How Grid Energy Storage Works
Yes, residential grid energy storage systems, like home batteries, can store energy from rooftop solar panels or the grid when rates are low and provide power during peak hours
Get a quote
Renewable integration and energy storage management and
The dynamic behaviours of battery energy storage systems (BESSs) make their cutting-edge technology for power grid applications. A BESS must have a Battery
Get a quote
Giant Batteries Are Transforming the World''s Electrical Grids
"Energy storage has become a linchpin" for avoiding disruptions, says Joseph Williamson, vice president for projects at esVolta LP, the company that developed and owns
Get a quote
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
ESSs use more electricity for charging than they can provide when discharging and supplying electricity. Because of this difference, EIA publishes data on both gross
Get a quote
Microsoft Word
The uses for this work include: Inform DOE-FE of range of technologies and potential R&D. Perform initial steps for scoping the work required to analyze and model the benefits that could
Get a quote
Off-Grid vs. Grid-Connected Energy Storage: Which Should You
It involves economic efficiency, energy independence, and safety assurance. If you want to save on electricity bills, grid-connected storage is the top choice. If you seek complete
Get a quote
Grid energy storage
This thermal storage can provide load-shifting or even more complex ancillary services by increasing power consumption (charging the storage) during off-peak times and lowering
Get a quote
Renewable integration and energy storage management and
This paper focuses on the critical significance of grid-connected energy storage systems (ESSs), specifically Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESSs), in developing modern
Get a quote
Role of energy storage technologies in enhancing grid stability
This paper provides an overview of energy storage, explains the various methods used to store energy (focusing on alternative energy forms like heat and electricity), and then
Get a quote
Why Batteries Are the Electric Grid''s Most Powerful Asset
The U.S. electric grid is a delicate system that requires a consistent balance between energy supply with energy demand. When a heat wave turns on millions of air
Get a quote
Navigating the Cost-Efficiency Frontier: Exploring the viability of
Battery electricity storage is recognized as a critical technology in facilitating the global transition towards a sustainable energy system [2], [3], [4]. These systems are crucial in
Get a quote
Grid Scale Energy Storage: An In-Depth Look
Energy systems that use grid-scale battery storage are more reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly. A top benefit is the ability to stabilize the grid during fluctuations from
Get a quote
Renewable Energy Storage Facts | ACP
Energy storage allows us to store clean energy to use at another time, increasing reliability, controlling costs, and helping build a more resilient grid. Get the
