800VA Pure Sine Wave Inverter''s Reference Design
Here H-bridge circuit converts battery DC voltage into AC using high frequency PWM (6 kHz to 20 KHz) thus feeding the 50-Hz transformer which Boost it to 120V/220V AC.
Get a quote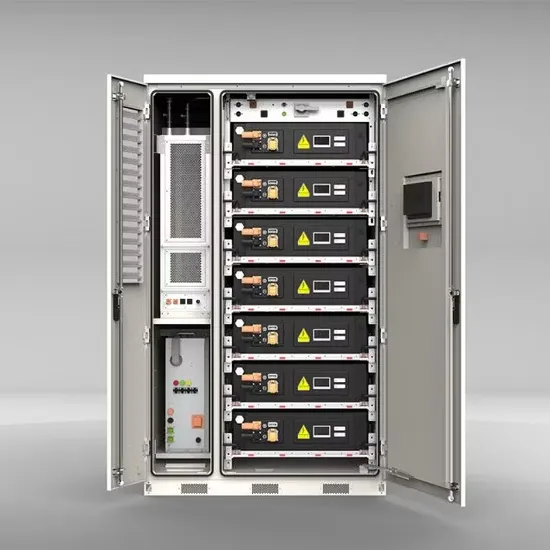
Smoothing modified sinewave Inverter | All About Circuits
A pure sine-wave inverter uses Pulse-Width-Modulation at a high frequency to switch its Mosfets completely on and off so they stay fairly cool, then the high frequency is
Get a quote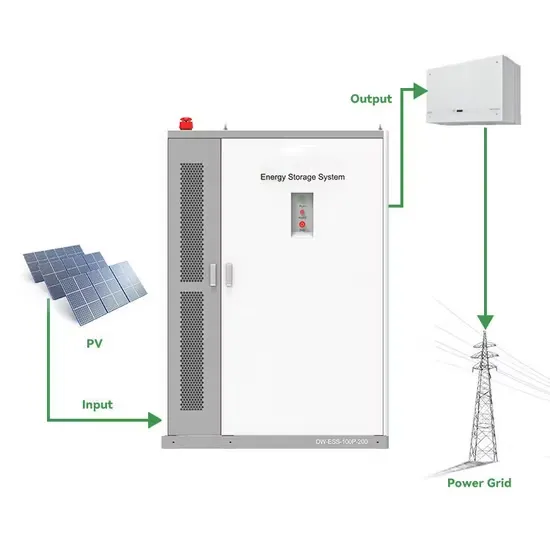
What Is a Pure Sine Wave Inverter?
Understanding Pure Sine Wave Inverters A pure sine wave inverter is a crucial device that converts direct current (DC) power from batteries or other DC sources into high
Get a quote
What Is a Pure Sine Wave Inverter and Why is it
A pure sine wave inverter is a type of inverter that converts DC power into AC power by producing a clean and consistent power supply. Unlike modified sine wave inverters,
Get a quote
Pure Sine Wave Inverter: All You Need to Know
In this blog post, we will explore the fundamentals of pure sine wave inverters, including what they are, how they work, the differences
Get a quote
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of inverter frequency, exploring its significance, factors affecting it, and its practical implications.
Get a quote
CHAPTER4
the sine wave is greater than the triangle and the comparator output is low when the sine wave or typically called the modulation signal is smaller than the triangle. This phenomenon is shown
Get a quote
Sine Wave Inverter Circuit Diagram With Full Explanation
In addition to providing a clear look at the components and operation of a sine wave inverter circuit, this diagram also illustrates why sine
Get a quote
Inverter PWM frequency
You have to use a PWM with a base frequency that is several times higher than the sine wave frequency you like to generate if you want the sine wave to be generated without too much
Get a quote
CHAPTER 2
generator. The filter capacitor across the input terminals of the inverter provides a constant dc link voltage. The inverter therefore is an adjustable-frequency voltage source. The configuration of
Get a quote
Convert a Square Wave Inverter into a Sine Wave Inverter
A pure sine-wave inverter uses Pulse-Width-Modulation at a high frequency to switch its Mosfets completely on and off so they stay fairly cool, then the high frequency is
Get a quote
What is a Pure Sine Wave UPS Inverter? | inverter
The appropriate scheme can effectively suppress harmonics, optimize the use of direct current voltage, and reduce voltage fluctuations.
