What are the types of Class I, II, III, 0, 01 in Electrical
Basically, a Portable appliance is given a Class rating by the manufacturer depending on how the user is protected from Electrical Shock. Electrical
Get a quote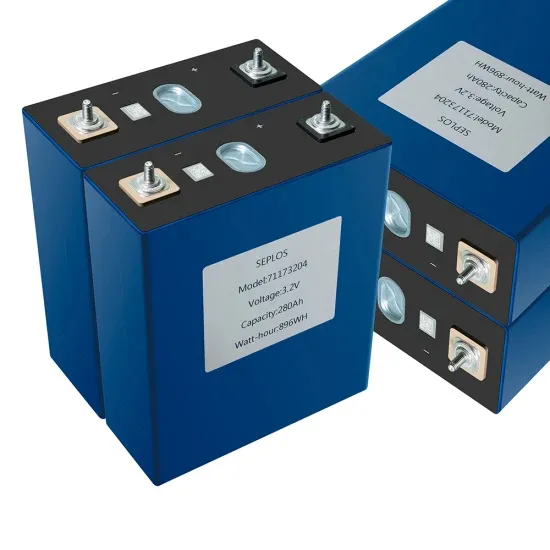
What are base station energy storage batteries used for?
Fundamentally, these batteries function as crucial operational linchpins within the telecommunications sector, providing indispensable
Get a quote
The Difference Between Class 2 and Class II Power Supplies
The power supply industry uses Class 2 and Class II terminology to refer to two very different types of power supplies. The industry has been using these terms for decades now.
Get a quote
What is IEC Power Supply Protection Classes
What is IEC Power Supply Protection Classes ? Class I and Class II Power Supplies The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
Get a quote
The Difference Between Class 2 and Class II Power Supplies:
Class 2 and Class II power supplies play vital roles in ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical devices across various industries. By understanding their unique
Get a quote
Selection and maintenance of batteries for communication base
Focused on the engineering applications of batteries in the communication stations, this paper introduces the selections, installations and maintenances of batteries for communication
Get a quote
Types of Batteries Used in Telecom Systems: A Guide
That''s where batteries come into play. They ensure that communication lines remain open, even during outages or emergencies. But not all batteries are created equal.
Get a quote
Biosafety Cabinets
Figure: Biosafety Cabinets. Image Source: Pro-Lab Diagnostics. Biosafety cabinets are classified into three classes by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Get a quote
Comprehensive Guide to Telecom Batteries
This comprehensive guide will delve into the types of telecom batteries, their applications, maintenance tips, and the latest advancements in battery technology.
Get a quote
What is the Difference Between IEC Class I and Class II Input?
The IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) is an international body that sets safety standards for the electrotechnology space. The Class I and Class II input
Get a quote
Understanding Requirements for Hazardous Locations
A hazardous (classified) location is an area where the possibility of fire or explosion exists because of flammable or combustible gases or vapors,
Get a quote
Hazardous (Classified) Locations, Classes I, II, and III
This section outlines the classification and requirements for electrical and electronic equipment in hazardous locations, specifically Classes I, II, and III, and Divisions 1 and 2.
Get a quote
NEC 111 CH 15 Flashcards | Quizlet
Class II division 1 locations require interlocked armor Type MC cable having an overall jacket of suitable polymeric material and provided with termination fittings and ________.
Get a quote
What are the types of Class I, II, III, 0, 01 in Electrical Appliances
Basically, a Portable appliance is given a Class rating by the manufacturer depending on how the user is protected from Electrical Shock. Electrical appliances classes defined in IEC 61140,
Get a quote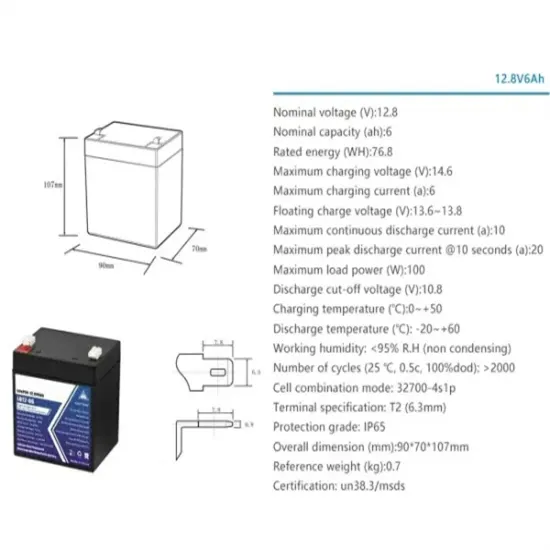
Use of Batteries in the Telecommunications Industry
The Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions is an organization that develops standards and solutions for the ICT (Information and Communications Technology) industry.
