The 3 Most Common Faults on Inverters and how to Fix Them
This can be caused by a missing supply voltage phase from a blown fuse or faulty isolator or contactor or internal rectifier bridge fault or simply low mains voltage.
Get a quote
Inverter Fault Light Solved
In many instances, you should be able to fix this. A fault light on the inverter usually means the voltage is either too high or low. The light also appears when the inverter is overloaded or
Get a quote
untitled []
3.1 Energizing a main circuit voltage when the circuit between G and E is open If a voltage is applied to the main circuit with the circuit between the gate and emitter open, the IGBT would
Get a quote
Inveter AC output voltage too high?
When I first got it, the output voltage was 129-130, so I ask the manufacture and they can I can adjust a POD inside and that has reduced it down to 125v (lowest it can go).
Get a quote
Growatt Inverter Problems, Warnings And Error
Inverters need to maintain a stable connection to the electrical grid to function properly: Grid voltage fluctuations: If the grid voltage falls outside the inverter''s
Get a quote
ALL INVERTER PROBLEMS AND SOLUTIONS
Bad input Voltage/frequency: If the input Voltage or frequency is too high or too low for the preset value of the Inverter or there is power fluctuation,
Get a quote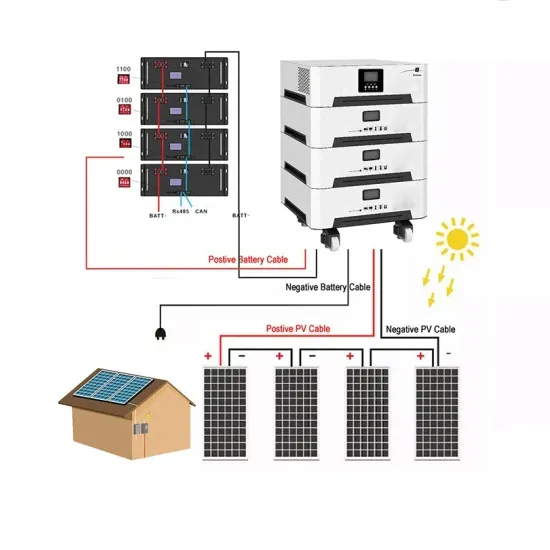
32 Common Faults in Inverters and Their Solutions
Discover the top 32 reasons for inverter failure and how to fix them with our comprehensive troubleshooting guide. Ensure your inverter is always working efficiently!
Get a quote
repair for Eaton 9PX UPS error "DC bus
As for the "DC bus - too high", this is referring to the voltage of the link between rectifier and inverter. Usually caused by either a defective rectifier not switching the IGBTs to regulate the
Get a quote
Inverter Fault Light Solved
In many instances, you should be able to fix this. A fault light on the inverter usually means the voltage is either too high or low. The light also appears
Get a quote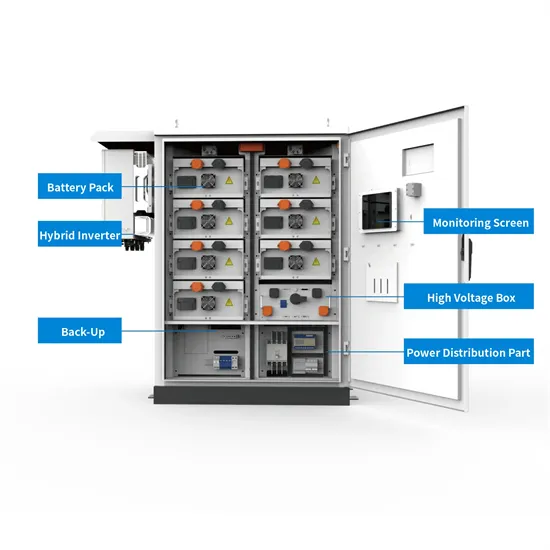
Inverter vs rectifier
Inverter: An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). It is commonly used in applications where AC power
Get a quote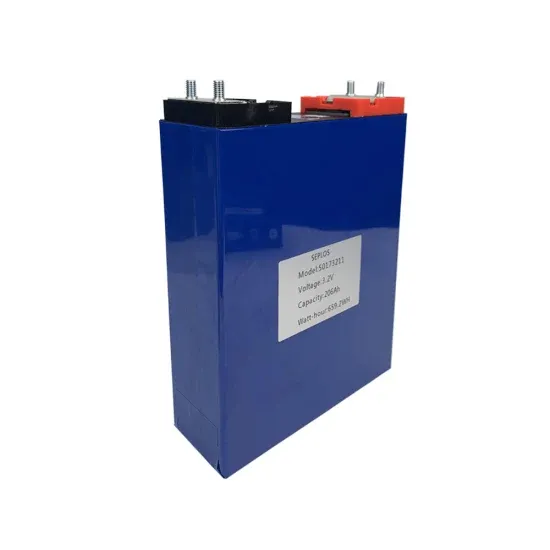
9 Common UPS Faults and Troubleshooting Tips for
Discover 9 common UPS faults, including battery and inverter issues. Learn expert troubleshooting steps to resolve power problems and keep your UPS
Get a quote
What is the cause of the overvoltage of the inverter? How to
From this article, you will get the answer for that what is the cause of the overvoltage of the inverter and how to prevent it.