Get a quote
Grid Connected PV System Connects PV Panels to
In recent years, however, the number of solar powered homes connected to the local electricity grid has increased dramatically. These Grid
Get a quote
Solar Integration: Solar Energy and Storage Basics
, when solar energy generation is falling. Temperatures can be hottest during these times, and people who work daytime hours get home and begin using
Get a quote
Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid: Technology Trends
Unlike a power plant, which can continue providing electricity as long as it remains connected to its fuel source, energy storage can provide electricity for only a limited amount of
Get a quote
Next-Generation Grid Technologies
Through this transformation, the grid of the future faces many challenges. Extreme weather events, variability and intermittency from renewable generation sources and other advanced
Get a quote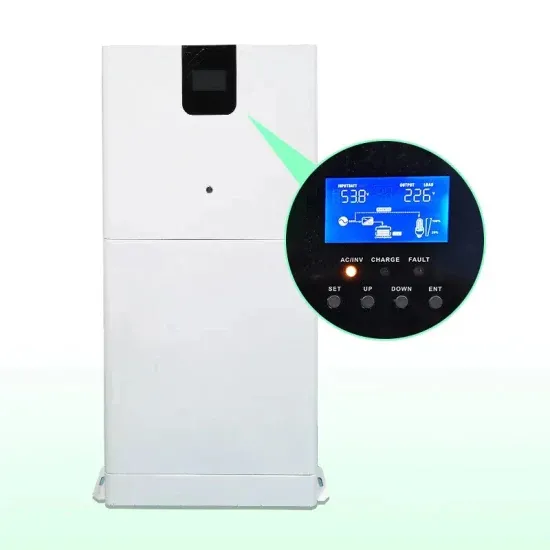
Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid:
Unlike a power plant, which can continue providing electricity as long as it remains connected to its fuel source, energy storage can provide
Get a quote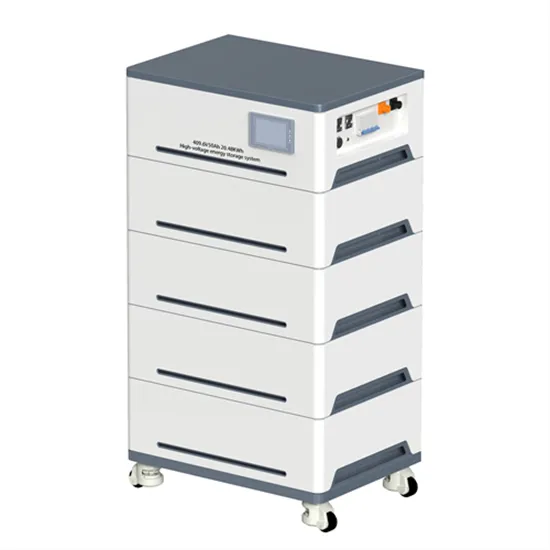
Grid-Connected Energy Storage Systems: State-of-the-Art
This article discusses pros and cons of available energy storage, describes applications where energy storage systems are needed and the grid services they can provide, and demonstrates
Get a quote
Grid Scale Energy Storage: An In-Depth Look
Energy systems that use grid-scale battery storage are more reliable, efficient, and environmentally friendly. A top benefit is the ability to
Get a quote
Grid energy storage
Electricity can be stored directly for a short time in capacitors, somewhat longer electrochemically in batteries, and much longer chemically (e.g. hydrogen), mechanically (e.g. pumped hydropower) or as heat. The first pumped hydroelectricity was constructed at the end of the 19th century around the Alps in Italy, Austria, and Switzerland. The technique rapidly expanded during the 196
Get a quote
Solar, battery storage to lead new U.S. generating capacity
This growth highlights the importance of battery storage when used with renewable energy, helping to balance supply and demand and improve grid stability. Energy
Get a quote
U.S. Grid Energy Storage Factsheet
Electrical Energy Storage (EES) refers to systems that store electricity in a form that can be converted back into electrical energy when needed. 1 Batteries are one of the most common
Get a quote
How Grid Energy Storage Works: Unlocking the Future of Power
The global shift towards renewable energy sources has spurred a revolution in how we generate, store, and use electricity. Nowadays, we increasingly rely on intermittent energy
Get a quote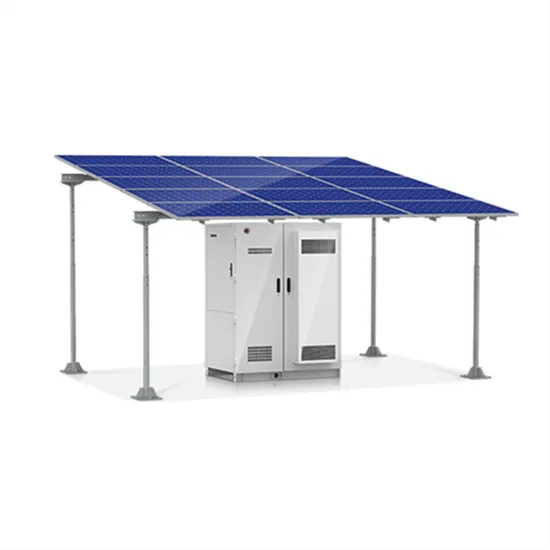
Why does energy storage need to be connected to the grid?
