Introduction to Grid Forming Inverters: A Key to Transforming
Why do we need Grid-forming (GFM) Inverters in the Bulk Power System? There is a rapid increase in the amount of inverter-based resources (IBRs) on the grid from Solar PV, Wind,
Get a quote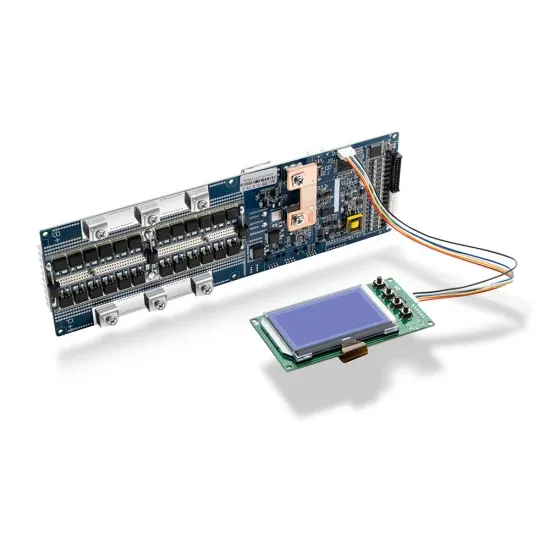
Reverse feeding a inverter?
It has limited utility to a grid tie system as you won''t get any more AC power available as the AC power is still limited by the off-grid inverter''s output. This is the guy in the
Get a quote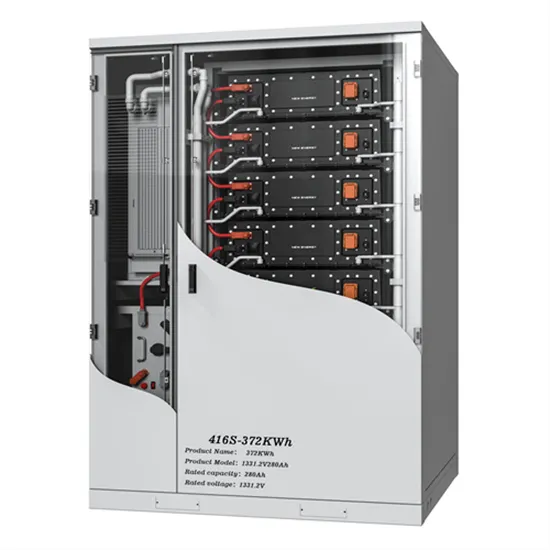
TOPIC: Power inverters and converters. Basic Electricity
TOPIC: Power inverters and converters. Basic Electricity NTC 3 A power inverter is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC).
Get a quote
An advanced guide to Understanding DC to AC inverters
The transmission of AC power from power plants to homes, industrial areas, and other spaces will need a high voltage of around 155,000 to 765,000 volts. With that much
Get a quote
DC to AC Inverters: Everything You Need to Know – Hinen
· AC power will always constantly reverse direction, normally at the frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz. By using the inverters, you can control the flow of DC electricity and make it
Get a quote
Power Inverters Explained: What They Are, How They Work, and
A power inverter is a device that transforms direct current (DC) from batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) — the standard power used in homes and appliances.
Get a quote
How Inverters Work
In this article we take a look at how an inverter works to convert direct current (DC) into Alternating current (AC). Inverters are used within Photovoltaic arrays to provide AC
Get a quote
DC to AC Inverters: Everything You Need to Know –
· AC power will always constantly reverse direction, normally at the frequency of 50 Hz or 60 Hz. By using the inverters, you can control the
Get a quote
CSM_Inverter_TG_E_1_1
Without an inverter, the AC motor would operate at full speed as soon as the power supply was turned ON. You would not be able to control the speed, making the applications for the motor
Get a quote
How Does an Inverter Generator Work? The Ultimate Guide in 2025
Inverter generators use electronics to first convert AC power into DC power, then invert it back into AC power. This process produces stable sine wave output with minimal
Get a quote
What does a power inverter do, and what can I use one for?