Get a quote
32 Common Faults in Inverters and Their Solutions
Discover the top 32 reasons for inverter failure and how to fix them with our comprehensive troubleshooting guide. Ensure your inverter is always
Get a quote
repair for Eaton 9PX UPS error "DC bus
As for the "DC bus - too high", this is referring to the voltage of the link between rectifier and inverter. Usually caused by either a defective rectifier not switching the IGBTs to
Get a quote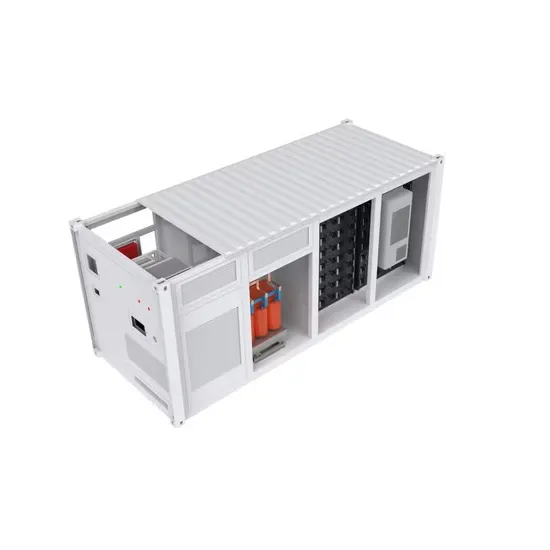
Over-voltage and Mitsubishi Heat Pumps | Information by
At any rate, the incoming power from the utility company is around 253.2V phase A-B and around 126V phase-ground. The manufacturer, and the HVAC company I worked
Get a quote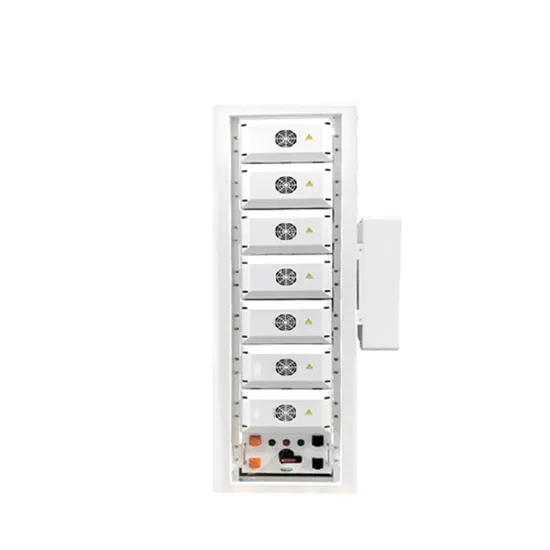
A Friendly Guide to Understanding Bridge Rectifier Failure
Overvoltage: Feeding the rectifier more voltage than it''s rated for can zap the diodes. Overcurrent: Too much current (say, from a load shorting out) can overheat and
Get a quote
4-kW 3-phase rectifier with high efficiency and wide
There are 6 modes in the full working state of a traditional 3-phase rectifier, and each mode is necessary for power factor correcting and for realizing the corresponding DC-link
Get a quote
On sunny days, Inverter switches off when DC voltage gets too
Too many volts suggests to me that some component might overheat and ignite, or its electronics burn out, or that the inverter fails completely, as the inverter would not switch
Get a quote
1. System Description
Rectifier high DC voltage Over temperature / Fuse fail Battery low stop Inverter abnormal "SELECT" key and "ENTER" key--Used to select and set LCD display function.
Get a quote
On sunny days, Inverter switches off when DC voltage gets too high
Too many volts suggests to me that some component might overheat and ignite, or its electronics burn out, or that the inverter fails completely, as the inverter would not switch
Get a quote
Inverter too high output voltage than normal, problem?
