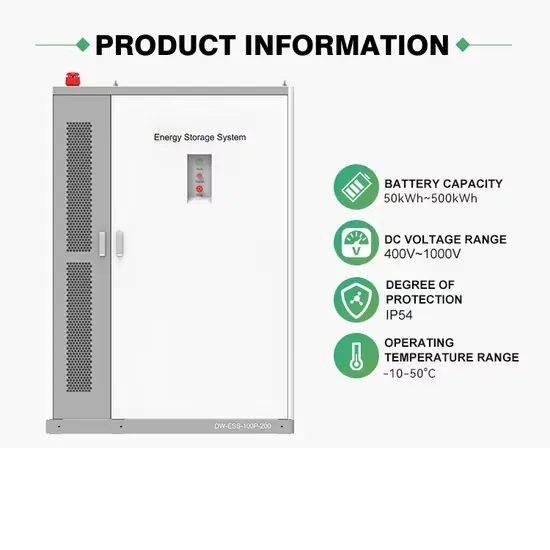
String Inverters for Energy Storage: A Distributed Approach for
The solar PV market embraced string inverters first, but energy storage is gaining momentum. In this post, we''ll take a closer look at string inverters and their benefits for energy storage.
Get a quote
Distributed or Centralized? Choosing the Best System for Your Energy
Discover the key differences between distributed and centralized energy storage systems and learn which is best for your unique needs.
Get a quote
Shared energy storage configuration in distribution networks: A
We examine the impacts of different energy storage service patterns on distribution network operation modes and compare the benefits of shared and non-shared energy storage
Get a quote
Centralized vs. String Energy Storage: Key Differences,
Centralized energy storage technology is particularly effective for large-scale projects, especially those connected to the power grid. In contrast, string energy storage is
Get a quote
Distributed Energy Storage → Term
Energy Arbitrage → Capitalizing on price differences between peak and off-peak electricity periods by charging storage when prices are low and discharging when prices are high.
Get a quote
Five major integration technologies for energy storage
Intelligent string type: Based on the distributed energy storage system architecture, innovative technologies such as battery module level
Get a quote
Approaches to Energy Storage: Centralized vs. String
Let''s examine two common configurations for large-scale energy storage systems: centralized and string setups, highlighting their strengths
Get a quote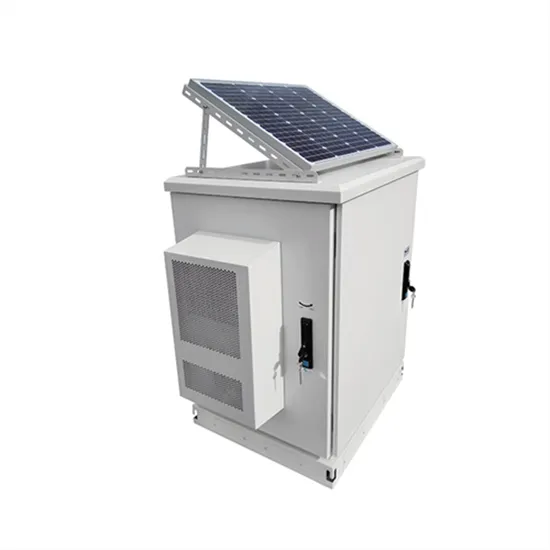
Approaches to Energy Storage: Centralized vs. String Systems
Let''s examine two common configurations for large-scale energy storage systems: centralized and string setups, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
Get a quote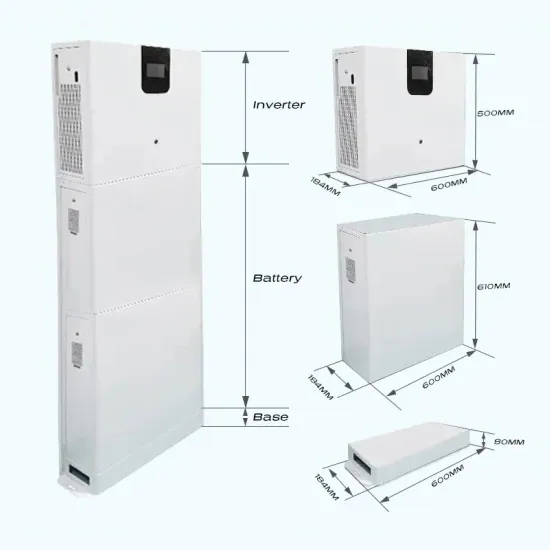
What Is Distributed Generation? | IBM
What is distributed generation? Distributed generation (DG) refers to electricity generation done by small-scale energy systems installed near the
Get a quote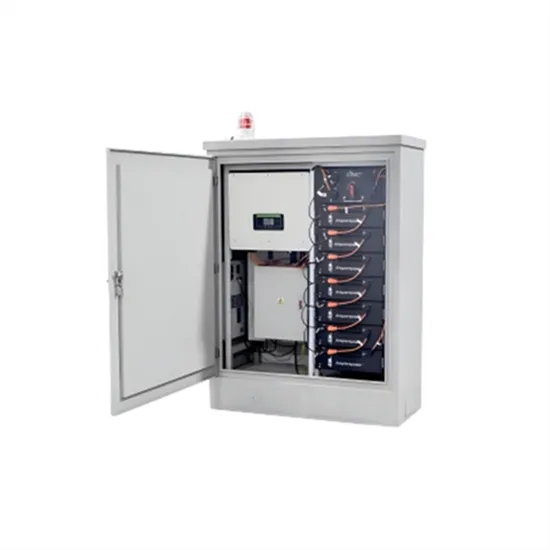
Energy Storage Interconnection
Energy storage, by itself and in combination with distributed generation (termed ES-DER), is a new and emerging technology that has been identified by FERC as a key functionality of the
Get a quote
Comprehensive review of energy storage systems technologies,
The applications of energy storage systems have been reviewed in the last section of this paper including general applications, energy utility applications, renewable energy
Get a quote
Distributed Energy Storage
Distributed energy storage is a powerful tool for the energy system, particularly as we transition to renewable energy sources. It can ease the adoption of renewable energy by smoothing out