The inverter draws its power from a 12 Volt battery (preferably deep-cycle), or several batteries wired in parallel. The battery will need to be recharged as the power is drawn out of it by the
Get a quote
What Is An Inverter? | Definition, Types, Uses, How It
An inverter is a vital electrical device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), which is used to power many household
Get a quote
Understanding the Inverter Role in Solar Power Plant Operation
Conclusion The inverter plays a multifaceted and pivotal role in the operation of solar power plants. By converting DC power from PV panels into AC power, regulating voltage and
Get a quote
Inverter vs. Converter: What''s the Difference, Which
A DC to AC converter, also referred to as an inverter, performs the reverse function of an AC to DC converter. It converts direct current (DC) into
Get a quote
Power inverter
With HVDC power transmission, AC power is rectified and high voltage DC power is transmitted to another location. At the receiving location, an inverter in a HVDC converter station converts
Get a quote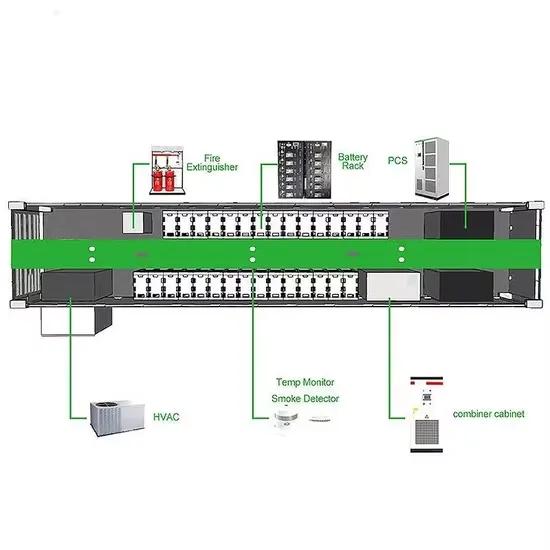
Inverter vs. Converter: What''s the Difference, Which Do You
A DC to AC converter, also referred to as an inverter, performs the reverse function of an AC to DC converter. It converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), making it essential
Get a quote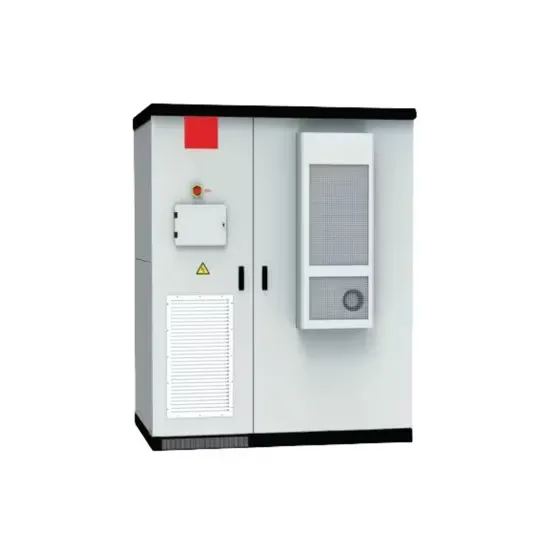
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
The fundamental principle is simple: DC power flows in one direction like water through a straight pipe, while AC power alternates direction 50-60
Get a quote
Understanding the inverters that electrics, hybrids use
The inverter is the controller for the AC electric motor. The "control" means that the power (measured in Kw) is delivered as needed (based on
