How Many kWh Can a Solar Panel Generate? Average Output
A solar panel''s output refers to the amount of electricity it generates, commonly measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). To illustrate, one kWh is the energy used when a 1,000-watt appliance
Get a quote
MPPT Solar Charge Controller – Working, Sizing and
However, the MPPT Solar Charge Controller can monitor the solar panel''s full power point in real-time to achieve maximum performance. When observing
Get a quote
Solar Panel Wattage Explained: How Many Watts Do
Most residential solar panels fall into the 250W to 450W range, depending on the technology and manufacturer. But though commercial
Get a quote
Solar Panel Wattage Explained: How Many Watts Do You Need?
Most residential solar panels fall into the 250W to 450W range, depending on the technology and manufacturer. But though commercial systems may use panels exceeding
Get a quote
Solar Panel Voltage: Understanding, Calculating and
Vmp refers to the voltage at which a solar panel operates most efficiently, corresponding to its maximum power point. At this voltage, the
Get a quote
All You Need to Know about Amps, Watts, and Volts in Solar
To calculate amps or to calculate amps from watts and voltage we use the formula from ohms law given below. Amps = Watts / Voltage. Calculated amps for power small equipment the typical
Get a quote
How much is the charging power of solar panels? | NenPower
The average output of a solar panel depends largely on its type, efficiency, and installation conditions. Typically, solar panels produce between 250 and 400 watts of power.
Get a quote
Standard Solar Panel Sizes And Wattages (100W
This is the typical classification of solar panel sizes (based on the solar cell size). It''s a bit theoretical and quite useless for most calculations. The only useful
Get a quote
Understanding Solar Panel Voltage and Current Output
Decode solar panels specifications to safely connect your panels to power station or charge controller. This quick guide unlocks full solar potential.
Get a quote
Ultimate Guide to Solar Panel Voltage
The voltage is usually based on the nominal voltages of appliances connected to the solar panel, including but not limited to inverters, batteries,
Get a quote
Understanding Solar Panel Voltage and Current Output
We''ll focus on the essential solar panel specifications so you don''t damage your power station or charge controller. We''ll cover voltage, current, and how to
Get a quote
Understanding Solar Panel Voltage for Better Output
Maximum Power Voltage: The voltage at which your panel produces the most power typically falls between 18V to 36V. So, when you''re
Get a quote
Solar Panel Output Voltage: How Many Volts Do PV Panel
Nominal 12V voltage is designed based on battery classification. With solar panels, we can charge batteries, and batteries usually have 12V, 24V, or 48V input and output voltage. It is
Get a quote
Understanding Solar Panel Voltage for Better Output
Maximum Power Voltage: The voltage at which your panel produces the most power typically falls between 18V to 36V. So, when you''re thinking about solar panel voltage,
Get a quote
Calculations for a Grid-Connected Solar Energy System
Of the various types of solar photovoltaic systems, grid-connected systems --- sending power to and taking power from a local utility --- is the most common. According to the Solar Energy
Get a quote
How to Draw an Electrical Diagram for a Photovoltaic
A photovoltaic (PV) installation consists of several key components that must be correctly represented on the electrical diagram. Each of these components
Get a quote
Key Parameters of Solar Panel Data Sheets
The power output, typically measured in watts (W), indicates the maximum electricity the solar panel can produce under standard test conditions (STC). Standard Test
Get a quote
Solar Panel Output Voltage: How Many Volts Do PV
Nominal 12V voltage is designed based on battery classification. With solar panels, we can charge batteries, and batteries usually have 12V, 24V, or 48V
Get a quote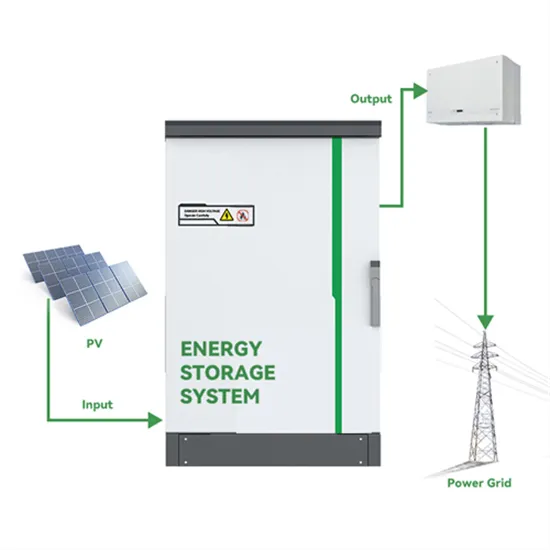
Ultimate Guide to Solar Panel Voltage
The voltage is usually based on the nominal voltages of appliances connected to the solar panel, including but not limited to inverters, batteries, charge controllers, loads, and
Get a quote
Solar-cell efficiency
Reported timeline of research solar cell energy conversion efficiencies since 1976 (National Renewable Energy Laboratory) Solar-cell efficiency is the portion of
Get a quote
Understanding Solar Panel Voltage: A Comprehensive Guide
On average, a solar panel can produce between 170 and 350 watts per hour, corresponding to a voltage range of approximately 228.67 volts to 466 volts. A single solar
Get a quote
How Many Volts Does a Solar Panel Generate? –
It is a fundamental aspect of solar energy production, determining the capacity of a panel to power devices or charge batteries. Essentially, the
Get a quote
Solar Panel Output: How Much Power Can You Expect?