Get a quote
String Inverters for Energy Storage
Conversely, string inverters use a distributed approach, breaking down the system into multiple smaller units. This method allows for more modular and scalable setups, making
Get a quote
Enel is developing energy storage systems, both centralized and
Electricity storage: centralised or distributed? Energy storage is a promising, growing industry in which the Enel Group is investing and experimenting, assessing the impact of a range of
Get a quote
5 Key Considerations for Energy Storage in Distributed Energy
There are fundamental differences between traditional fossil fuel energy and the renewable energy used in DERs. Wind and solar energy rely on the wind blowing and the sun
Get a quote
Comparison Of Centralized And String Based Energy
The centralized and string based energy storage technology routes occupy important positions in the current energy storage field, each with
Get a quote
An Overview of Distributed Energy
DPV, wind, and energy storage may be behind-the-meter (BTM) or in front-of-the-meter (FTM) and utility owned, customer owned, or third-party owned, although very little BTM wind and
Get a quote
Centralized vs. String Energy Storage: Key
Centralized energy storage technology is particularly effective for large-scale projects, especially those connected to the power grid. In contrast,
Get a quote
Comparison Of Centralized And String Based Energy Storage
The centralized and string based energy storage technology routes occupy important positions in the current energy storage field, each with unique advantages and
Get a quote
Centralized and String Energy Storage Technologies:
Discover the advantages and disadvantages of centralized and string energy storage technologies, crucial for efficient renewable energy utilization and grid stability.
Get a quote
Centralized vs. distributed energy storage
This study investigates the potential economic savings to a UK electricity consumer as a function of energy storage coordination scheme, i.e., central vs. distributed, as well as the
Get a quote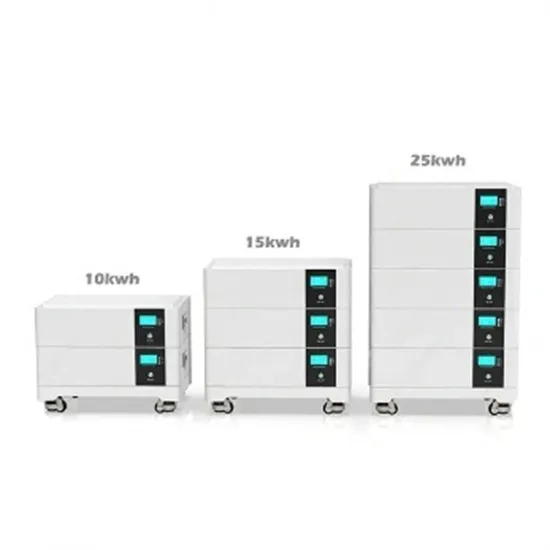
Solar Integration: Distributed Energy Resources and
Households and other electricity consumers are also part-time producers, selling excess generation to the grid and to each other. Energy storage, such as
Get a quote
What''s front of the meter vs. behind the meter of energy storage
As energy storage continues to revolutionize the renewable energy landscape, two major types of deployment have emerged: Front-of-the-Meter (FTM) and Behind-the-Meter (BTM) energy
Get a quote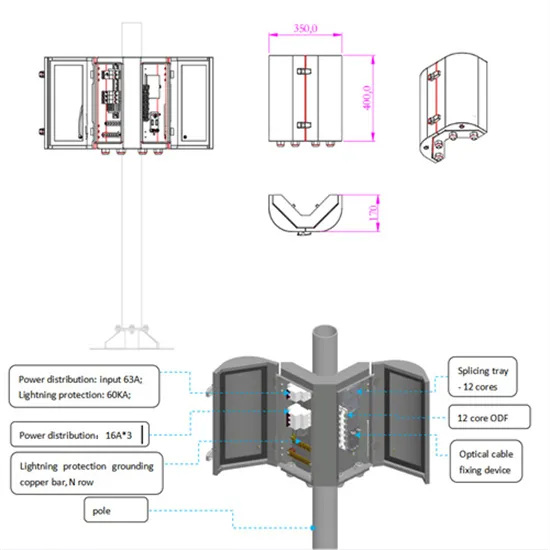
Five major integration technologies for energy storage power
This article mainly introduces five major energy storage integration technologies and the comparison of different energy storage integration technology routes.
