Power Generation: what it is, trends, and main types of power generation
The generation of electricity is essential to modern society, as it powers industries, cities, and homes. There are several ways to generate it, each with its own characteristics,
Get a quote
The Future of Energy Storage | MIT Energy Initiative
Energy storage is a potential substitute for, or complement to, almost every aspect of a power system, including generation, transmission, and demand
Get a quote
What does energy storage and power transmission
Energy storage and power transmission refer to the methods and technologies involved in retaining and transferring electrical energy. 1. Energy
Get a quote
Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid:
By leveraging all the individual storage devices from participating customers, Green Mountain Power can meet peak electricity demand while
Get a quote
An Overview of Energy Storage Systems (ESS) for Electric
The continuation method is used to gradually increase the amount of transfer power to the thermal limits of transmission paths, including the overload of line, transformer or a substation
Get a quote
Electricity Storage | US EPA
One way to help balance fluctuations in electricity supply and demand is to store electricity during periods of relatively high production and low demand, then release it back to
Get a quote
Sizing capacities of renewable generation, transmission, and energy
To decrease carbon dioxide emission, a high penetration level of renewable energy will be witnessed over the world in the future. By then, energy storage will play an important
Get a quote
Projected material requirements for the global electricity
We analyse how the global material stocks and flows related to the electricity sector may develop towards 2050. We focus on three electricity sub-systems, being generation,
Get a quote
Energy Storage for a Modern Electric Grid: Technology Trends
By leveraging all the individual storage devices from participating customers, Green Mountain Power can meet peak electricity demand while lowering the cost it pays to its
Get a quote
How It Works: Electric Transmission
The focus of this primer is on the transmission and distribution segments: the power lines, substations, and other infrastructure needed to move power from generation sources to end
Get a quote
Electric Power System
Electrical energy has grown immensely over two centuries because the flexibility it provides for its use. The variety of use has led its demand to increase monotonously. However, as the load or
Get a quote
What does energy storage and power transmission mean?
In summary, the intricate relationship between energy storage and power transmission is crucial for modern electrical networks. Energy storage technologies provide
Get a quote
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior
Get a quote
Understanding the generation, transmission and distribution of electricity
At each stage of the electricity generation, transmission, and distribution process, the main goal is to ensure safe and reliable delivery of power throughout the system.
Get a quote
Understanding Power Transmission and Distribution: The
Explore the crucial role of transmission and distribution in the electricity grid, and learn how transmission lines ensure reliable energy delivery to communities.
Get a quote
The Future of Energy Storage | MIT Energy Initiative
Energy storage is a potential substitute for, or complement to, almost every aspect of a power system, including generation, transmission, and demand flexibility.
Get a quote
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or
Get a quote
How to meet global energy demand in the age of
Integrated infrastructure planning: Coordinating power generation, transmission, storage and demand management helps prevent waste and
Get a quote
Electricity explained Energy storage for electricity generation
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or device, which is
Get a quote
Electricity Basics | American Public Power Association
Electricity is the flow of electrical charge. Homes, buildings, and businesses get electricity through an interconnected system that generates, transmits, and distributes electricity – also called the
Get a quote
Introduction to Energy Storage and Conversion | ACS
The predominant concern in contemporary daily life revolves around energy production and optimizing its utilization. Energy storage systems have emerged as the
Get a quote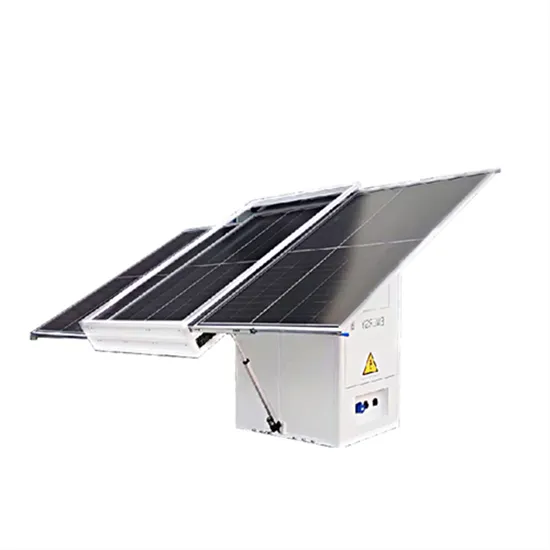
Energy storage as a transmission asset: Definitions and use cases
This paper reviews regulatory proceedings to define three types of energy storage assets than can interact with the transmission system: storage as a transmission asset,
Get a quote
Renewable Energy Storage Facts | ACP