Get a quote
Ultimate Guide to Pure Sine Wave Inverter
From this page, you will learn everything about a pure sine wave inverter, including what it is, its benefits, how it works, pure vs. modified sine wave inverter, and how to choose
Get a quote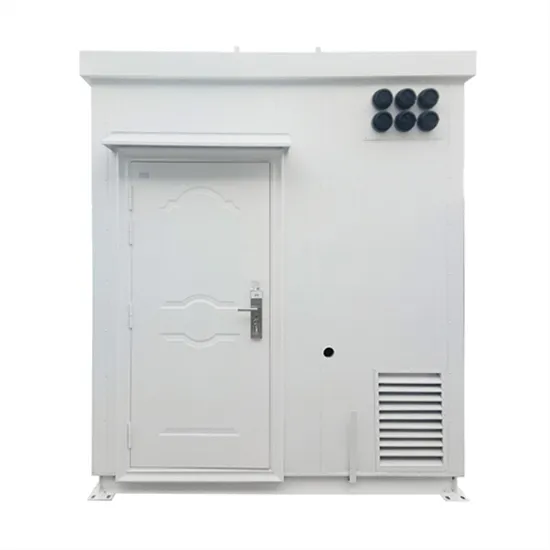
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
The construction of quasi sine wave inverter is much simpler than pure sine wave inverter but a bit complex than pure square wave inverter. The output wave of
Get a quote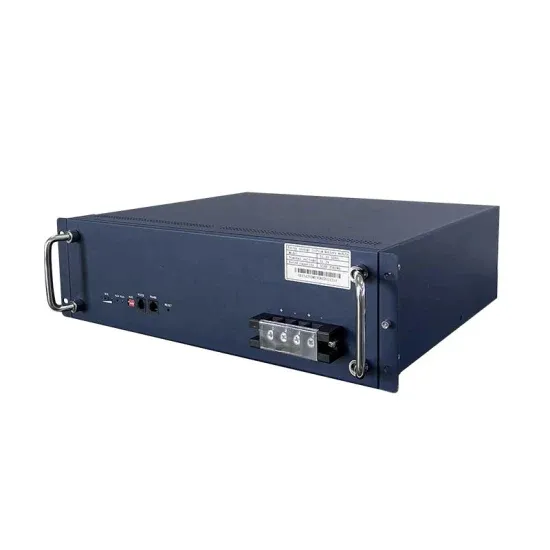
Convert a Square Wave Inverter into a Sine Wave Inverter
In this post I have explained a few circuit concepts which can be employed for converting or modifying any ordinary square wave inverter to sophisticated sine wave inverter
Get a quote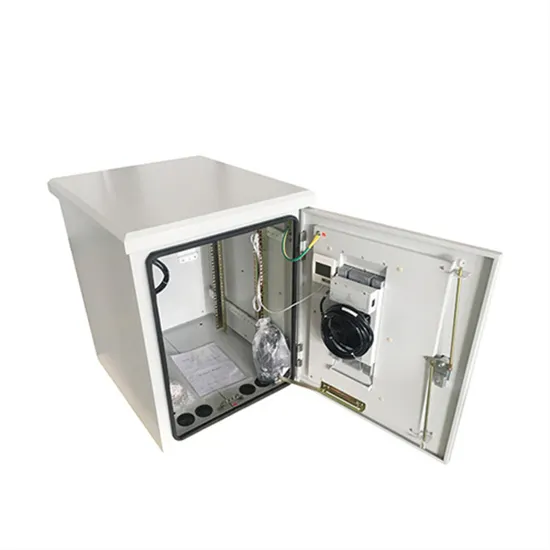
Pure Sine Wave Inverter: Clean Power Guide 2025 – PowerGen
In this comprehensive guide, we''ll delve into the fundamentals of pure sine wave inverters examining their operational principles, technical advantages over modified sine wave
Get a quote
Sine Wave Inverter Circuit Diagram With Full Explanation
By using a pure sine wave inverter, you get a smooth and efficient power conversion that won''t cause any interference with sensitive devices.
Get a quote
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters | EME 812
Combination of pulses of different length and voltage results in a multi-stepped modified square wave, which closely matches the sine wave shape. The low frequency inverters typically
Get a quote
What Is A Modified Sine Wave Inverter? | Definition, How It Works
Learn all about what a modified sine wave inverter is, its definition, how it works, advantages, disadvantages, and applications. Find out how to choose the right inverter for
Get a quote
What is a Pure Sine Wave Inverter?