It has a detection voltage range of 180V to 260V and turns on when the electricity voltage is higher or lower when it is set to UPS Mode. Its detection mode is higher (they do not
Get a quote
High Voltage Synchronous Rectifier Design Considerations
The first hurdle to designing a high voltage SR system is the high voltage itself. Traditional methods of synchronous rectification (SR) attempt to directly sense voltage or current, which is
Get a quote
Rectifier vs. Inverter — What''s the Difference?
A rectifier takes an AC input and transforms it into DC output by allowing current to flow in only one direction. An inverter, on the other hand,
Get a quote
High Voltage Thyristors (SCRs) and Their Applications
WeEn Semiconductors, as an industry leader in thyristors, has successfully introduced high voltage SCRs covering the 1200V - 1600V range.
Get a quote
Troubleshooting Inverter Problems: A Step-by-Step Guide
Use a multimeter to measure the voltage. If it''s below the required level, recharge the battery or replace it if it''s defective. Inspect the Connections: Loose or corroded
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Inverter rectifier voltage is too high]
What causes a DC inverter to overvoltage?
This can arise from high inertia loads decelerating too quickly, the motor turns into a generator and increases the inverter’s DC voltage. There are other causes of DC overvoltage, however. POSSIBLE FIXES: Turn the overvoltage controller is on. Check supply voltage for constant or transient high voltage. Increase deceleration time.
What if the frequency inverter voltage is too high?
When the system voltage is too high, the frequency inverter may not be able to stop at a numerical point in order to avoid triggering the DC bus over-voltage protection for its own protection. In such cases, it is recommended to connect the transformer taps to 105%.
What are the most common faults on inverters?
In this article we look at the 3 most common faults on inverters and how to fix them: 1. Overvoltage and Undervoltage Overvoltage This is caused by a high intermediate circuit DC voltage. This can arise from high inertia loads decelerating too quickly, the motor turns into a generator and increases the inverter’s DC voltage.
How do I know if my inverter is overloaded?
Here’s what to do: Check the Battery Voltage: Continuous beeping often indicates low battery voltage. Use a multimeter to check the voltage. If it’s low, charge the battery or replace it if necessary. Overload Warning: The inverter beeps if it is overloaded. Reduce the number of devices connected to the inverter and see if the beeping stops.
Can a power supply cause an inverter to overvoltage?
Most of the inverters now have an input voltage of up to 460V, so the overvoltage caused by the power supply is extremely rare. The protection measures for the overvoltage of the inverter vary according to the cause of the overvoltage of the inverter.
How do I fix a faulty inverter?
Here’s how to address common error codes: Low Voltage Error: Indicates that the battery voltage is too low. Charge the battery and reset the inverter. Overload Error: Reduce the connected load to within the inverter’s rated capacity. Over Temperature Error: Move the inverter to a cooler location and ensure adequate ventilation.
Guess what you want to know
-
 High voltage 100 000V inverter
High voltage 100 000V inverter
-
 Low voltage inverter high voltage grid connection
Low voltage inverter high voltage grid connection
-
 The impact of high voltage on inverter
The impact of high voltage on inverter
-
 600kv high voltage inverter
600kv high voltage inverter
-
 High voltage battery connected to inverter
High voltage battery connected to inverter
-
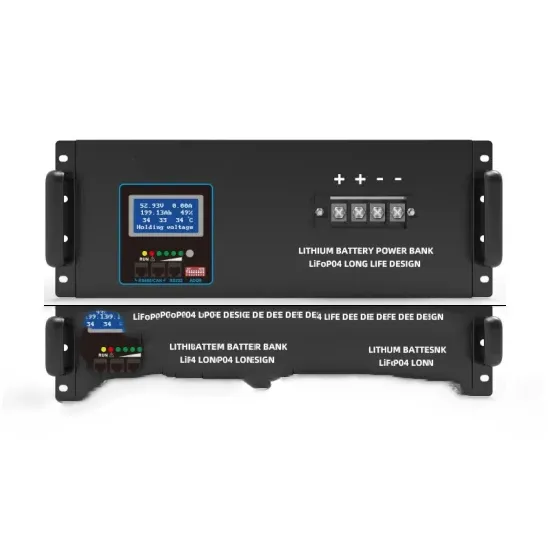 12v high voltage pulse inverter
12v high voltage pulse inverter
-
 Belize high voltage inverter manufacturer
Belize high voltage inverter manufacturer
-
 Inverter high voltage front stage
Inverter high voltage front stage
-
 1224v inverter converted to high voltage AC
1224v inverter converted to high voltage AC
-
 Turkmenistan high voltage inverter manufacturer
Turkmenistan high voltage inverter manufacturer
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


