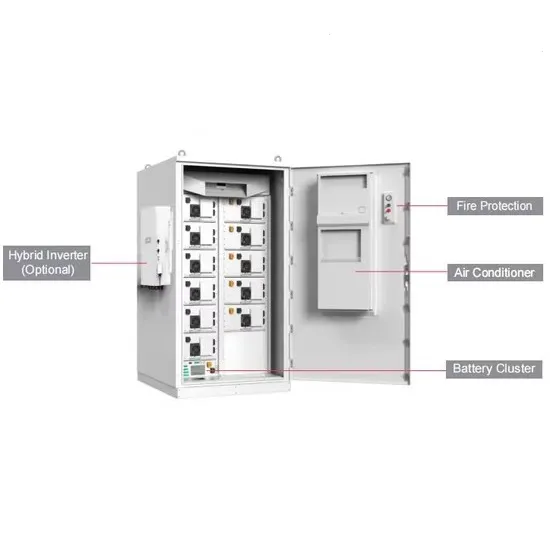
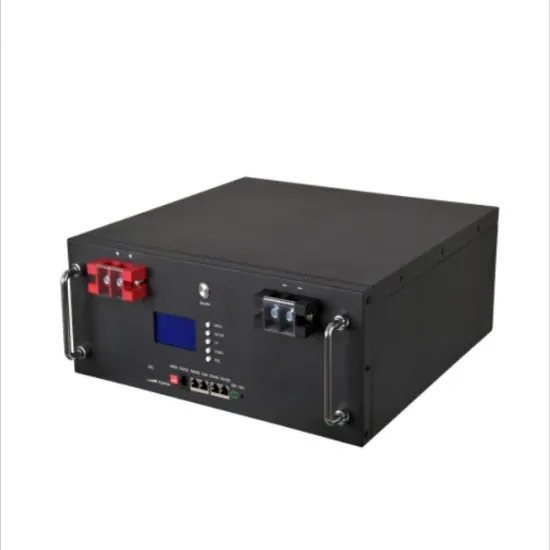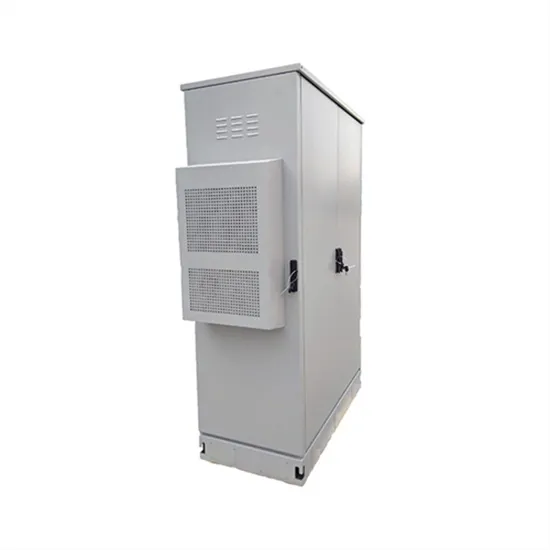
A High Performance High Frequency Inverter Architecture with
In this work, a high frequency inverter system that can work in a wide range of inductive or capacitive load is proposed, which includes Class D inverter, novel
Get a quote
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which is Right for
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation and characteristics, and the
Get a quote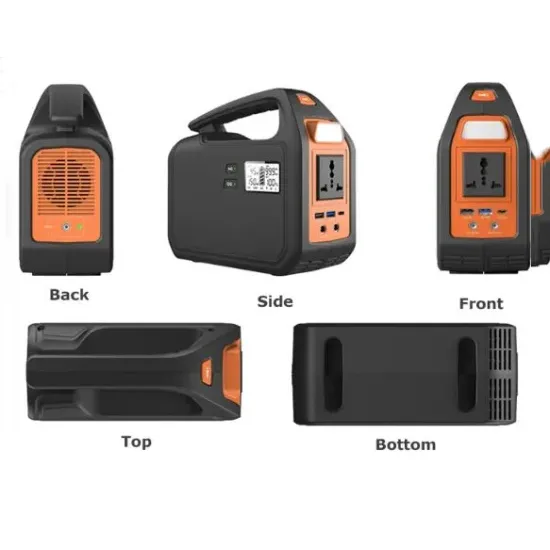
Low Frequency/High Frequency Inverters and Inductive Loads
HF inverters have no meaningful surge in most cases. They don''t have the large transformers present in LF units, and can''t do it. Their surge ratings are often for an AC cycle
Get a quote
Understanding inverter frequency – effects and adjustments
The choice between a low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) inverter depends on various factors, including the application requirements, load characteristics, and budget
Get a quote
Selecting the Proper Inverter / Frequency Converter for your
Therefore, for high-frequency topology inverters (GL and CGL Series), Nova Electric suggests maintaining a ratio of 3:1 between the power output rating of the inverter in VA, and the rating
Get a quote
Low Frequency VS High Frequency Inverter
Discover the differences between low-frequency and high-frequency off-grid inverters, their efficiency, weight, and ideal applications for your solar system.
