Distributed generation
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), [1] or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of
Get a quote
Distributed Generation, Battery Storage, and Combined Heat
Distributed generation (DG) in the residential and commercial buildings sectors and in the industrial sector refers to onsite, behind-the-meter energy generation.
Get a quote
An Overview of Distributed Energy
DERs are resources connected to the distribution system close to the load, such as DPV, wind, combined heat and power, microgrids, energy storage, microturbines, and diesel generators.
Get a quote
What Are Distributed Energy Resources (DER)? | IBM
Distributed energy resources, or DER, are small-scale energy systems that power a nearby location. DER can be connected to electric grids or isolated, with energy flowing only to
Get a quote
Distributed energy systems: A review of classification,
Distributed generation (DG) is typically referred to as electricity produced closer to the point of use. It is also known as decentralized generation, on-site generation, or distributed
Get a quote
Distributed Generation, Battery Storage, and Combined Heat and Power
Distributed generation (DG) in the residential and commercial buildings sectors and in the industrial sector refers to onsite, behind-the-meter energy generation. DG often
Get a quote
5 Key Considerations for Energy Storage in Distributed Energy
Our power grid is changing, becoming more distributed and more renewable than ever before. Battery energy storage is a critical technology component to reducing our
Get a quote
What is DER (Distributed Energy Resources)?
DER (Distributed Energy Resources) includes small-scale, decentralized energy production and storage systems. These resources can either connect to the grid or operate
Get a quote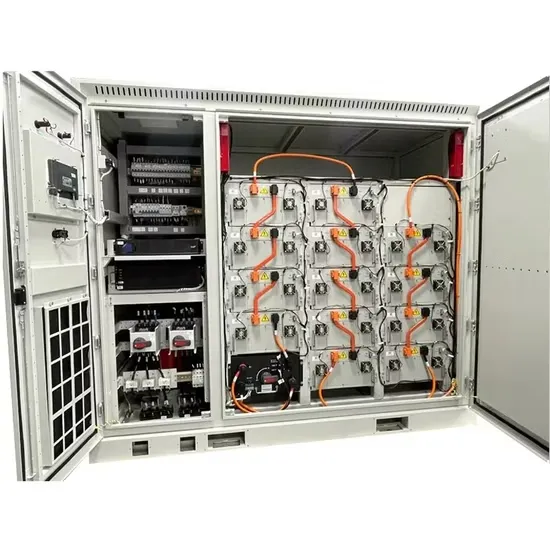
5 Key Considerations for Energy Storage in Distributed Energy
Residential homes or small communities can also use energy storage to achieve better energy independence and environmental sustainability by connecting energy storage
Get a quote
What Is Distributed Energy and How Does It Work?
Distributed energy refers to an electricity generation system that incorporates multiple small-scale devices rather than a centralized power plant
Get a quote
Distributed Generation, Battery Storage, and Combined Heat
Distributed Generation, Battery Storage, and Combined Heat and Power System Characteristics and Costs in the Buildings and Industrial Sectors Distributed generation (DG) in the residential
Get a quote
What are Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)?
Summary Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) is a general term referring to a variety of small-scale electricity generation and storage devices
Get a quote
Distributed Energy Storage → Term
In straightforward terms, DES refers to energy storage systems that are located closer to the point of energy consumption, rather than being centralized at large power plants.
Get a quote
Distributed generation
SummaryTechnologiesOverviewIntegration with the gridMitigating voltage and frequency issues of DG integrationStand alone hybrid systemsCost factorsMicrogrid
Distributed energy resource (DER) systems are small-scale power generation or storage technologies (typically in the range of 1 kW to 10,000 kW) used to provide an alternative to or an enhancement of the traditional electric power system. DER systems typically are characterized by high initial capital costs per kilowatt. DER systems also serve as storage device and are often called Distributed energy storage systems (DESS).