Get a quote
What is the difference between distributed energy resources and
Distributed energy resources (DER) are energy generation or storage systems located close to the point of consumption, such as solar panels or battery storage in homes and businesses.
Get a quote
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
Energy storage for electricity generation An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an
Get a quote
Distributed energy storage systems: Electrical, electrochemical,
This unpredictable state of renewable resources has led to advances in energy storage technology. For the past several decades, research has been carried out on energy
Get a quote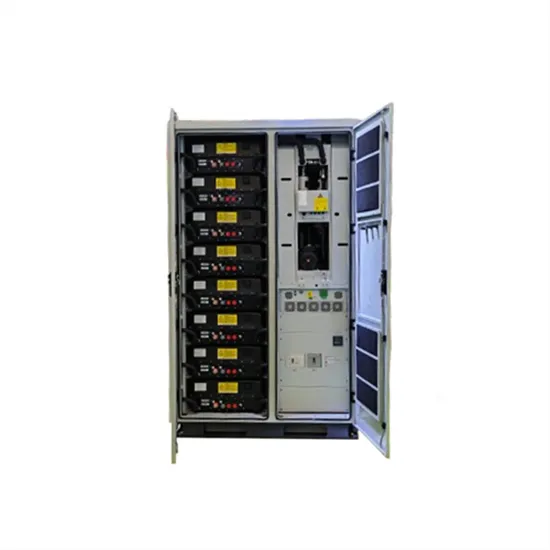
6 FAQs about [The difference between distributed energy storage and string energy storage]
What is distributed energy storage?
Distributed energy storage is a solution for increasing self-consumption of variable renewable energy such as solar and wind energy at the end user site. Small-scale energy storage systems can be centrally coordinated by "aggregation" to offer different services to the grid, such as operational flexibility and peak shaving.
Should you choose a central or string inverter for energy storage?
As markets and technologies for inverters grow, so does the importance of choosing between central and string inverters for energy storage projects. Typically, central inverters have been the standard for commercial and utility-scale energy storage applications.
Should energy storage aggregation be a trade-off between private and system benefits?
From modelling method perspective, this implies that models of the electricity system should account for the trade-offs between private and system benefits of energy storage aggregation. Yet it is unlikely that consumers will allow an aggregator to control their resources at all unless they are paid a financial incentive to do so .
Does centralized coordination affect energy storage savings?
Small-scale energy storage systems can be centrally coordinated by "aggregation" to offer different services to the grid, such as operational flexibility and peak shaving. This paper shows how centralized coordination vs. distributed operation of residential electricity storage (home batteries) could affect the savings of owners.
How does storage aggregation affect private benefits?
Private benefits of storage aggregation drops by 20% if aggregated storage devices increase five-fold. Distributed energy storage is a solution for increasing self-consumption of variable renewable energy such as solar and wind energy at the end user site.
What is energy storage (EES)?
The terms EES, “electricity storage”, “energy storage”, and “storage” are interchangeably used in this paper for referring to technologies that can store electricity and discharge it back at a reasonable response time. Examples of such technologies include secondary electro-chemical batteries, flow batteries, pumped hydropower storage (PHS), etc.