Get a quote
KH NEC Hazardous Location Class and Division
ClAss II GrouPs E, F, AND G Dust-ignition-proof equipment is also further divided into groups based on the diferent types of combustible dust that may be present.
Get a quote
Key Differences in Class I, II, and III Power Supplies
Understanding the differences between Class I, Class II, and Class III power supplies helps engineers and designers choose the right power supply for their projects. Each class is
Get a quote
Selection and maintenance of batteries for communication base stations
Focused on the engineering applications of batteries in the communication stations, this paper introduces the selections, installations and maintenances of batteries for communication
Get a quote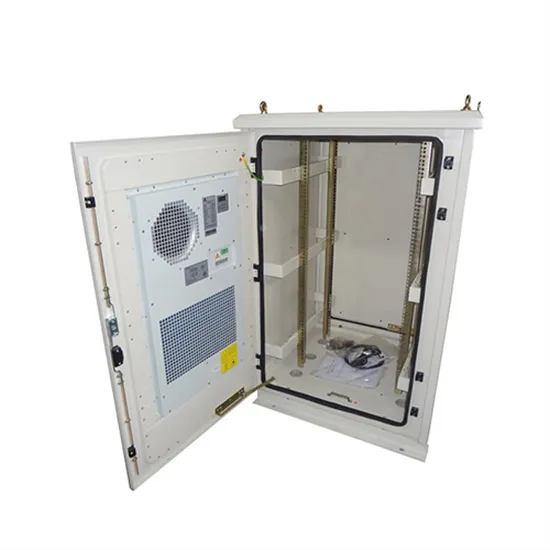
What are Class I, Class II and Class III luminaires?
LED luminaires are classified into four categories according to their insulation properties, i.e. Class 0, Class I, Class II and Class III luminaires. What is the
Get a quote
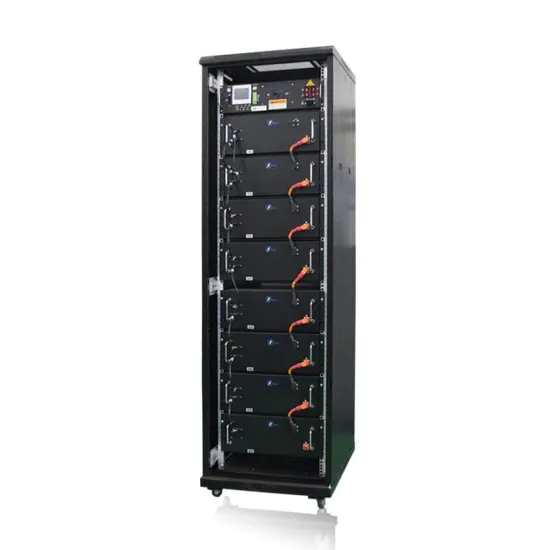
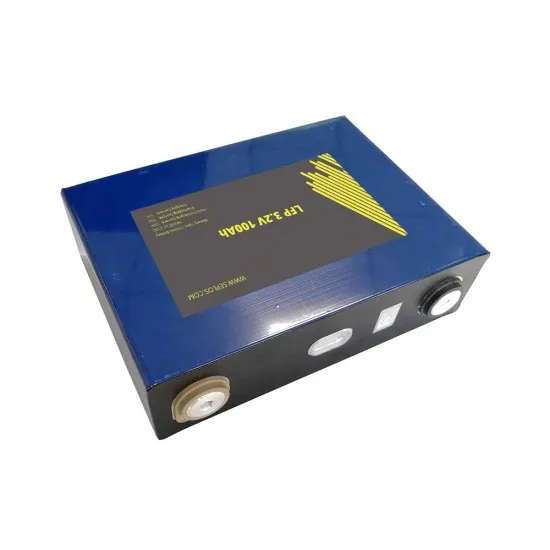
Battery technology for communication base stations
In order to ensure the reliability of communication, 5G base stations are usually equipped with lithium iron phosphate cascade batteries with high energy density and high charge and
Get a quote
Explanation of Hazardous Locations – Class II Div. 1, Groups
They are Class I (gases & vapors), Class II (flammable dusts) & Class III (fibers), the focus of today''s Blog is on Class II locations. Class II locations are those that are
