Active and Reactive Power Control in a Three-Phase
An easier three-phase grid-connected PV inverter with reliable active and reactive power management, minimal current harmonics, seamless
Get a quote
Power Control and Voltage Regulation for Grid
This paper proposes a robust voltage control strategy for grid-forming (GFM) inverters in distribution networks to achieve power support and
Get a quote
Optimal Structures for Voltage Controllers in Inverters
In this paper, we pose an optimal voltage control problem for ac inverter systems and study the structure of the resulting feedback laws.
Get a quote
Regulating Voltage: Recommendations for Smart Inverters
This report from GridLab provides an introduction to voltage regulation concepts, including advantages and disadvantages of various control modes. The authors include
Get a quote
(PDF) Frequency and Voltage Control Techniques through Inverter
Therefore, new paradigms are required for voltage and frequency regulation by inverter-interfaced DGs (IIDGs). Notably, employing effective voltage and frequency regulation
Get a quote
A Unified Control Design of Three Phase Inverters Suitable for
The primary cascaded control loops and the phase-locked loop (PLL) can enable voltage source inverter operation in grid-forming and grid-following mode. This article
Get a quote
Grid-connected photovoltaic inverters: Grid codes, topologies and
The proliferation of solar power plants has begun to have an impact on utility grid operation, stability, and security. As a result, several governments have developed additional
Get a quote
Grid-connected PV inverter system control optimization using
The inverter power and power from the grid steady-state performance shows how well the GWO + PID control method works to guarantee a steady power supply under various
Get a quote
Over-Voltage Regulation of Distribution Networks by
The increase of Photovoltaics (PV) units'' penetration factor in the power grids might create overvoltage over the network buses. The active
Get a quote
A Unified Control Design of Three Phase Inverters
The primary cascaded control loops and the phase-locked loop (PLL) can enable voltage source inverter operation in grid-forming and grid
Get a quote
Inverter-Based Local Control Methods for Mitigating
Three of these methods use one smart control functionality of PV inverters, while the other uses two smart control functionalities in a coordinated way. Power flow simulations
Get a quote
Voltage Regulation in Distribution Grid Using PV Smart
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: section II presents the reactive power capability of PV smart inverters and the existing control methods; section III introduces the two new
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency
There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical
Get a quote
Voltage Control Methods of Inverter – PWM Technique
The voltage control is primarily achieved by varying the firing angle of the ac voltage controller that feeds the ac load. In this method, there is a
Get a quote
(PDF) Frequency and Voltage Control Techniques
Therefore, new paradigms are required for voltage and frequency regulation by inverter-interfaced DGs (IIDGs). Notably, employing effective
Get a quote
Automatic voltage regulation application for PV inverters in low
For reactive power management, three main categories can be defined according to communication needs, e.g., local, centralized, and distributed control. In the local control
Get a quote
Power Control and Voltage Regulation for Grid-Forming Inverters
This paper proposes a robust voltage control strategy for grid-forming (GFM) inverters in distribution networks to achieve power support and voltage optimization.
Get a quote
REGULATING VOLTAGE: RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
ACTIVE POWER-REACTIVE POWER (WATT-VAR) MODE: Reactive power injection or absorption is based on active power injection or absorption following a specified watt-var "curve."
Get a quote
Dead‐beat predictive direct power control of voltage
This study presents a novel dead-beat predictive direct power control (PDPC) strategy working at nearly constant switching frequency for the
Get a quote
Active and Reactive Power Control in a Three-Phase Photovoltaic Inverter
An easier three-phase grid-connected PV inverter with reliable active and reactive power management, minimal current harmonics, seamless transitions, and quick response to
Get a quote
Voltage regulation in unbalanced power distribution systems with
This paper proposes an advanced supervisory control methodology, with the reactive power control and voltage regulation at residential PV inverters, as an effective means
Get a quote
MATHEMATICAL MODELING AND ADVANCED CONTROL
This thesis explores the core advantages of grid-forming inverters comparing to conventional inverters, develops mathematical models for voltage and frequency control, and proposes
Get a quote
Consistency control of grid-connected substation voltage
To address this, a consistency control method for the voltage regulation in the grid-connected substations is proposed, based on the photovoltaic-inverter power coordination.