One of the foremost benefits of connecting energy storage to the grid is its contribution to grid stability. The ability to absorb excess energy during periods of high
Get a quote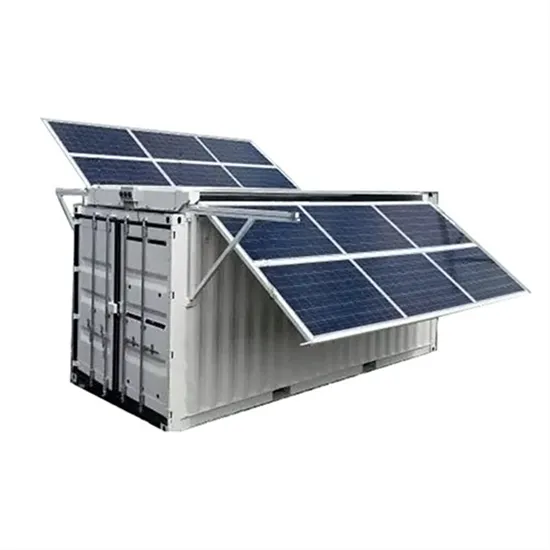
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
ESSs use more electricity for charging than they can provide when discharging and supplying electricity. Because of this difference, EIA publishes data on both gross generation and net
Get a quote
Grid connected solar panel with battery energy
A grid-connected battery energy storage system (BESS) is a crucial component in modern electrical grids that enables efficient management of
Get a quote
Analysis Insights: Energy Storage
Energy storage has the potential to offer multiple benefits to the power grid and to be an enabling and complementary technology for increasing penetrations of variable renewable energy
Get a quote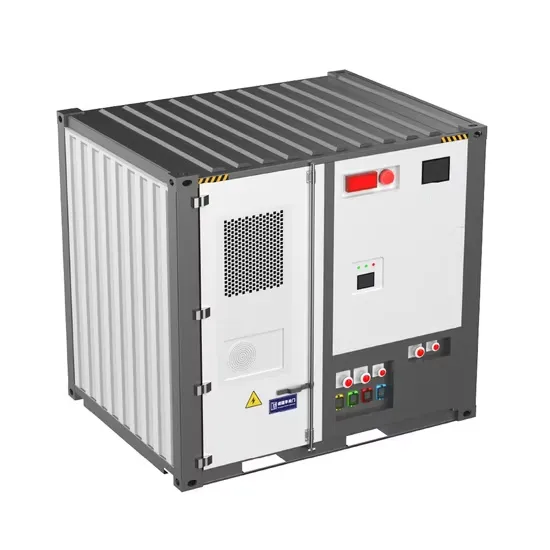
6 FAQs about [Can grid-connected energy storage generate more electricity ]
Can a residential grid energy storage system store energy?
Yes, residential grid energy storage systems, like home batteries, can store energy from rooftop solar panels or the grid when rates are low and provide power during peak hours or outages, enhancing sustainability and savings. Beacon Power. "Beacon Power Awarded $2 Million to Support Deployment of Flywheel Plant in New York."
Why do power grids need energy storage systems?
Modern power grids depend on energy storage systems (ESS) for reliability and sustainability. With the rise of renewable energy, grid stability depends on the energy storage system (ESS). Batteries degrade, energy efficiency issues arise, and ESS sizing and allocation are complicated.
What is grid energy storage?
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variable renewables such as solar and inflexible sources like nuclear power, releasing it when needed.
Are grid-connected energy storage systems economically viable?
Economic aspects of grid-connected energy storage systems Modern energy infrastructure relies on grid-connected energy storage systems (ESS) for grid stability, renewable energy integration, and backup power. Understanding these systems' feasibility and adoption requires economic analysis.
How can energy storage make grids more flexible?
Energy storage is one option to making grids more flexible. An other solution is the use of more dispatchable power plants that can change their output rapidly, for instance peaking power plants to fill in supply gaps.
How do grid-scale energy storage systems work?
To overcome this challenge, grid-scale energy storage systems are being connected to the power grid to store excess electricity at times when it’s plentiful and then release it when the grid is under periods of especially high demand.