So, what makes a pure sine wave inverter special? It''s all about the quality of the electricity it produces. Electricity comes in waves, and the "pure sine wave"
Get a quote
Pure Sine Wave Inverter: All You Need to Know
In this blog post, we will explore the fundamentals of pure sine wave inverters, including what they are, how they work, the differences between modified and pure sine wave
Get a quote
High Frequency Inverter vs low Frequency Inverter
Introduction What is a High Frequency Inverter? What is a Low Frequency Inverter? Introduction By the early 1980s, pure sine wave inverters had become more commercially available,
Get a quote
Sine Wave Inverter Circuit Diagram With Full Explanation
In addition to providing a clear look at the components and operation of a sine wave inverter circuit, this diagram also illustrates why sine wave inverters are superior to other
Get a quote
High-Quality Sine Wave Generation Using a Differential Boost
Conventional linear and nonlinear control techniques fail to produce a high-quality sine wave output at higher operating frequency. A nonlinear feedback linearization technique
Get a quote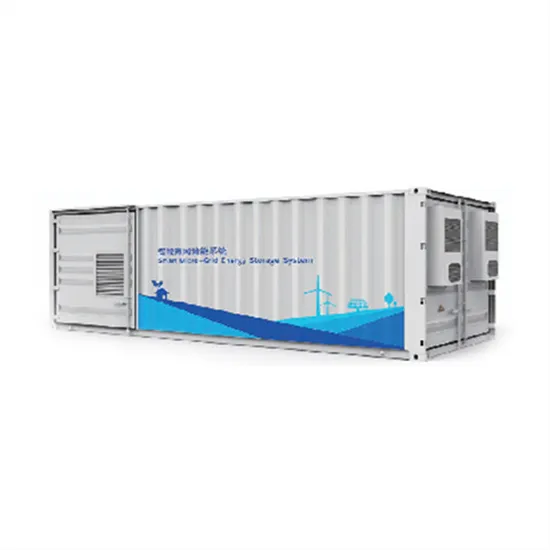
High-Quality Sine Wave Generation Using a Differential Boost Inverter
Conventional linear and nonlinear control techniques fail to produce a high-quality sine wave output at higher operating frequency. A nonlinear feedback linearization technique
Get a quote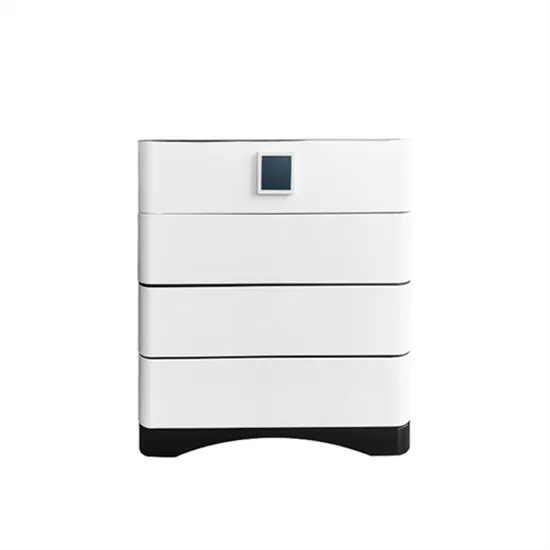
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
Combination of pulses of different length and voltage results in a multi-stepped modified square wave, which closely matches the sine wave shape. The low
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What is the appropriate boost frequency for a sine wave inverter ]
What type of inverter is used to produce a sine wave?
Also, transformers are used here to vary the output voltage. Combination of pulses of different length and voltage results in a multi-stepped modified square wave, which closely matches the sine wave shape. The low frequency inverters typically operate at ~60 Hz frequency. To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used.
How do high frequency inverters produce a sine wave output?
To produce a sine wave output, high-frequency inverters are used. These inverters use the pulse-width modification method: switching currents at high frequency, and for variable periods of time. For example, very narrow (short) pulses simulate a low voltage situation, and wide (long pulses) simulate high voltage.
Why is a sine wave inverter so hot?
If you try to filter the waves then the output transistors must operate linearily which will make them extremely hot. A pure sine-wave inverter uses Pulse-Width-Modulation at a high frequency to switch its Mosfets completely on and off so they stay fairly cool, then the high frequency is filtered out at the output.
How does a pure sine wave inverter work?
DC Power Input: The pure sine wave inverter is connected to a DC power source, such as a battery or a DC power supply. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM): The DC power is converted into a high-frequency AC signal using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
Is a pure sine wave inverter better than a modified sine wave?
