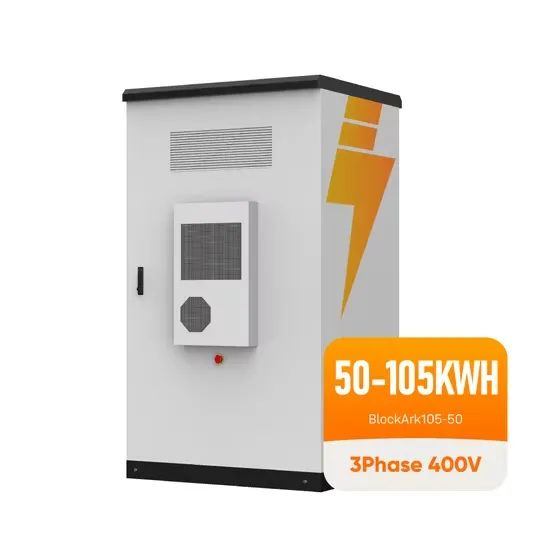
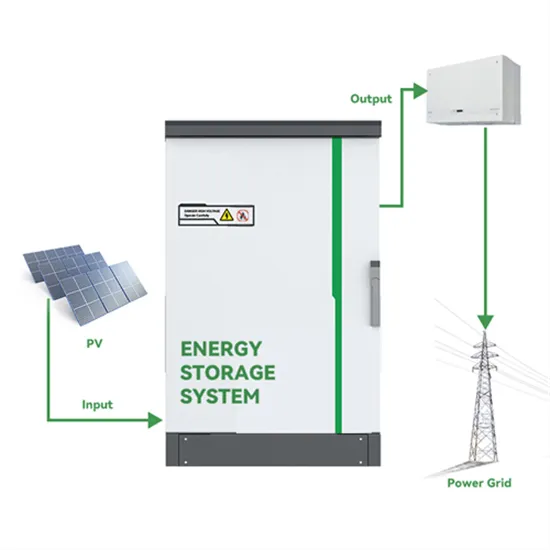
What is a 24V UPS Inverter and How Does It Work
A 24V UPS inverter is a device that converts the 24-volt direct current (DC) stored in batteries into stable alternating current (AC) power to ensure uninterrupted electricity supply
Get a quote
12V VS 24V Inverter: What are the Differences and
This versatile inverter integrates an MPPT Solar Controller, inverter, and charger into a single unit, delivering pure sine wave output for stable and efficient
Get a quote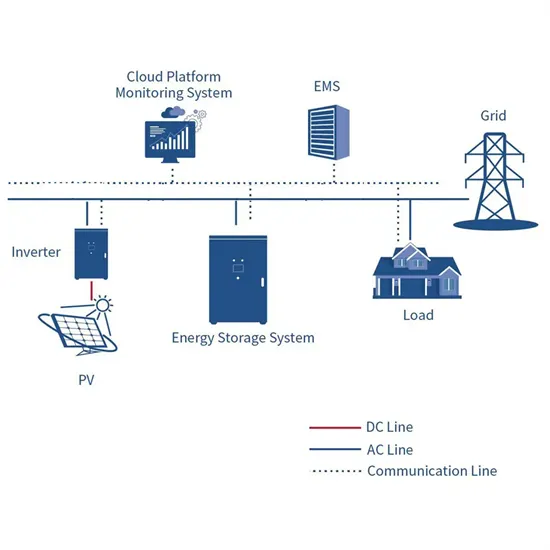
Differences Between 12V, 24V and 48V Inverter Systems
Most inverters will fall into three categories for their input requirements: 12VDC, 24VDC and 48VDC. This is referring to the nominal DC voltage that the inverter will invert to AC voltage
Get a quote
The Difference Between 12V & 24V: Which is Best for
Compare 12V and 24V systems to find the best fit for your needs. Discover their pros, cons, and uses for RVs, solar setups, and high-power equipment.