Guess what you want to know
-
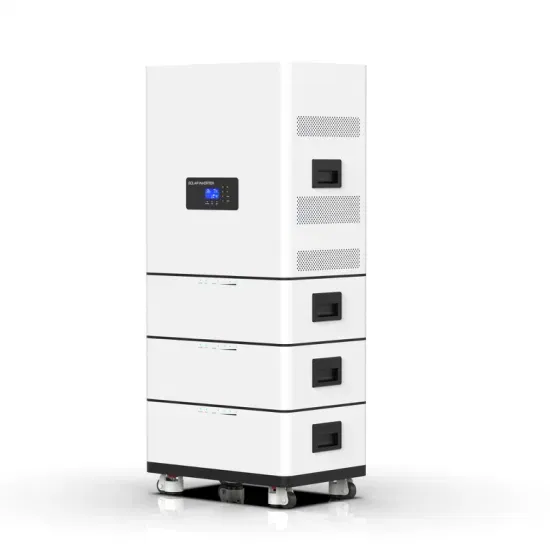 Using flywheel energy storage to generate electricity
Using flywheel energy storage to generate electricity
-
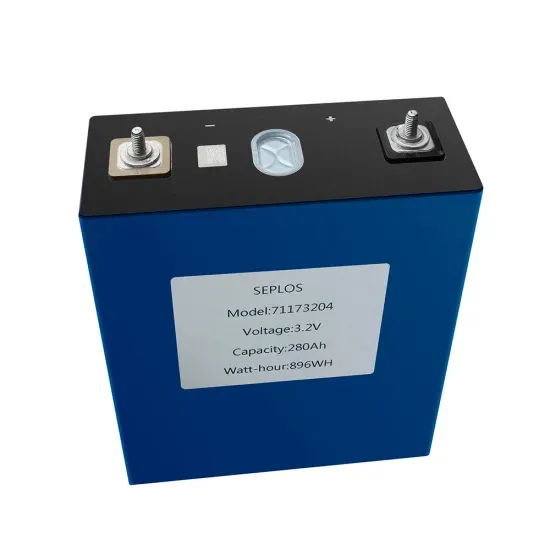 The communication base station energy storage system is difficult to generate electricity
The communication base station energy storage system is difficult to generate electricity
-
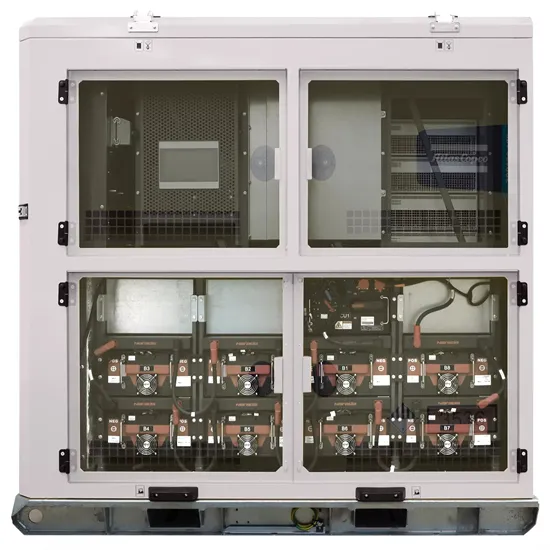 Grid-connected industrial and commercial energy storage design scheme
Grid-connected industrial and commercial energy storage design scheme
-
 Household Energy Storage Grid-Connected Inverter
Household Energy Storage Grid-Connected Inverter
-
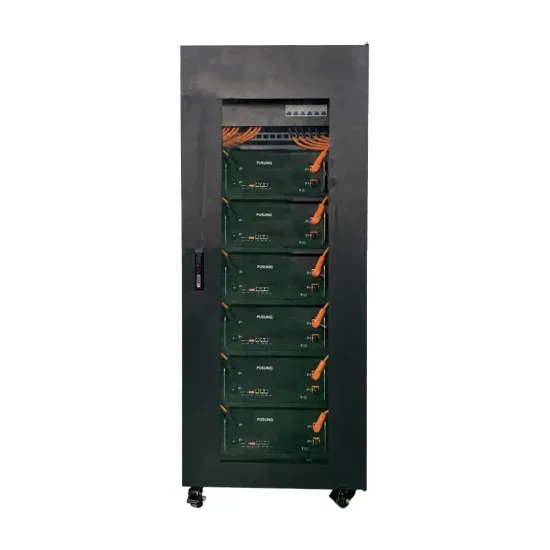 Grid-connected photovoltaic energy storage inverter
Grid-connected photovoltaic energy storage inverter
-
 Is energy storage equipment related to electricity
Is energy storage equipment related to electricity
-
 Grid-connected energy storage supports the construction of new power systems
Grid-connected energy storage supports the construction of new power systems
-
 Solar panels generate electricity directly connected to storage containers
Solar panels generate electricity directly connected to storage containers
-
 Energy storage power generation transmission and electricity use
Energy storage power generation transmission and electricity use
-
 50kw grid-connected energy storage
50kw grid-connected energy storage
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