Get a quote
How many batteries do I need for a 3.5 kVA inverter
What load can a 3.5 kVA inverter carry? The inverter size you have determines the appliances it can carry. The 3.5kva -5kva can carry electric irons but would deplete back power if it is not
Get a quote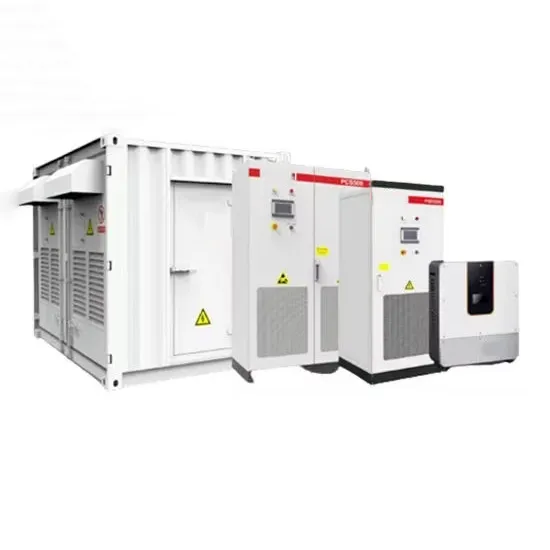
A High Frequency Variable Load Inverter Architecture
This thesis presents the design, physical prototype, controller, and experimental results of a high-frequency variable load inverter architecture (referred to as HFVLI) that can directly drive
Get a quote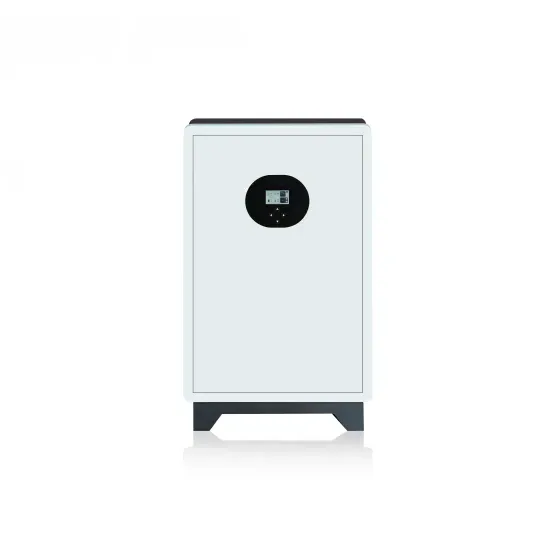
Learn About High vs. Low Frequency Inverters: Which
High-frequency inverters and low-frequency inverters are two common types of inverters. They have significant differences in their operation
Get a quote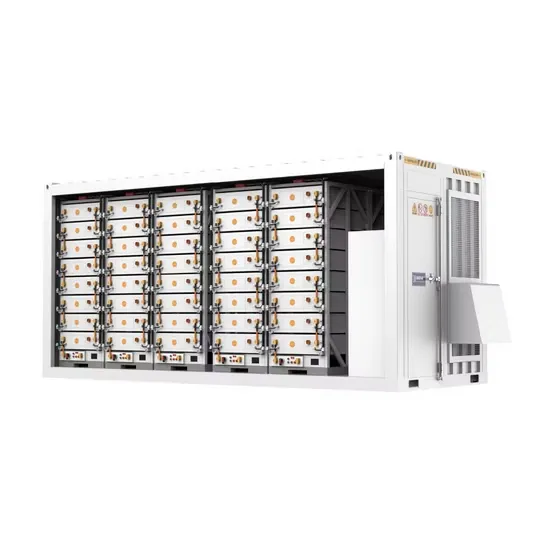
High-Frequency Variable Load Inverter Architecture
The invented high-frequency inverter system enables HF power delivery directly into highly variable impedance loads with a relatively high efficiency. A pair of inverters are coupled and
Get a quote
TPEL2691668
In terms of mechanical construction, the number of inputs and outputs can dictate the design complexity. Also, on the elec-trical point of view, the average and rms current amplitude as
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
The debate between line-frequency and high-frequency inverters is not about which is "better," but which is "right" for a specific task. The line-frequency inverter is a powerful,
Get a quote
How Long Will a 1000W Inverter Run on a 100Ah
A 1000W inverter connected to a 100Ah battery can typically run for about 0.96 hours (or approximately 58 minutes) under full load, assuming an
Get a quote
Selective Dual Duty Cycle Controlled High Frequency Inverter
Dual duty cycle control scheme is used to provide a wide range of high frequency AC output power regulation that is important in many high frequency inverter applications. It found that a
Get a quote
A High Frequency Inverter for Variable Load Operation
Inverters operating at high frequency (HF, 3-30MHz) are important to numerous industrial and commercial applications such as induction heating, plasma generation, and wireless power
Get a quote
Comparing Carrier-Based PWM Techniques in High
This article explores the potential of carrier-based pulse width modulation techniques such as sawtooth, triangular, and sinusoidal, and
Get a quote
Power Frequency Inverter vs High-Frequency Inverter
On the other hand, high-frequency inverters can provide the same power at high frequency with a much smaller and lighter transformer. As a result, the high-frequency inverter
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High
The debate between line-frequency and high-frequency inverters is not about which is "better," but which is "right" for a specific task. The line-frequency inverter is a powerful,
Get a quote
A High Performance High Frequency Inverter Architecture with Wide Load
In this work, a high frequency inverter system that can work in a wide range of inductive or capacitive load is proposed, which includes Class D inverter, novel