Get a quote
12V vs 24V Inverter: What''s the difference between 12
The difference between a 12V and 24V inverter is the amount of input volts it can handle. This is the voltage flowing from the battery into the inverter before the
Get a quote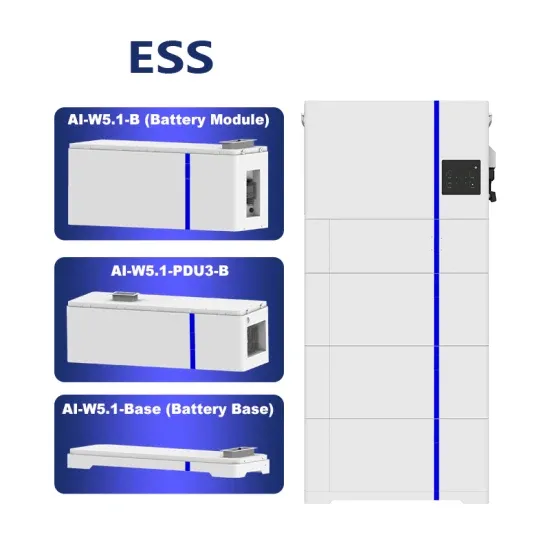
12V vs 24V: What''s The Difference in Battery Systems?
12V tells us that the battery supplies 12 volts under a nominal load. The same principle holds for a 24V battery bank in that it provides 24 volts. As we discussed before,
Get a quote
12V vs 24V Inverters Key Differences and Which One is Right for
A 12V inverter is designed to handle lower power output and is typically suited for smaller applications, while a 24V inverter offers higher efficiency and can power larger
Get a quote
Everything You Need to Know About Inverters: Types,
Unlock the potential of power supply with our comprehensive guide on all about inverters - discover types, benefits, and tips for the perfect
Get a quote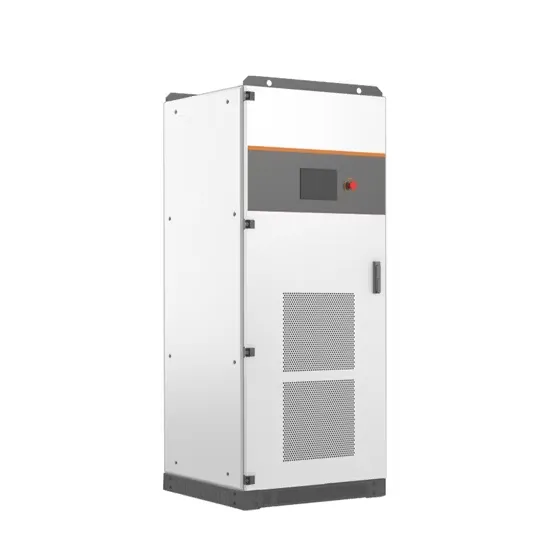
What Are 12v and 24v Inverters and Why Are They
The inverter can be connected to solar panels or wind turbines, enabling users to convert the DC power the latter is producing into usable AC electricity. Indeed,
Get a quote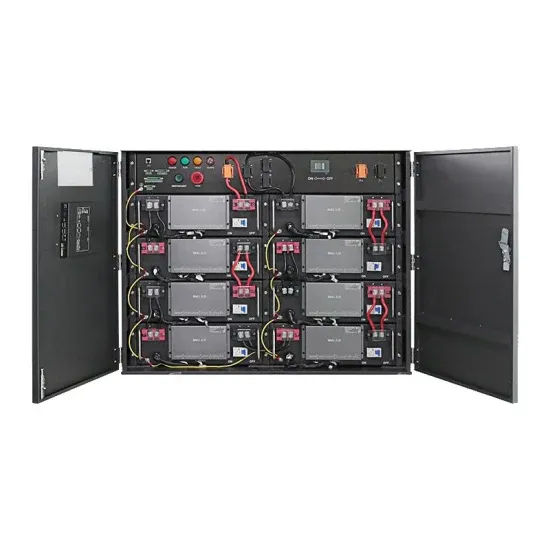
The difference between DC power supply and AC power supply
Frequency = 50Hz or 60Hz, but the naked eye does not feel the light bulb after it is energized. 3. Power structure composition First of all, we need to know the structure of the DC
Get a quote
What Are 12v and 24v Inverters and Why Are They Important?