Learn how much power a solar panel produces and what impacts output, from panel type to sunlight exposure, to help you plan your solar investment.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What is the typical charging power of photovoltaic panels ]
What are the different solar panel voltages?
Namely, we have to come to terms with the fact that there are several different voltages we are using for solar panels (don’t worry, all of these make sense, we’ll explain it). These solar panel voltages include: Nominal Voltage. This is your typical voltage we put on solar panels; ranging from 12V, 20V, 24V, and 32V solar panels.
How does a solar panel charge a battery?
With solar panels, we can charge batteries, and batteries usually have 12V, 24V, or 48V input and output voltage. It is the job of the charge controller to produce a 12V DC current that charges the battery. Open circuit 20.88V voltage is the voltage that comes directly from the 36-cell solar panel.
How much voltage does a solar panel produce per hour?
Check here. The voltage output of a solar panel per hour is influenced by factors such as sunlight intensity, angle of incidence, and temperature. On average, a solar panel can produce between 170 and 350 watts per hour, corresponding to a voltage range of approximately 228.67 volts to 466 volts.
Do solar panels produce a higher voltage than nominal voltage?
As we can see, solar panels produce a significantly higher voltage (VOC) than the nominal voltage. The actually solar panel output voltage also changes with the sunlight the solar panels are exposed to.
What is a solar panel nominal voltage?
Nominal voltage is an approximate solar panel voltage that can help you match equipment. The voltage is usually based on the nominal voltages of appliances connected to the solar panel, including but not limited to inverters, batteries, charge controllers, loads, and other solar panels.
What is a solar panel voltage & how does it work?
Let’s break it down in simple terms. Voltage is the push behind the electricity that flows through your solar panels. Speaking of panels, every solar panel has a certain voltage output. Keep in mind that this output might vary based on factors like sunlight, temperature, and the number of solar cells in the panel.
Guess what you want to know
-
 What is the size of the photovoltaic panels in the Jamaica power station
What is the size of the photovoltaic panels in the Jamaica power station
-
 What is the DC charging current of photovoltaic panels
What is the DC charging current of photovoltaic panels
-
 Electricity storage container solar power generation charging station photovoltaic panels
Electricity storage container solar power generation charging station photovoltaic panels
-
 What is the difference in power generation between vertical and diagonal photovoltaic panels
What is the difference in power generation between vertical and diagonal photovoltaic panels
-
 Photovoltaic power generation installed on solar panels
Photovoltaic power generation installed on solar panels
-
 Advantages and disadvantages of bidirectional power generation of photovoltaic panels
Advantages and disadvantages of bidirectional power generation of photovoltaic panels
-
 What are photovoltaic panels
What are photovoltaic panels
-
 Does photovoltaic power generation monocrystalline panels decay
Does photovoltaic power generation monocrystalline panels decay
-
 Daily power generation of photovoltaic panels at level A
Daily power generation of photovoltaic panels at level A
-
 Annual power generation of photovoltaic panels in the Middle East
Annual power generation of photovoltaic panels in the Middle East
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