Get a quote
Principle of Anti-Reverse Current of Photovoltaic Inverter
For household low-power grid-connected inverters, the output current is small, generally less than 80A current models (within 50KW), you can directly use a DC anti-reverse
Get a quote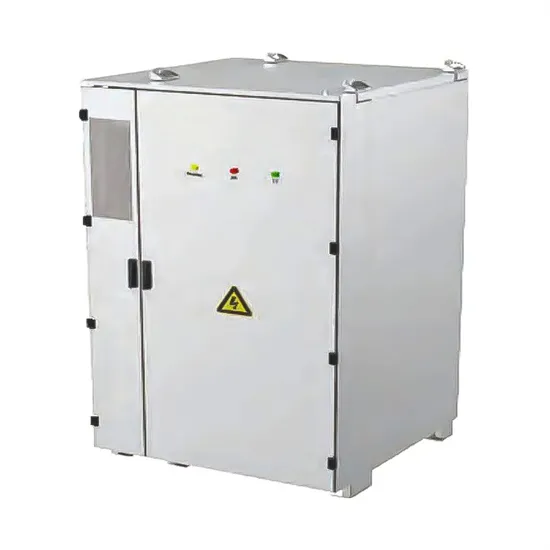
What are Inverters and How Do They Work? | RELiON
Inverters convert direct current (DC) electricity from the power source into alternating current electricity (AC). The inverter is able to accomplish this conversion by rapidly changing the
Get a quote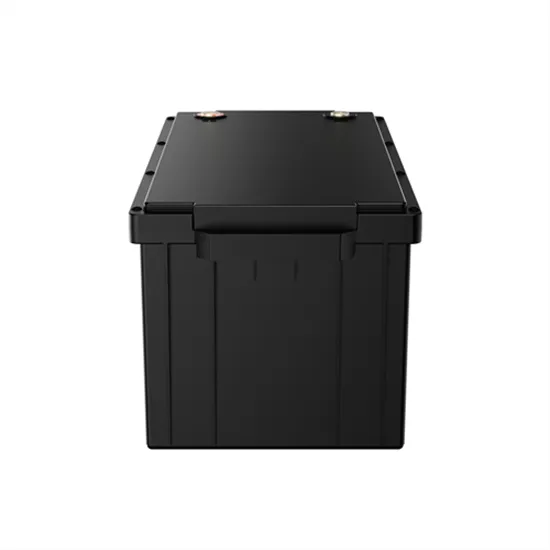
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To Power Conversion
The fundamental principle is simple: DC power flows in one direction like water through a straight pipe, while AC power alternates direction 50-60 times per second, like water
Get a quote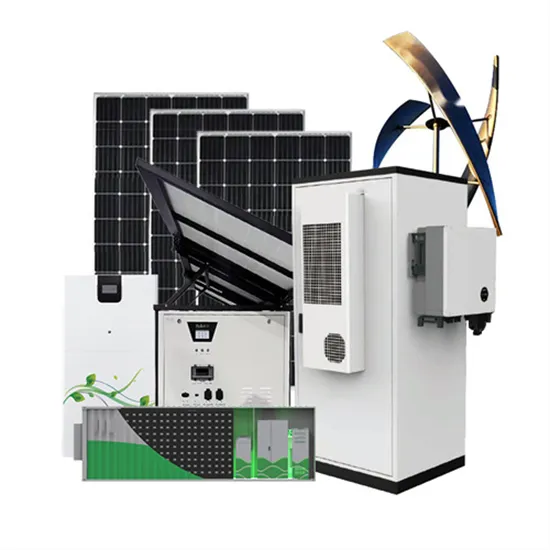
How Does a Power Inverter Work? (Simplest Explanation)
How Does an Inverter Convert from DC to AC? Well, the basic way is to use switches. Placing switches in the circuit allow you to change where the electrons flow to get them to change
Get a quote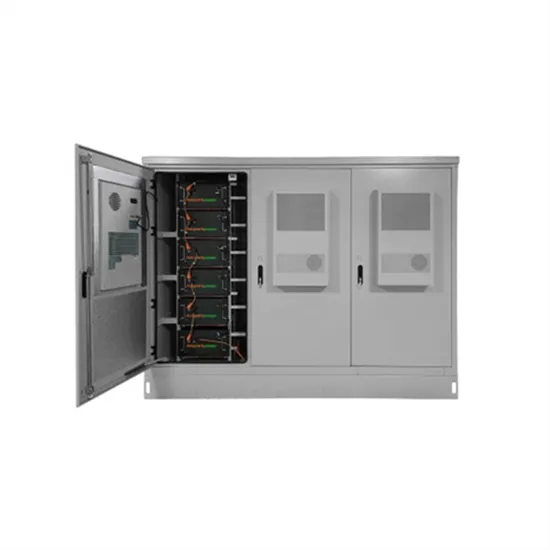
A Guide to Solar Inverters: How They Work & How to
What is a solar power inverter? How does it work? A solar inverter is really a converter, though the rules of physics say otherwise. A solar power inverter
Get a quote
How Does a Power Inverter Work? (Simplest
How Does an Inverter Convert from DC to AC? Well, the basic way is to use switches. Placing switches in the circuit allow you to change where the
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Does the inverter first transmit AC reverse power ]
How does an inverter work?
An inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). It works by converting the DC power from batteries or solar panels into AC power, which is used by most household appliances and electronics.
What does an inverter convert?
Inverters are used in various applications such as household energy storage, electronic vehicle (EV) motors, industrial photovoltaic (PV) inverters to provide power for factory equipment, grid-connected photovoltaic power generation, etc. It converts DC to AC, which is the reverse work of a power supply.
Why do we need to convert between a DC and AC inverter?
Both types of power have their uses and limitations so we often need to convert between the two to maximise their use. An inverter is a device which is used to convert between Direct Current (DC) and Alternating Current (AC).
How does an inverter control a motor?
An inverter uses this feature to freely control the speed and torque of a motor. This type of control, in which the frequency and voltage are freely set, is called pulse width modulation, or PWM. The inverter first converts the input AC power to DC power and again creates AC power from the converted DC power using PWM control.
What is a power inverter?
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.
Which type of inverter converts DC power into AC power?
Both Voltage Source Inverters and Current Source Inverters convert DC power into AC power and can be further classified as single-phase or three-phase inverters. When categorizing inverters by the type of output waveform they produce, there are three main kinds: square wave inverters, pure sine wave inverters, and modified sine wave inverters.
Guess what you want to know
-
 AC power connection inverter
AC power connection inverter
-
 Battery inverter converts AC power
Battery inverter converts AC power
-
 Inverter DC to AC 380V high power 9kw
Inverter DC to AC 380V high power 9kw
-
 Inverter can supply AC power
Inverter can supply AC power
-
 28V high power inverter
28V high power inverter
-
 Eastern European Solar Power Inverter
Eastern European Solar Power Inverter
-
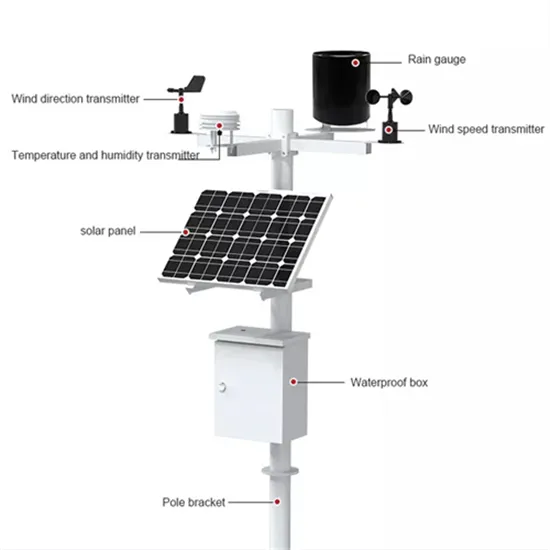 Inverter power regulation method
Inverter power regulation method
-
 What are the requirements for EU inverter parallel three-phase power
What are the requirements for EU inverter parallel three-phase power
-
 Battery power frequency inverter
Battery power frequency inverter
-
 Tuvalu power frequency inverter manufacturer
Tuvalu power frequency inverter manufacturer
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