Get a quote
Harmonic Overload: Impacts Of High-Frequency
During the CIGRE Grid of the Future symposium and workshop, harmonics were recognized as a critical focus in modern electrical systems, where high
Get a quote
Inversion Methods Explained: High Frequency vs Low Frequency
They are typically less expensive, have smaller footprints, and have a lower tolerance for industrial loads. HF inverters have over twice the number of components and use multiple,
Get a quote
A new architecture for high-frequency variable-load inverters
Mentioning: 5 - Abstract-Efficient generation and delivery of high-frequency (HF, 3-30 MHz) power into variable load impedances is difficult, resulting in HF inverter (or power amplifier) systems
Get a quote
IBC12-3KW Pure Sine Wave Inverter (High Frequency) User
1.1 Product overview IBC series pure sine wave high frequency inverter, the product integrates pure sine wave inverter, mains bypass load. Adopts full digital intelligent control Technology,
Get a quote
Surge vs. Efficiency: Choosing Between Low and High-Frequency Inverters
Deconstructing High-Frequency Inverters High-frequency inverters represent a more modern approach, engineered to overcome the size and weight limitations of their line
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [How much load can a high-frequency inverter carry ]
What is a high frequency variable load inverter architecture?
This thesis presents a high frequency variable load inverter architecture along with a physical prototype and e ciency optimizing controller. The inverter architecture consists of two constituent inverters, one connected directly through the load and the other connected through an immittance converter, which acts as a lossless power combiner.
What is a high frequency inverter?
Applications: These inverters are more suitable for off-grid systems where heavy loads and extreme conditions are expected, such as in industrial applications or in remote locations with harsh environments. Weight: High-frequency inverters are lighter than low-frequency inverters, using smaller, lighter transformers.
Can a high frequency inverter be used for a motor / compressor load?
Motor / Compressor Load: Nova Electric does not recommend the use of high frequency inverters (GL or CGL) for motor or compressor loads in general, though they can be modified for such use in certain applications where weight savings are critical (consult factory for details).
Does victron use a high frequency inverter?
Victron combines both inverters, which they call Hybrid HF or Combined high frequency and line frequency technologies. What frequency inverter does growatt use? Growatt uses a high-frequency inverter. Which one is best? Low or high frequency? The best inverter is the low-frequency inverter.
What determines a high or low frequency inverter?
Size and tolerances of the transistors used in the inversion process, and the speed at which they operate determines the classification of high or low frequency. The large majority of inverters available in the retail market are high frequency.