Thermal energy storage is most commonly associated with concentrated solar power (CSP) plants, which use solar energy to heat a working fluid that drives a steam turbine to generate
Get a quote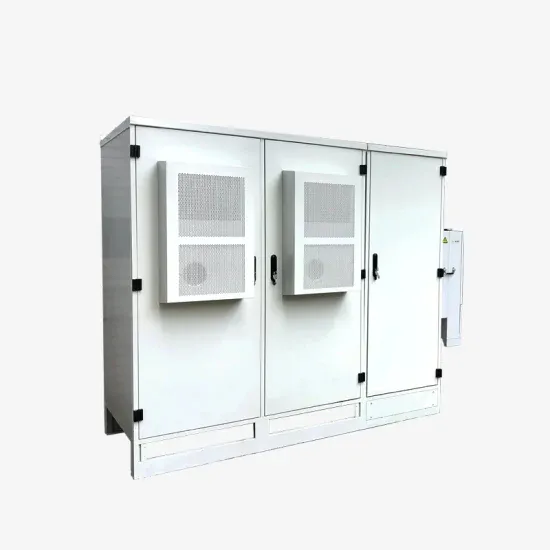
Comprehensive review of energy storage systems technologies,
For enormous scale power and highly energetic storage applications, such as bulk energy, auxiliary, and transmission infrastructure services, pumped hydro storage and
Get a quote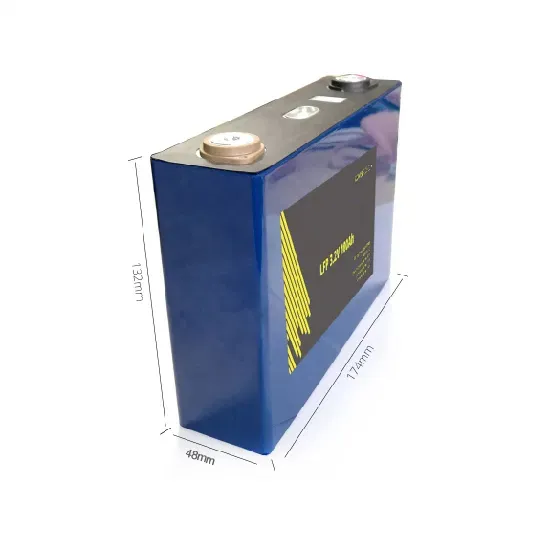
What does energy storage and power transmission
In summary, the intricate relationship between energy storage and power transmission is crucial for modern electrical networks. Energy storage
Get a quote
Energy storage and transmission expansion planning:
The massive development of energy storage systems (ESSs) may significantly help in the supply–demand balance task, especially under the
Get a quote
Electricity Basics | American Public Power Association
Electricity is the flow of electrical charge. Homes, buildings, and businesses get electricity through an interconnected system that generates, transmits, and
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Energy storage power generation transmission and electricity use]
Why is energy storage important?
Energy storage is a potential substitute for, or complement to, almost every aspect of a power system, including generation, transmission, and demand flexibility. Storage should be co-optimized with clean generation, transmission systems, and strategies to reward consumers for making their electricity use more flexible.
What is an energy storage system?
An energy storage system (ESS) for electricity generation uses electricity (or some other energy source, such as solar-thermal energy) to charge an energy storage system or device, which is discharged to supply (generate) electricity when needed at desired levels and quality. ESSs provide a variety of services to support electric power grids.
How can storage help balance electricity supply and demand?
One way to help balance fluctuations in electricity supply and demand is to store electricity during periods of relatively high production and low demand, then release it back to the electric power grid during periods of lower production or higher demand. In some cases, storage may provide economic, reliability, and environmental benefits.
What are the different types of energy storage systems?
Batteries. Similar to common rechargeable batteries, very large batteries can store electricity until it is needed. These systems can use lithium ion, lead acid, lithium iron or other battery technologies. Thermal energy storage. Electricity can be used to produce thermal energy, which can be stored until it is needed.
What makes energy storage unique?
One attribute that makes energy storage unique is its scalability. It can be implemented as a large utility-scale project to help meet peak energy demand and stabilize the grid, or as a small system sited in a residence or commercial facility to manage electricity costs and provide backup power.
What is energy storage & how does it work?
One game-changing technology that is part of this transformation is energy storage, which allows utilities, utility customers and third parties to store or release electricity on demand. Energy storage includes an array of technologies, such as electrochemical batteries, pumped storage hydropower, compressed air and thermal storage.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Small-scale solar power generation and energy storage for household use
Small-scale solar power generation and energy storage for household use
-
 Energy storage power generation for home use
Energy storage power generation for home use
-
 Multi-energy solar energy storage cabinet power generation system
Multi-energy solar energy storage cabinet power generation system
-
 Democratic Republic of Congo villa power generation and energy storage
Democratic Republic of Congo villa power generation and energy storage
-
 Energy storage power stations increase basic electricity charges
Energy storage power stations increase basic electricity charges
-
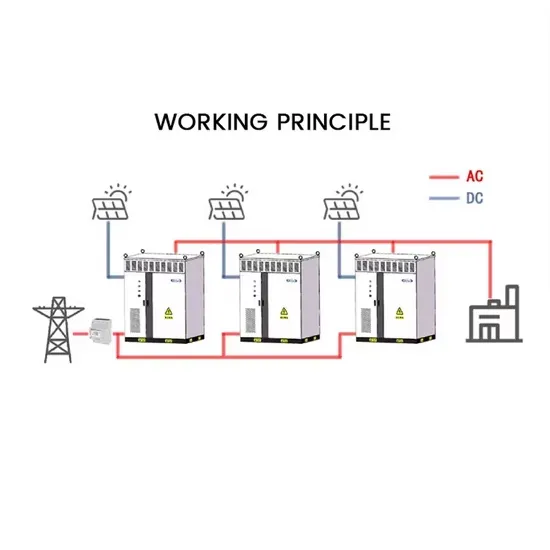 The difference between photovoltaic power generation and energy storage
The difference between photovoltaic power generation and energy storage
-
 Moldova photovoltaic power generation and energy storage difficulties in the northwest
Moldova photovoltaic power generation and energy storage difficulties in the northwest
-
 Hybrid energy storage power generation construction demand
Hybrid energy storage power generation construction demand
-
 Georgia villa power generation and energy storage system price
Georgia villa power generation and energy storage system price
-
 Zambia Photovoltaic Energy Storage Power Generation Project
Zambia Photovoltaic Energy Storage Power Generation Project
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