The inverter can be connected to solar panels or wind turbines, enabling users to convert the DC power the latter is producing into usable AC electricity. Indeed, 24v and 12v inverters are a
Get a quote
12V vs 24V Inverter: What''s the difference between 12 and 24
The difference between a 12V and 24V inverter is the amount of input volts it can handle. This is the voltage flowing from the battery into the inverter before the electricity is converted from DC
Get a quote
12V Inverter vs 24V Inverter — What Is The Difference & Which
This article will explore the differences between 12v inverter vs 24v inverter, considering factors such as energy loss, battery requirements, and suitability for different
Get a quote
How DC/AC Power Inverters Work | HowStuffWorks
What kind of power inverter is the right one for the job? How do you install one? And how exactly does an inverter change the current from one form to another? Don''t worry,
Get a quote
12V vs 24V: What''s The Difference in Battery Systems?
12V tells us that the battery supplies 12 volts under a nominal load. The same principle holds for a 24V battery bank in that it provides 24
Get a quote
How Does A Split-Phase Power Inverter Work?
A split-phase inverter generates dual 120V AC waveforms offset by 180°, enabling 240V potential between phases. This setup powers 120V devices (outlets) and 240V loads
Get a quote
12 Volt vs. 24 Volt Inverters: What''s the Difference?
Inverters are devices that convert battery power to AC (alternating current) power. The two types of inverters available on the market today are
Get a quote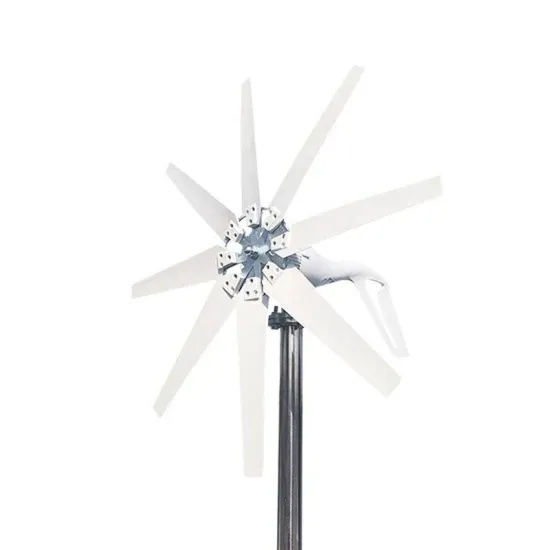
What is Inverter? – Meaning, Types and Application
The DC power input to the inverter is obtained from an existing power supply source or from a rotating alternator through a rectifier or a battery, fuel cell, photovoltaic array
Get a quote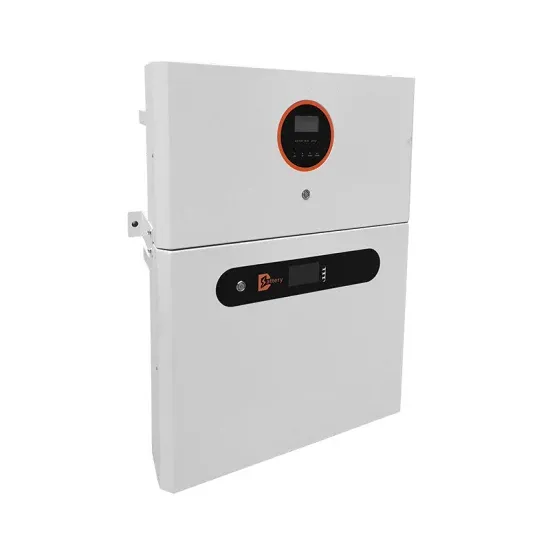
AC Vs DC Power: A Beginner''s Guide
What does AC power mean? Alternating Current (AC) is a type of electricity where the flow of electrical charge changes direction back and forth. This
Get a quote
12 Volt vs. 24 Volt Inverters: What''s the Difference?
Inverters are devices that convert battery power to AC (alternating current) power. The two types of inverters available on the market today are 12 volt and 24-volt inverters. They
Get a quote
12V VS 24V Inverter: What are the Differences and How to Choose
This versatile inverter integrates an MPPT Solar Controller, inverter, and charger into a single unit, delivering pure sine wave output for stable and efficient energy conversion.