Get a quote
Optimization of distributed energy resources planning and battery
The findings presented in this study underscore the critical synergies between Distributed Resources (DR), specifically Renewable Energy Sources (RES) and Battery
Get a quote
Enhancing energy efficiency in distributed systems with hybrid energy
The employed distributed energy system incorporates hybrid energy storage, merging thermal energy storage with power storage technologies such as supercapacitors and
Get a quote
Distributed battery energy storage systems for deferring
This paper examines the technical and economic viability of distributed battery energy storage systems owned by the system operator as an alternative to distribution
Get a quote
Sizing Hybrid Energy Storage Systems for Distributed Power
However, the deployment of distributed generation systems can affect power system economy and stability. In this paper, under different time scales, system economy, stability, carbon
Get a quote
Overview of energy storage systems in distribution networks:
An optimally sized and placed ESS can facilitate peak energy demand fulfilment, enhance the benefits from the integration of renewables and distributed energy sources, aid
Get a quote
What are Distributed Energy Resources? Explained
Discover how distributed energy resources like solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage play a crucial role in a sustainable energy future.
Get a quote
What Is Distributed Energy and How Does It Work?
Distributed energy refers to an electricity generation system that incorporates multiple small-scale devices rather than a centralized power plant and distribution network.
Get a quote
Distributed Energy Resources: A How-To Guide
What are distributed energy resources? Distributed energy resources are small, modular, energy generation and storage technologies that provide electric capacity or energy where you need
Get a quote
Distributed Generation: Concepts and Technologies
Explore the fundamentals of distributed generation, including key concepts and technologies, and understand its role in modern energy systems and sustainability.
Get a quote
A Comprehensive Guide to Distributed Energy Resources
While both terms relate to decentralized power generation, distributed energy resources encompass a broader range of technologies, including energy storage and load management
Get a quote
An Introduction to Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
Distributed Energy Resources, also known as DERs, are small-scale units of local power generation that operate in conjunction with or
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Is energy storage considered distributed power ]
What is distributed energy?
Distributed generation, also distributed energy, on-site generation (OSG), or district/decentralized energy, is electrical generation and storage performed by a variety of small, grid -connected or distribution system-connected devices referred to as distributed energy resources (DER).
What is the difference between distributed energy resources and decentralized power generation?
While both terms relate to decentralized power generation, distributed energy resources encompass a broader range of technologies, including energy storage and load management systems while distributed generation focuses primarily on power production.
What are distributed energy resources?
Distributed energy resources, or DER, are small-scale energy systems that power a nearby location. DER can be connected to electric grids or isolated, with energy flowing only to specific sites or functions. DER include both energy generation technologies and energy storage systems.
What is energy storage?
Energy storage is the capturing and holding of energy in reserve for later use. Examples of energy storage technologies used as distributed energy resources include: Battery storage is the most common form of electricity storage.
How are distributed energy resources transforming the traditional energy paradigm?
Distributed Energy Resources (DER) are transforming the traditional energy paradigm by decentralizing power generation, storage, and management. They enhance energy efficiency, resilience, and environmental sustainability, making electricity more flexible and reliable.
Why do we need distributed energy systems?
It particularly studied DES in terms of types, technological features, application domains, policy landscape, and the faced challenges and prospective solutions. Distributed energy systems are an integral part of the sustainable energy transition. DES avoid/minimize transmission and distribution setup, thus saving on cost and losses.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Flywheel energy storage distributed power generation
Flywheel energy storage distributed power generation
-
 Distributed Energy Storage Power Station Solution
Distributed Energy Storage Power Station Solution
-
 Is an energy storage power station considered an asset
Is an energy storage power station considered an asset
-
 Distributed Energy Storage in Jamaica
Distributed Energy Storage in Jamaica
-
 Mozambique lithium energy storage power supply manufacturer
Mozambique lithium energy storage power supply manufacturer
-
 Wind power plant energy storage
Wind power plant energy storage
-
 Qatar Mobile Energy Storage Power Supply
Qatar Mobile Energy Storage Power Supply
-
 Dc24v energy storage power supply
Dc24v energy storage power supply
-
 Sudan energy storage power station manufacturer
Sudan energy storage power station manufacturer
-
 Container Industrial Energy Storage Power Supply Specifications
Container Industrial Energy Storage Power Supply Specifications
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


