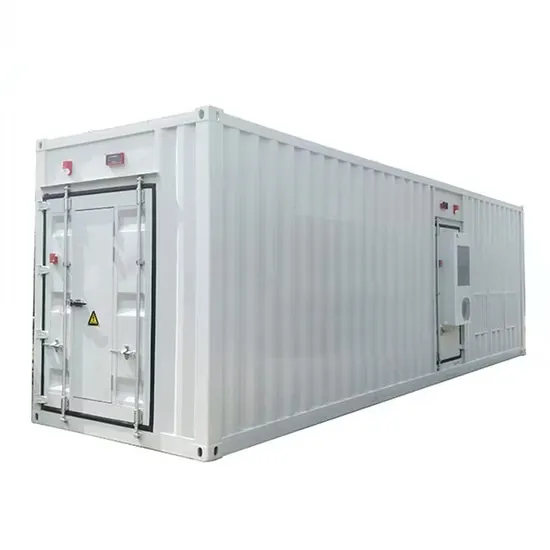
A Soft Switching Scheme for Multiphase DC/Pulsating-DC
Moreover, on the back-end pulsating-dc/ac converter, the proposed soft-switching scheme reduces the switching frequency requirements for the associated switchers, which
Get a quote
Novel DC–AC inverter based on phase-shift shoot
Based on the commonly used two-stage isolated inverter, this study proposed a novel DC–AC inverter that combines dual-active-bridge
Get a quote
Novel static inverters with high frequency pulse DC link | IEEE
A novel combined soft switching technique and a novel topological family of the static inverter with high frequency pulse dc link are proposed in this paper. The topological structure is constituted
Get a quote
Analysis, design and performance of a soft-switching
This proposed voltage clamp soft-switching step up/down DC-link circuit is generated from modified buck–boost DC/DC converter and uses new
Get a quote
Frontiers | Soft switching modulation strategy based
High Frequency-Link (HFL) Inverters have been employed to integrate renewable energy sources into utility grids and electric vehicles. The
Get a quote
High-frequency soft-switching inverter with comprehensive
In the single-tube active-clamp forward high-frequency pulsed DC link circuit, the input voltage 18~32VDC after passing through the LC input filter is converted into a high-frequency pulse
Get a quote
A Digitally Controlled Three-Phase Cycloconverter Type High
Abstract In this paper, a three phase cycloconverter type high frequency AC link inverter is discussed. The configuration consists of high frequency full-bridge inverter and a high
Get a quote
High-Frequency Link Matrix Converters and Inverters
High-frequency link matrix converters and inverters represent a transformative development in power electronics, combining direct AC–AC conversion with high-frequency pulse width...
Get a quote
High-frequency soft-switching inverter with
The high-frequency pulse DC link circuit adopts the input voltage feedforward pulse width modulation, and the DC/AC inverter bridge adopts the output
Get a quote
High-frequency soft-switching inverter with comprehensive
The high-frequency pulse DC link circuit adopts the input voltage feedforward pulse width modulation, and the DC/AC inverter bridge adopts the output voltage and filter inductor current
Get a quote
Novel DC–AC inverter based on phase-shift shoot-through
Based on the commonly used two-stage isolated inverter, this study proposed a novel DC–AC inverter that combines dual-active-bridge (DAB) converter, switched capacitor
Get a quote
Novel DC–AC inverter based on phase-shift shoot-through
In this paper, a novel bidirectional inverter based on HFPDCL is proposed. The topological structure consists of a dual-active-bridge (DAB) converter, a SC circuit and a full-bridge inverter.
Get a quote
Novel DC–AC inverter based on phase-shift shoot-through
Utilising the strategy of phase-shift shoot-through control, DAB will generate a high-frequency pulse DC link cooperated with switched capacitor. As a result, during the shoot-through period,
Get a quote
A High-Frequency Pulsating DC-Link for Electric Vehicle Drives
Abstract This paper proposes a motor drive suitable for electric vehicles (EVs) with notably reduced losses as compared to conventional drives. The proposed drive feeds the dc-link with
Get a quote
High Gain DC–AC High-Frequency Link Inverter With Improved
This article presents a high gain pure sine- wave inverter based on the full-bridge dc–ac high-frequency link cycloconverter topology for telecom or general-purpose
Get a quote
Novel Static Inverters With High Frequency Pulse DC Link
A combined three-phase inverter based on the duty cycle extended active clamp forward mode inverter with high frequency pulse dc link is proposed in this paper.