Get a quote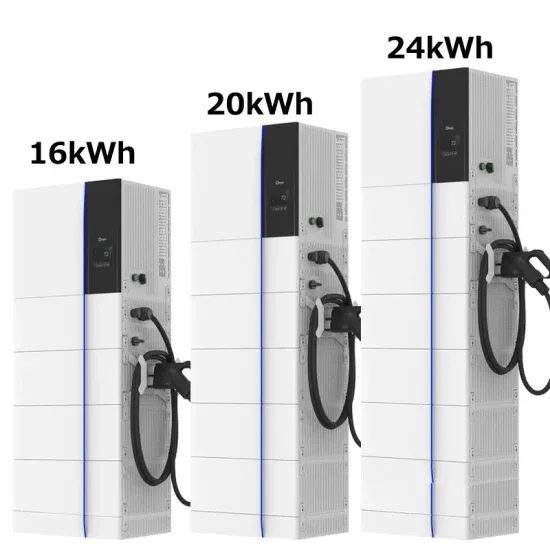
12V vs 24V Inverter: What''s The Difference & Which is Better
Inverters play a crucial role in modern power systems, converting DC (direct current) to AC (alternating current) for use in everyday devices. When choosing between a 12 voltage
Get a quote
What Is a Split Phase Inverter and How Does It Work?
Split Phase Inverter: A split phase inverter is a device that converts DC (Direct Current) power, generated by sources such as generators,
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What does DC24V inverter mean ]
What is the difference between a 12V and 24V inverter?
The difference between a 12V and 24V inverter is the amount of input volts it can handle. This is the voltage flowing from the battery into the inverter before the electricity is converted from DC to AC. So a 12V inverter is designed for 12 volts input from the battery. And a 24V inverter is designed for 24 volts input from the battery.
What is a 24V inverter?
24V Inverters: These systems generally offer higher efficiency, particularly in larger installations, thanks to lower current demands and reduced wire losses. This improved efficiency translates into energy savings, longer battery life, and potentially smaller system components.
Can a 12V inverter run on a 24v battery?
If you try to use a 12V inverter on a 24V battery it will be overloaded. Contrastingly, using a 24V inverter with a 12V battery will lead to a lack of electrical force. Knowing your inverter's voltage and what that means is critical in order for everything to run correctly.
What is the difference between DC and AC inverters?
It shows how well DC power is converted to AC, affecting the system’s performance and cost. Here’s the difference: 12V Inverters: Common in small setups but less efficient because they need higher current, leading to more energy loss as heat and voltage drops.
Why is a 24V inverter better than a battery?
This is because 24V inverters are more efficient, which means they lose less energy and cost less to run over time. Additionally, 24V systems need thinner and cheaper wiring because they use less current. However, 24V batteries and some components can be more expensive at the start.
What are the benefits of using a 24V inverter?
This improved efficiency translates into energy savings, longer battery life, and potentially smaller system components. For instance, a 2400W inverter would require 200A at 12V but only 100A at 24V, significantly reducing wire size and cost.