Can a high-frequency variable load inverter directly drive widely variable loads?
Typically a tunable matching network is used to transform the varying load into a ciency and impairing transient response. This thesis presents the design, physical prototype, controller, and experimental results of a high-frequency variable load inverter architecture (referred to as HFVLI) that can directly drive widely variable loads.
Guess what you want to know
-
 How big is a high-frequency inverter
How big is a high-frequency inverter
-
 How many kilowatts does a 60v inverter carry
How many kilowatts does a 60v inverter carry
-
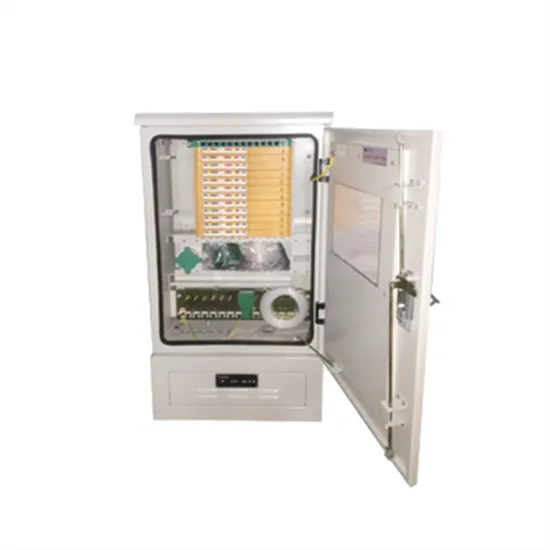
 How to connect the mobile energy storage site inverter to the grid
How to connect the mobile energy storage site inverter to the grid
-
 How big can a 48V AC inverter be
How big can a 48V AC inverter be
-
 How big of an inverter should I use for a 24 volt
How big of an inverter should I use for a 24 volt
-
 How many volts can the inverter convert to 220
How many volts can the inverter convert to 220
-
 How big an inverter do I need to convert 7200v to 220v
How big an inverter do I need to convert 7200v to 220v
-
 How to connect DC inverter to the grid
How to connect DC inverter to the grid
-
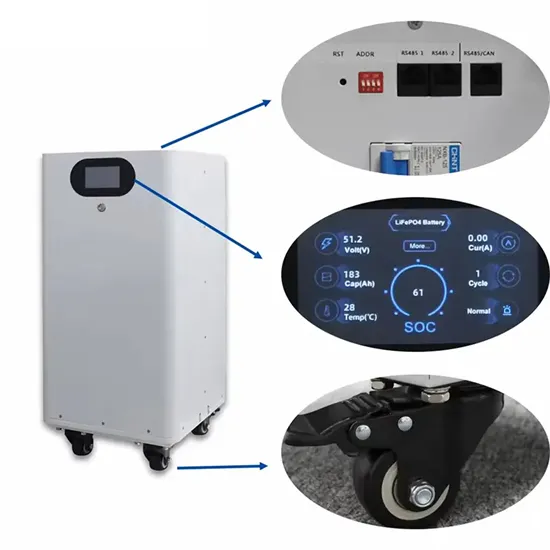
 How to measure high-frequency batteries for wind power in communication base stations
How to measure high-frequency batteries for wind power in communication base stations
-
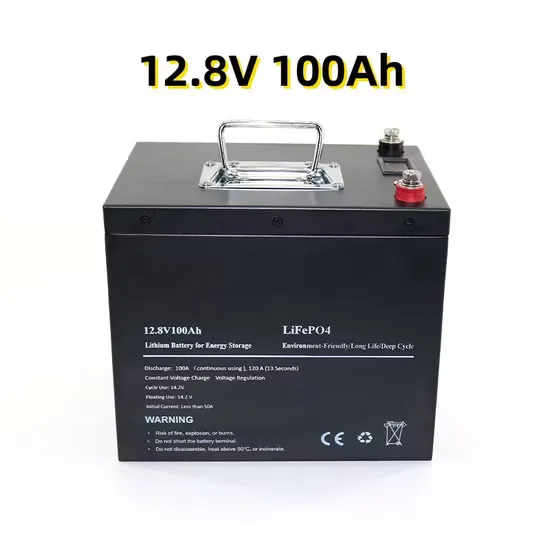
 How big an inverter can I use with a 12v 50AH lithium battery
How big an inverter can I use with a 12v 50AH lithium battery
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