Guess what you want to know
-
 The difference between the grid side and the user side of energy storage power supply
The difference between the grid side and the user side of energy storage power supply
-
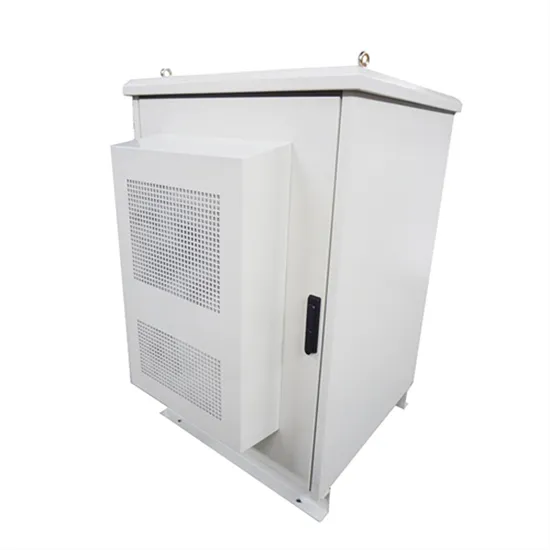 Distributed Energy Storage Cabinet Basics
Distributed Energy Storage Cabinet Basics
-
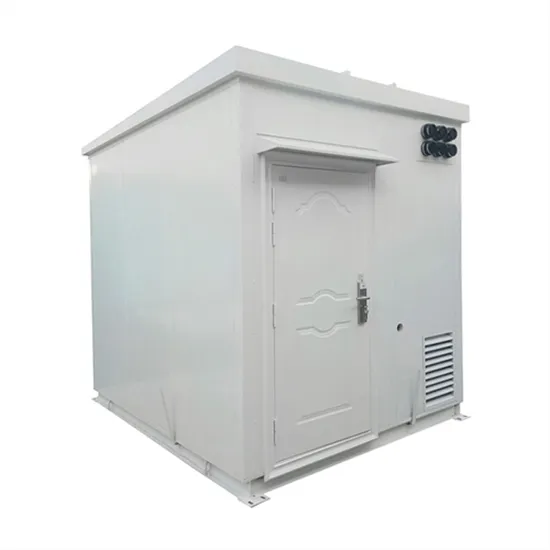 Is energy storage considered distributed power
Is energy storage considered distributed power
-
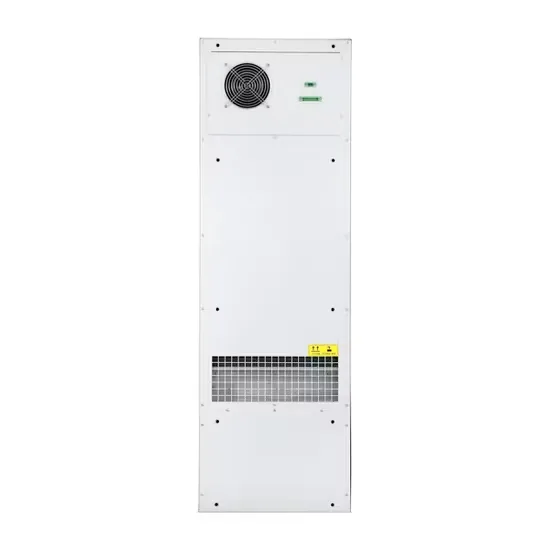 Huijue Distributed Energy Storage New
Huijue Distributed Energy Storage New
-
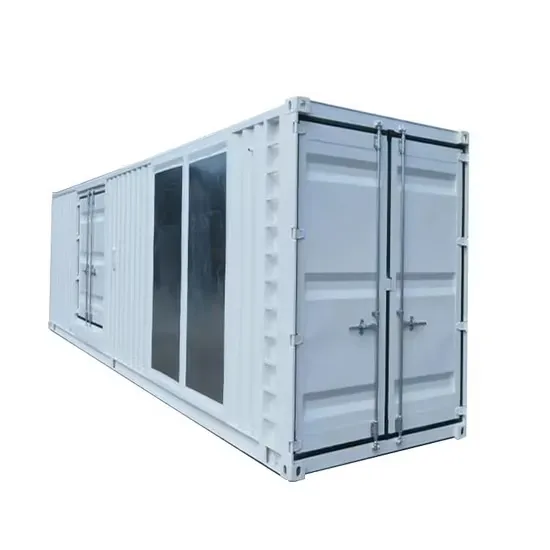 Distributed Energy Storage in Jordan
Distributed Energy Storage in Jordan
-
 Flywheel energy storage distributed power generation
Flywheel energy storage distributed power generation
-
 Where is the best distributed energy storage cabinet in Zambia
Where is the best distributed energy storage cabinet in Zambia
-
 Distributed Energy Storage Benefits in Angola
Distributed Energy Storage Benefits in Angola
-
 Distributed Energy Storage Project Design
Distributed Energy Storage Project Design
-
 Kosovo distributed photovoltaic energy storage enterprise
Kosovo distributed photovoltaic energy storage enterprise
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