Get a quote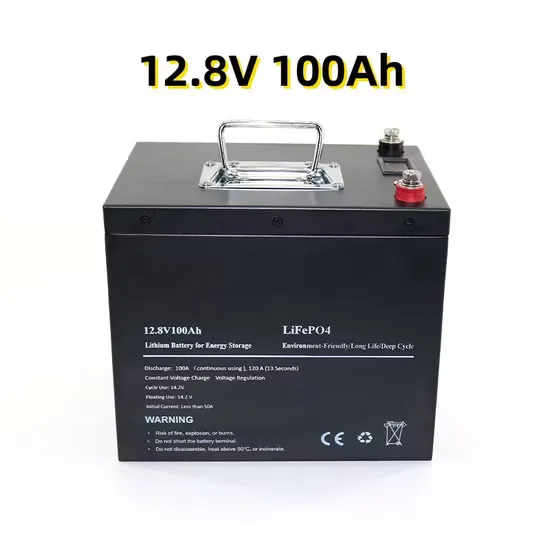
Class I and Class II Equipment Explained
Understanding the difference between Class I and Class II equipment is not just a matter of theory. This knowledge is crucial for anyone involved in PAT (Portable Appliance Testing) and
Get a quote
MHC Class I vs II: Structure, Function, and Immune Roles
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is essential in the immune system by presenting antigens to T cells, which is vital for immune recognition and response. MHC
Get a quote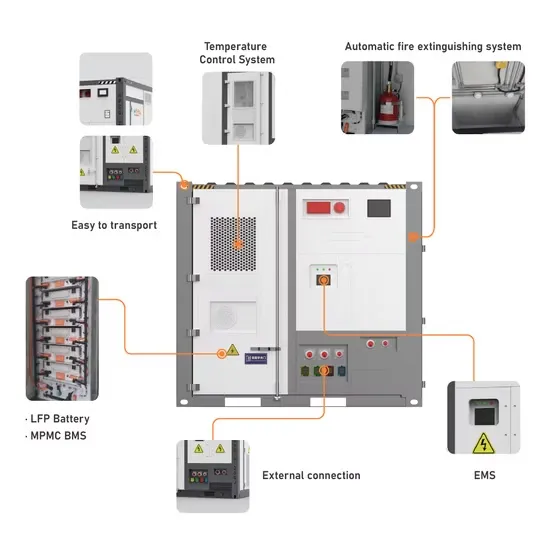
1926.407
Fixed general-purpose equipment in Class I locations, other than lighting fixtures, which is acceptable for use in Class I, Division 2 locations need not be marked with the class, group,
Get a quote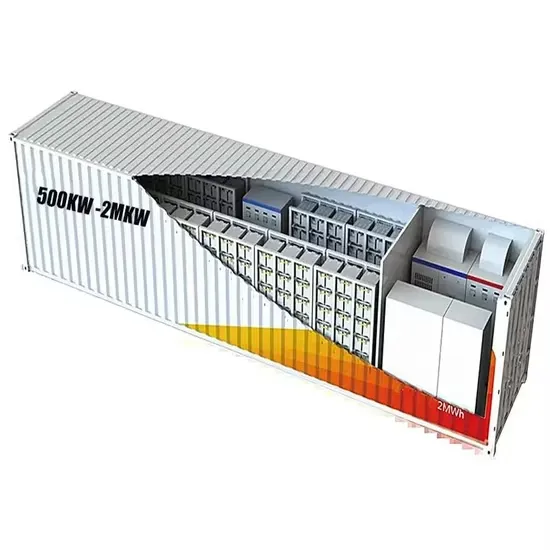
What are base station energy storage batteries used for?
Fundamentally, these batteries function as crucial operational linchpins within the telecommunications sector, providing indispensable backup capabilities, energy stabilization
Get a quote
Class I and Class II Equipment Explained
Understanding the difference between Class I and Class II equipment is not just a matter of theory. This knowledge is crucial for anyone involved in PAT
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Batteries for communication base stations are divided into Class I and Class II]
Are lithium-ion batteries a good choice for a telecom system?