In summary, pure sine wave inverters are generally considered to be more suitable for powering sensitive electronic devices and appliances, while modified sine wave inverters may be a more cost-effective option for basic power needs. When Do You Need a Pure Sine Wave Inverter?
Why do you need a sine wave inverter?
In healthcare environments, maintaining uninterrupted and noise-free power is vital. Pure sine wave inverters are required for powering devices like CPAP machines, oxygen concentrators, defibrillators, and diagnostic imaging systems, where electrical noise or failure can impact patient safety.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Power frequency pure sine wave control inverter
Power frequency pure sine wave control inverter
-
 What is the price of 3kw sine wave inverter
What is the price of 3kw sine wave inverter
-
 Branded industrial frequency pure sine wave inverter
Branded industrial frequency pure sine wave inverter
-
 Power frequency inverter sine wave
Power frequency inverter sine wave
-
 High frequency pure sine wave inverter 12V to 48V
High frequency pure sine wave inverter 12V to 48V
-
 What are the benefits of a sine wave inverter
What are the benefits of a sine wave inverter
-
 Photovoltaic power frequency inverter and pure sine wave inverter
Photovoltaic power frequency inverter and pure sine wave inverter
-
 Sine wave inverter structure
Sine wave inverter structure
-
 Cook Islands sine wave inverter installation
Cook Islands sine wave inverter installation
-
 Pure Sine Wave Inverter vs Sine Wave
Pure Sine Wave Inverter vs Sine Wave
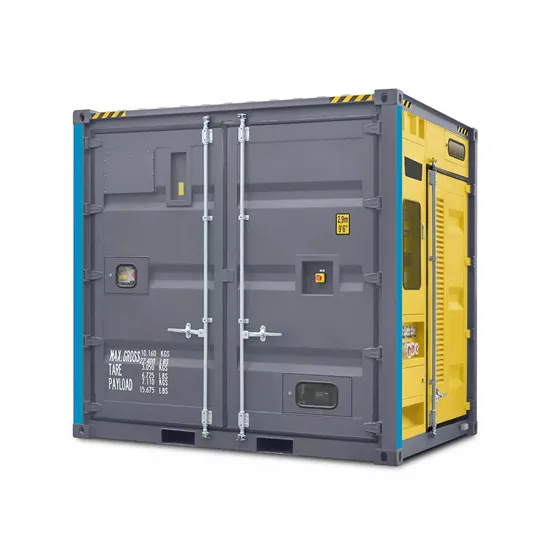
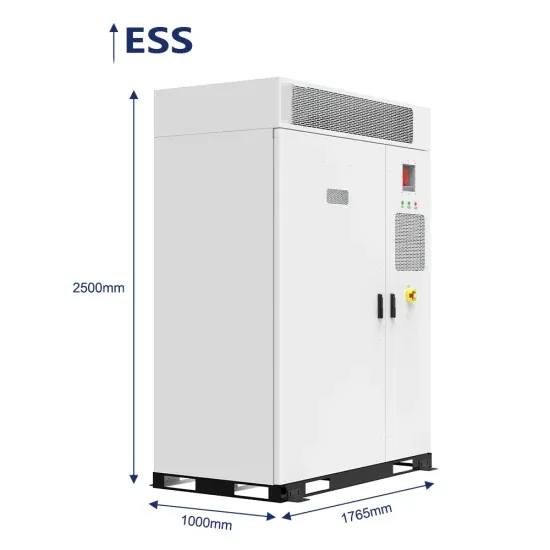
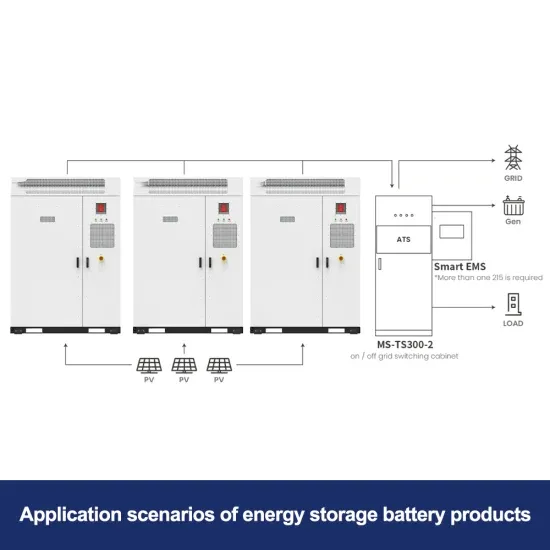
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