Get a quote
Inverter Design and Droop Parallel Control Strategy Based on
The present work is aimed at improving the performance of the multiobjective energy parallel step-by-step power generation system and enhancing the reliability and
Get a quote
Comparison of Reactive Power Control Techniques
Thus, the reactive power control of PV inverters has emerged as a viable solution for localized voltage regulation. This paper presents a detailed
Get a quote
Photovoltaic inverter voltage regulation method
How does an inverter regulate voltage levels in a utility grid? The proposed novel method enables an inverter to inject the required level of reactive powerto regulate the voltage levels of the
Get a quote
Adaptive power regulation-based coordinated frequency regulation method
The proposed coordinated frequency regulation method can provide bi-directional frequency regulation, effectively addressing the issue of insufficient frequency regulation
Get a quote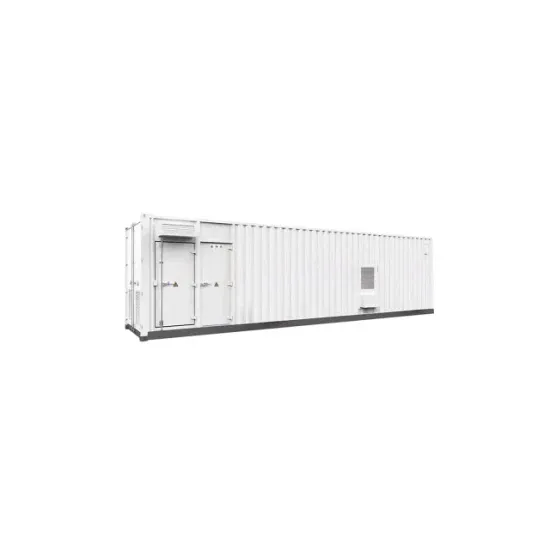
Combined PS-PDM control method for voltage-source
This paper proposes a new control method for a voltage-source series-resonant inverter (SRI) of the induction heating system. The proposed
Get a quote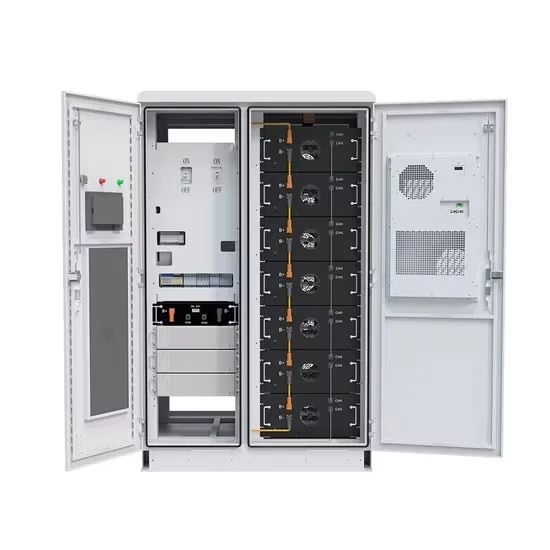
Consistency control of grid-connected substation voltage regulation
To address this, a consistency control method for the voltage regulation in the grid-connected substations is proposed, based on the photovoltaic-inverter power coordination.
Get a quote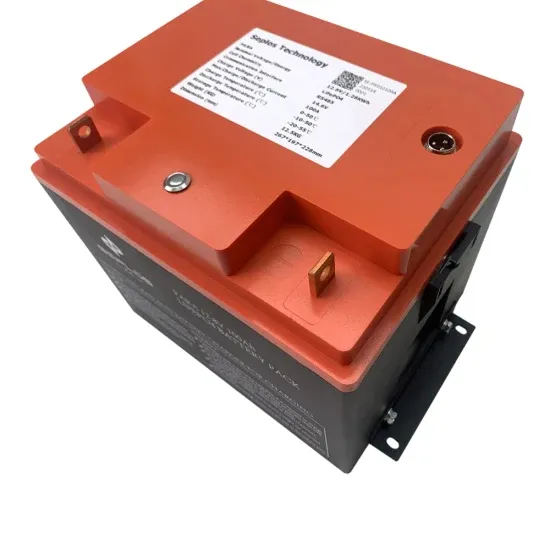
6 FAQs about [Inverter power regulation method]
Can PV inverters be used for voltage control?
Another potential solution is the utilization of PV inverters for voltage control due to their control of active and reactive power generation capabilities . It is to be noted that power electronic converters based PV systems are able to provide reactive power support for their entire operational range.
How do grid-forming inverters achieve power support and voltage optimization?
This paper proposes a robust voltage control strategy for grid-forming (GFM) inverters in distribution networks to achieve power support and voltage optimization. Specifically, the GFM control approach primarily consists of a power synchronization loop, a voltage feedforward loop, and a current control loop.
Can GFM inverters achieve power support and voltage governance?
This paper proposed a robust voltage control strategy for GFM inverters in distribution networks to realize power support and voltage governance. At the load terminal, the GFM control approach included three control loops comprising a power synchronization control loop, a voltage feedforward control loop, and a current control loop.
What is unified control for inverters?
This article proposes a unified control for such inverters with current control, voltage control, and power control loops, including the PLL impact on - transformations as the building blocks. Small-signal-based linearization techniques are adopted to achieve the resultant linear time-invariant model.
Can data-driven control of PV inverters be used for voltage regulation?
Moreover, in , a common information model (CIM) based data exchange framework is proposed for data-driven control of PV inverters for voltage regulation. Fig. 6. Specific laboratory deployment for AVR app. 4.2. Automatic voltage regulation (AVR) app
How a coordination control is implemented in a PV inverter?
The block diagram shown in Fig. 5 depicts how the coordination control is implemented in the local controller of each PV inverter. Δ QPV, j and Δ Qc, j of each PV inverter will be calculated from the coordination control (AVR app) and sent to individual local control via the communication network.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Simple inverter power regulation
Simple inverter power regulation
-
 Off-grid inverter power distribution method
Off-grid inverter power distribution method
-
 High power inverter equipment
High power inverter equipment
-
 Photovoltaic power station inverter selection
Photovoltaic power station inverter selection
-
 Communication base station inverter wind power generation function
Communication base station inverter wind power generation function
-
 24V to 220V inverter actual power
24V to 220V inverter actual power
-
 Photovoltaic inverter pv power
Photovoltaic inverter pv power
-
 Photovoltaic energy storage inverter power supply
Photovoltaic energy storage inverter power supply
-
 The inverter power gradually decreases
The inverter power gradually decreases
-
 Is the inverter normal after photovoltaic power generation
Is the inverter normal after photovoltaic power generation
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