Lithium-ion batteries have rapidly gained popularity in telecom systems. Their efficiency is unmatched, providing higher energy density compared to traditional options. This means they can store more power in a smaller footprint.
What are the different types of Telecom batteries?
These batteries are integral to data centers, cell towers, and other communication infrastructures. There are several types of telecom batteries, each with unique characteristics suited for different applications: Lead-Acid Batteries: Commonly used due to their reliability and cost-effectiveness. They come in two main types:
What is a telecom battery?
Telecom batteries play a crucial role in powering equipment, supporting backup systems, and facilitating smooth operations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the types of telecom batteries, their applications, maintenance tips, and the latest advancements in battery technology. 1. Understanding Telecom Batteries 2.
What type of battery does a telecom system need?
Beyond the commonly discussed battery types, telecom systems occasionally leverage other varieties to meet specific needs. One such option is the flow battery. These batteries excel in energy storage, making them ideal for larger installations that require consistent power over extended periods.
What are the classification and requirements for electrical and electronic equipment?
This section outlines the classification and requirements for electrical and electronic equipment in hazardous locations, specifically Classes I, II, and III, and Divisions 1 and 2. It details the scope of coverage, including areas with potential fire or explosion hazards due to flammable gases, vapors, and combustible dusts.
Are lithium-ion batteries the future of telecommunication?