Guess what you want to know
-
 What does a wide voltage inverter mean
What does a wide voltage inverter mean
-
 What does sufficient inverter power mean
What does sufficient inverter power mean
-
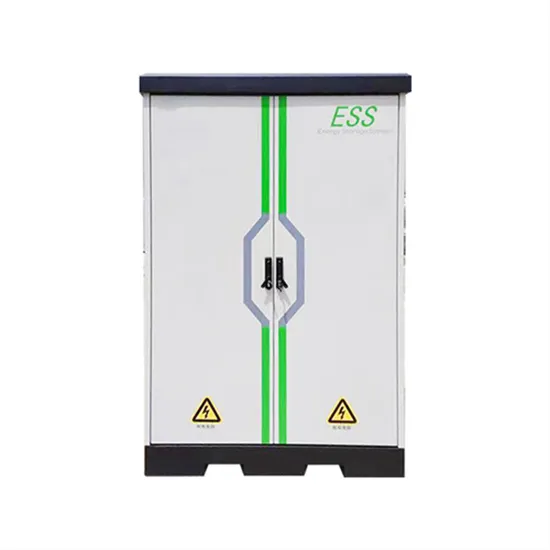
 What does adjustable power of an inverter mean
What does adjustable power of an inverter mean
-
 What does a few watts of solar panels mean
What does a few watts of solar panels mean
-
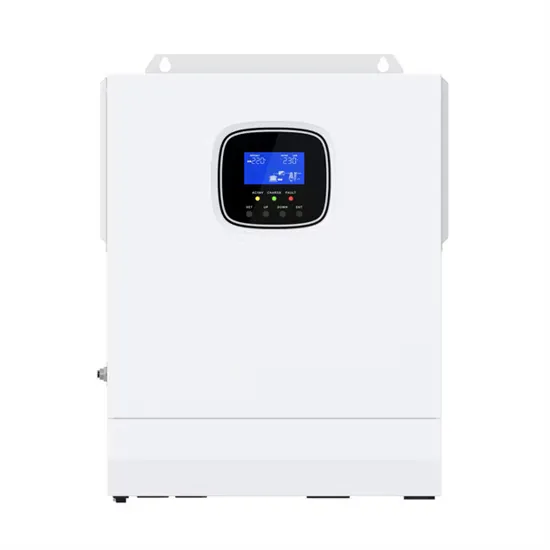 What is the rated power of the inverter
What is the rated power of the inverter
-
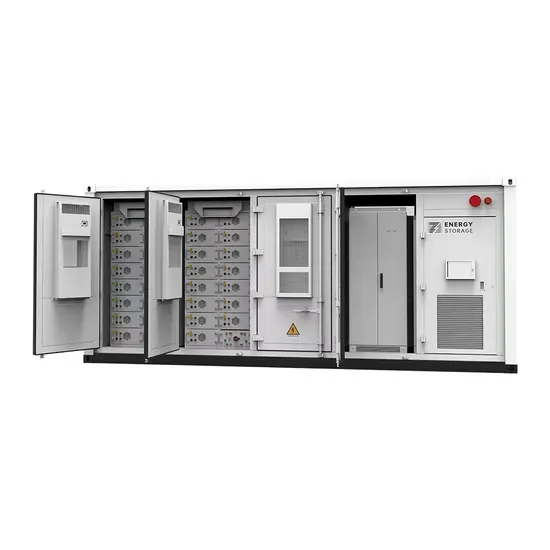
 What is a three-phase energy storage inverter
What is a three-phase energy storage inverter