Get a quote
Analysis, design and performance of a soft-switching single
This proposed voltage clamp soft-switching step up/down DC-link circuit is generated from modi fied buck –boost DC/DC converter and uses new control strategy to obtain high frequency
Get a quote
A bidirectional, sinusoidal, high-frequency inverter design
A new method for the design of a bidirectional inverter based on the sinusoidal pulse-width modulation principle and the use of a low-cost and lightweight ferrite-core transformer is
Get a quote
High-Frequency Link: A Solution for Using Only One
This paper presents a solution to improve the already mentioned drawbacks of ACHB inverters by using a high-frequency link using only one dc
Get a quote
Parallel inverters with high frequency pulse dc link
A parallel inverter based on the duty cycle extended active clamp forward mode inverter with high frequency pulse dc link is proposed. The circuit topology, steady principle, control strategy of
Get a quote
High frequency link DC/AC converter with PWM cycloconverter
A high-frequency link DC/AC converter developed for flexible, compact, and high-efficiency uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems is discussed. The DC/AC converter consists of a
Get a quote
A New Family of High-Frequency DC Link Two
Traditional multilevel inverters (MLIs), such as neutral-point clamped (NPC) and active neutral-point clamped (ANPC) configurations, often rely on bulky capacitors, increasing system size
Get a quote
Voltage Fed Full Bridge DC-DC & DC-AC Converter High
This application report documents the implementation of the Voltage Fed Full Bridge isolated DC-DC converter followed by the Full-Bridge DC-AC converter using TMS320F28069 ( C2000TM)
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [High frequency pulse DC link inverter]
What is a high frequency inverter?
In many applications, it is important for an inverter to be lightweight and of a relatively small size. This can be achieved by using a High-Frequency Inverter that involves an isolated DC-DC stage (Voltage Fed Push-Pull/Full Bridge) and the DC-AC section, which provides the AC output.
Is a DC-AC inverter based on a dual-active-bridge converter?
Based on the commonly used two-stage isolated inverter, this study proposed a novel DC–AC inverter that combines dual-active-bridge (DAB) converter, switched capacitor and full-bridge inverter. Utilising the strategy of phase-shift shoot-through control, DAB will generate a high-frequency pulse DC link cooperated with switched capacitor.
Which power supply topologies are suitable for a high frequency inverter?
The power supply topologies suitable for the High-Frequency Inverter includes push-pull, half-bridge and the full-bridge converter as the core operation occurs in both the quadrants, thereby, increasing the power handling capability to twice of that of the converters operating in single quadrant (forward and flyback converter).
Is resonant DC link converter a new concept in static power conversion?
‘The resonant DC link converter–a new concept in static power conversion’, IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl., 1989, 25, (2), pp. 317–325 12. Chen Y.: ‘A new quasi-parallel resonant DC link for soft-switching PWM inverters’, IEEE Trans. Power Electron., 1998, 13, (3), pp. 427–435 13. 14. Li R. and Xu D.:
Can soft switching improve conversion efficiency of DC–AC inverters?
In order to improve the conversion efficiency, realising soft switching will become the essential technology in the research of DC–AC inverters. Based on the commonly used two-stage isolated inverter, this study proposed a novel DC–AC inverter that combines dual-active-bridge (DAB) converter, switched capacitor and full-bridge inverter.
How can a full-bridge inverter achieve zero-voltage switching (ZVS)?
Utilising the strategy of phase-shift shoot-through control, DAB will generate a high-frequency pulse DC link cooperated with switched capacitor. As a result, during the shoot-through period, when the DC link is in zero-voltage-stage, the full-bridge inverter could realise zero-voltage switching (ZVS) through discrete pulse modulation.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Pulse inverter is divided into high frequency and low frequency
Pulse inverter is divided into high frequency and low frequency
-
 5kva high frequency power inverter
5kva high frequency power inverter
-
 Small high frequency inverter
Small high frequency inverter
-
 Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
Household Energy Storage High Frequency Inverter
-
 1000kv high voltage pulse inverter price
1000kv high voltage pulse inverter price
-
 High frequency inverter square wave
High frequency inverter square wave
-
 High frequency inverter turns
High frequency inverter turns
-
 High frequency open type inverter and its
High frequency open type inverter and its
-
 The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
The inverter output high voltage frequency is too low
-
 Malaysia high frequency inverter price
Malaysia high frequency inverter price
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