With advancements continually being made in battery technology, lithium-ion remains at the forefront of innovative solutions for telecommunication needs. Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries have carved out a niche in telecom systems due to their durability and reliability.
Guess what you want to know
-
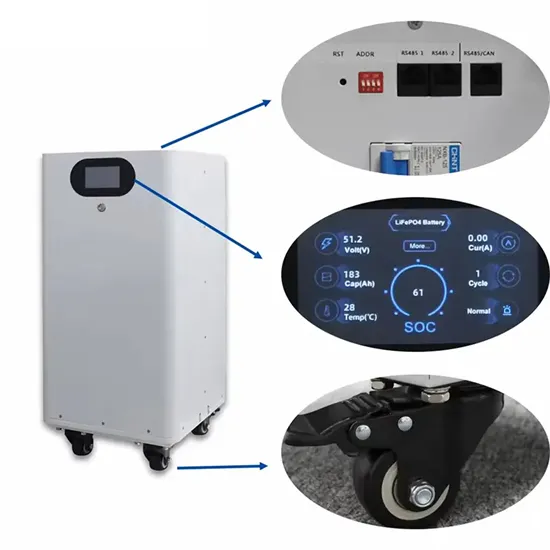 Are energy storage batteries for communication base stations useful
Are energy storage batteries for communication base stations useful
-
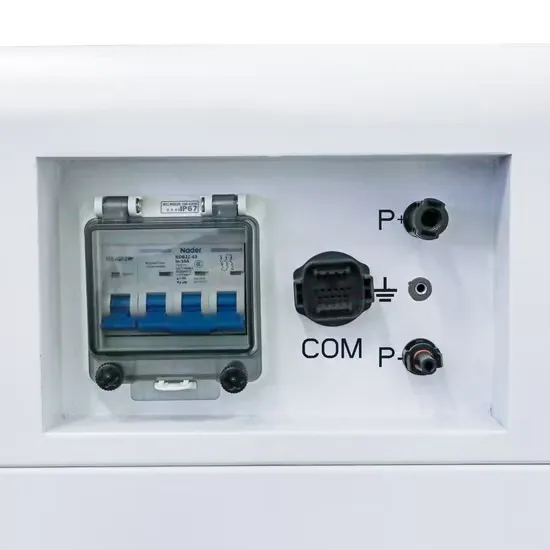 Why are the batteries in communication base stations different
Why are the batteries in communication base stations different
-
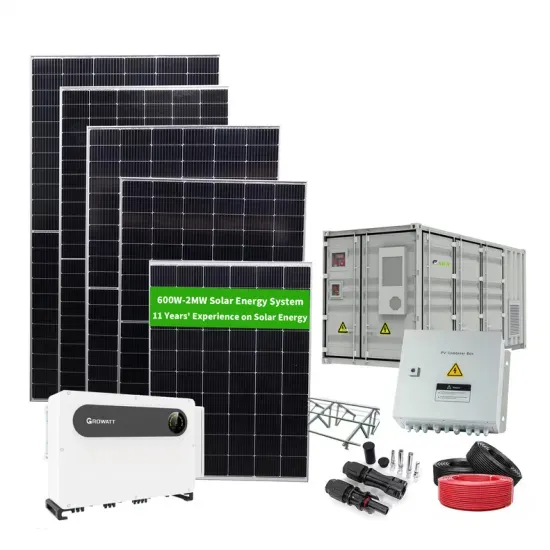 Which one has more liquid flow batteries for Bolivian communication base stations
Which one has more liquid flow batteries for Bolivian communication base stations
-
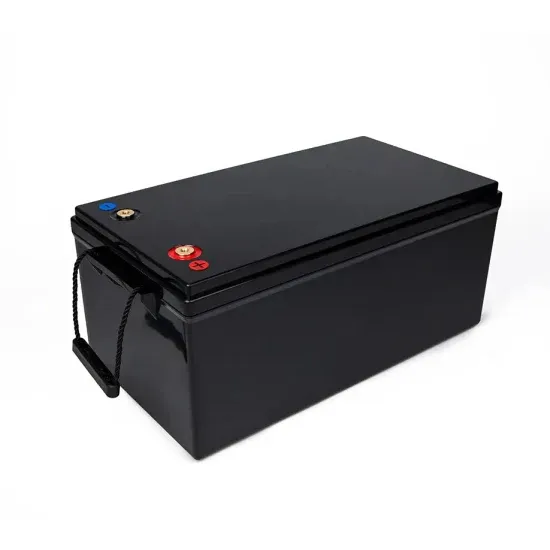 Price of lead-acid batteries for communication base stations in Egypt
Price of lead-acid batteries for communication base stations in Egypt
-
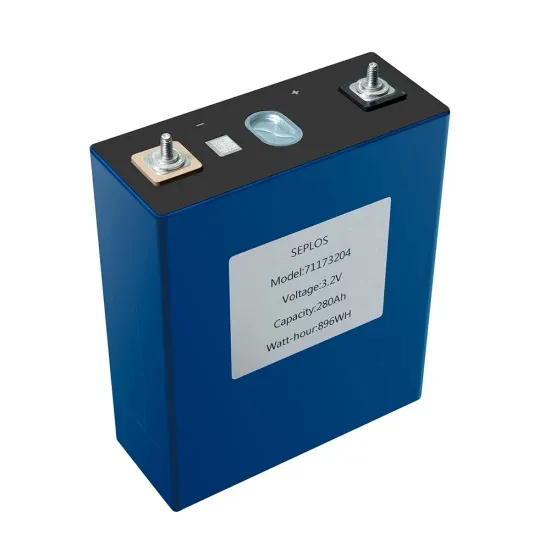 Tender for batteries for communication base stations
Tender for batteries for communication base stations
-
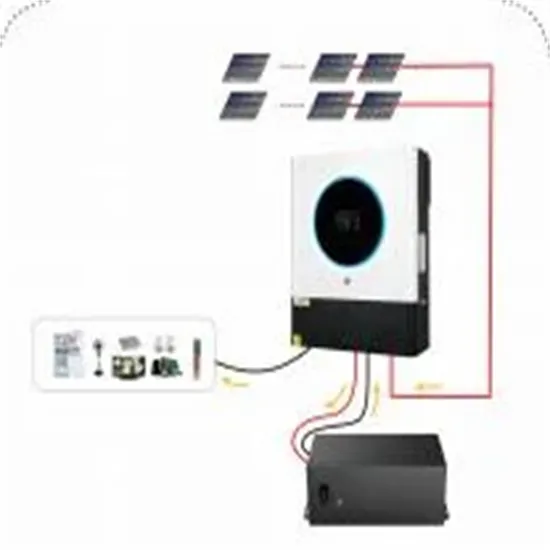 Why do communication base stations use 2V batteries
Why do communication base stations use 2V batteries
-
 Do communication network base stations have batteries
Do communication network base stations have batteries
-
 Commercial use of energy storage batteries for communication base stations
Commercial use of energy storage batteries for communication base stations
-
 Things to note when using batteries in communication base stations
Things to note when using batteries in communication base stations
-
 Where are the lead-acid batteries for communication base stations in Uzbekistan
Where are the lead-acid batteries for communication base stations in Uzbekistan
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