-
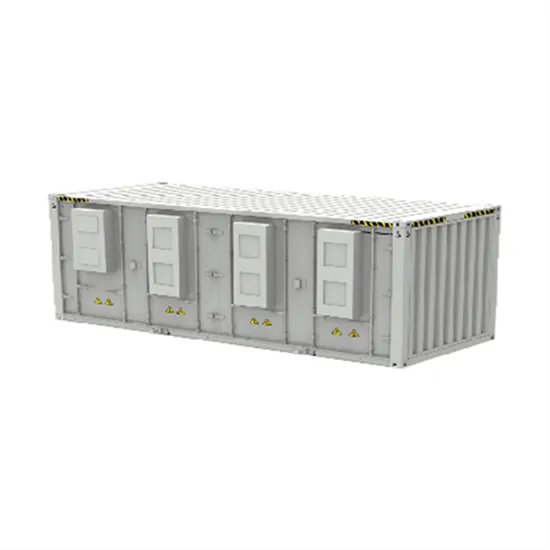 What is the appropriate boost frequency for a sine wave inverter
What is the appropriate boost frequency for a sine wave inverter
-
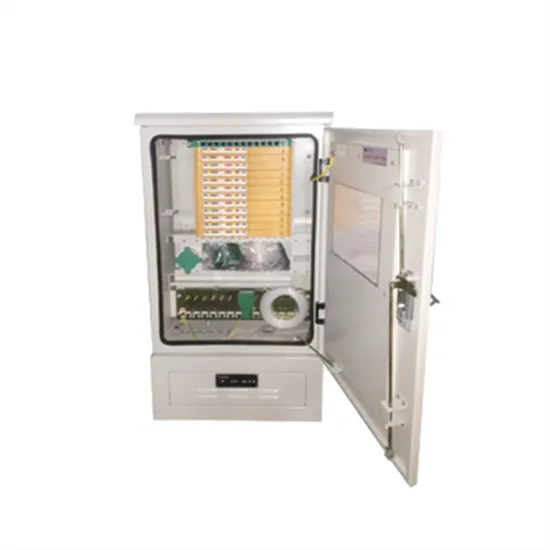 What types of outdoor inverter components are there
What types of outdoor inverter components are there
-
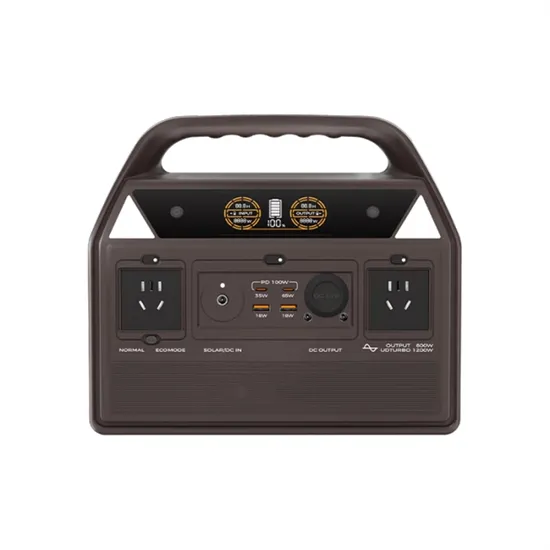 What size battery should I use with an 8600w inverter
What size battery should I use with an 8600w inverter
-
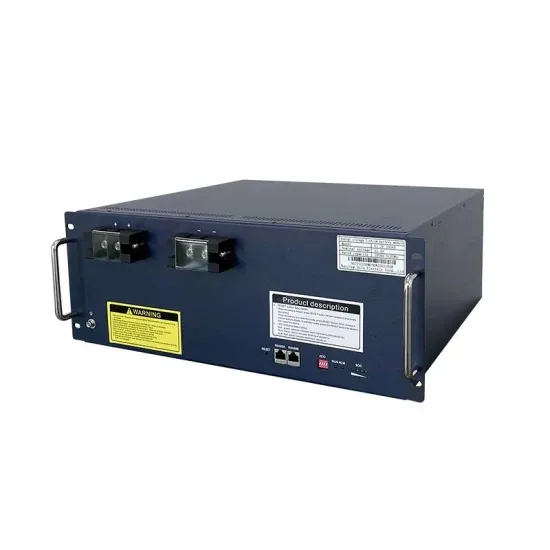 What does EMS mean
What does EMS mean
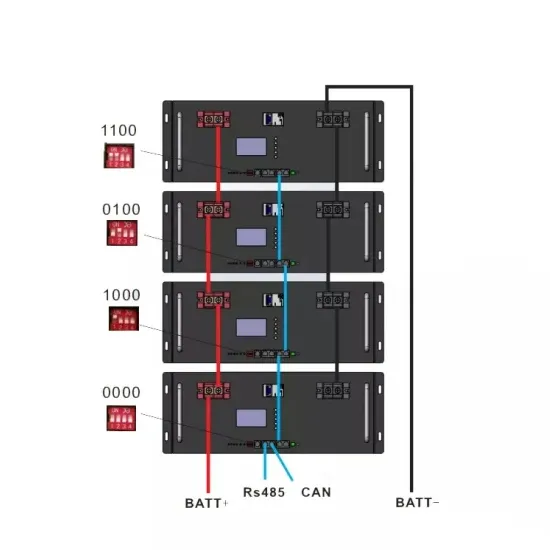
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.