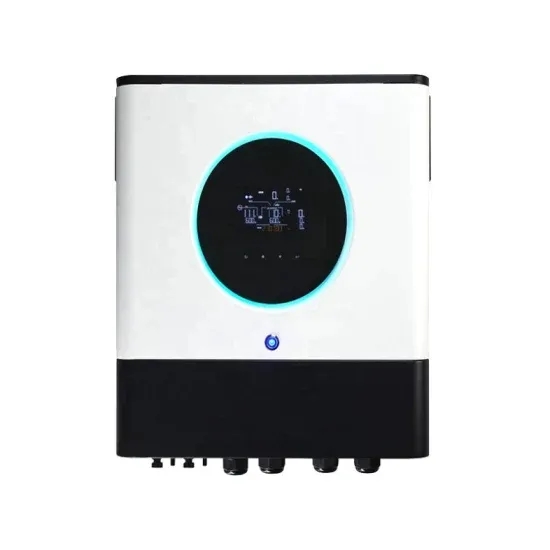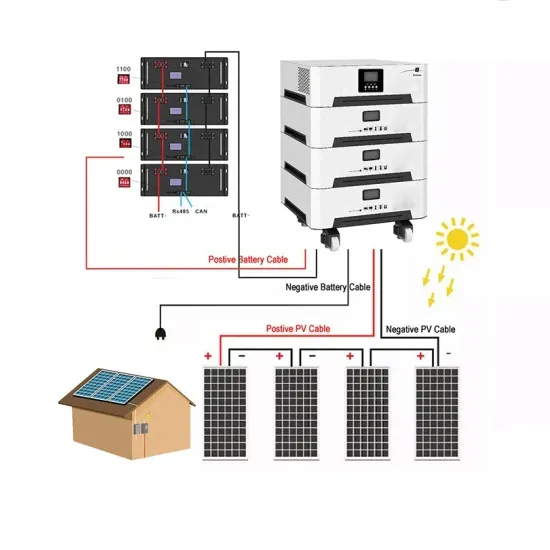
Inverter Question: "What is the difference between a
by Justin Gray Pure Sine or "Normal Sine, Sine, Pure Sine, PSW, True Sine" is the smooth sine wave as seen in the picture above. In the
Get a quote
What is the Difference Between a Power Inverter and
Explore the differences between pure sine wave and standard power inverters to choose the right solution for your commercial or industrial
Get a quote
What are the Differences: Pure Sine Wave Inverter vs Modified
Pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are two common types of inverters. They have some differences in working principle, performance characteristics,
Get a quote
Square Wave vs Sine Wave Inverter
Confused between a square wave and sine wave inverter? Learn the key differences in performance, efficiency, and cost to choose the right inverter for
Get a quote
True sine wave inverter vs Pure sine wave any difference?
There are: Square wave inverters (rare, old) Mod-sine inverters (very close to square wave but slightly better) Stepwise sine wave (old Trace SW series) True sine wave
Get a quote
What is the Difference Between True Sine Wave and Pure Sine
True and pure sine wave inverters are essentially the same thing. Regardless of the term used to describe the inverter, true or pure pertains to the smooth and curved peaks
Get a quote
What is the Difference Between a Power Inverter and a Pure Sine Wave
Explore the differences between pure sine wave and standard power inverters to choose the right solution for your commercial or industrial applications.
Get a quote
Sine Wave vs Square Wave Inverters: What''s the Key Difference?
Learn the difference between sine wave and square wave inverters, their pros and cons, and how to choose the best inverter for your devices and power system.
Get a quote
Benefits of Pure Sine Wave vs. Modified Sine Wave Inverters
When shopping for inverters, you''ll quickly find there are two main types: modified sine wave inverters and pure sine wave inverters. Let''s break down the differences between those
Get a quote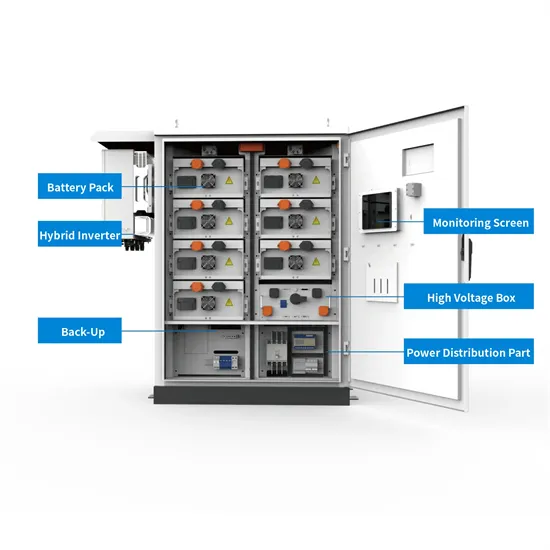
Choosing the Best Pure Sine Wave Inverter: A Comprehensive
Explanation of the Difference between Pure Sine Wave and Modified Sine Wave Inverters: When it comes to choosing an inverter for your off-grid solar system, understanding
Get a quote
Sine Wave vs Normal Inverter: What''s the Difference
Compare sine wave and normal inverters on performance, efficiency, and compatibility with various appliances to choose the best inverter for your needs.
Get a quote
Pure Sine Wave vs Modified Sine Wave Inverters: Which One Do
Learn the difference between pure sine wave vs modified sine wave inverters, and why pure sine is the way to go for a camper van.
Get a quote
What is the Difference Between True Sine Wave and Pure Sine Wave?
True and pure sine wave inverters are essentially the same thing. Regardless of the term used to describe the inverter, true or pure pertains to the smooth and curved peaks
Get a quote
Pure Sine Wave Inverters: Necessary or Overkill?
Most electronic devices can work without a pure sine wave inverter, but there are some important points to consider before buying one.
Get a quote
Pure vs. Modified Sine Wave Inverter: Key Differences Explained
Considering pure sine wave vs modified sine wave inverters? Learn the key differences in waveform quality, efficiency and more to choose the right inverter.
Get a quote
Difference between the Sine Wave and Square Wave of Inverter
Sine Wave Inverters: What Is It? A pure sinewave inverter, or sine wave inverter, is a piece of electrical equipment that matches the AC power output of a grid power source
Get a quote
What are the Differences: Pure Sine Wave Inverter vs Modified Sine Wave
Pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are two common types of inverters. They have some differences in working principle, performance characteristics,
Get a quote
Modified vs. Pure Sine Wave Inverter: What''s the Difference?
Pure sine inverters are more sophisticated devices that can exactly replicate an AC sine wave from a DC power source. Because of their added complexity, they''ve historically
Get a quote
An overall introduction of inverter waveform and the
This article will give you a detailed introduction and comparison of inverter waveform, including the principles of generating different waveforms,
Get a quote
Pure vs. Modified Sine Wave Inverters: Which Is Best?
Pure sine wave inverters produce a smooth, consistent wave of electricity, closely mimicking the power you get from your local grid. On the other hand, modified sine wave
Get a quote
Pure Sine Wave Inverter vs Power Inverter: Choosing the Right
Choosing the right inverter, between a pure sine wave and a regular power inverter, can make all the difference. This guide simplifies the jargon and helps you find a reliable
Get a quote
What Is a Pure Sine Wave Inverter and How Does It Work?
A pure sine wave inverter is a specialty device that transforms direct current (DC) electricity from sources like batteries or solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, generating a
Get a quote
Difference Between Hybrid Inverters and Pure Sine
Of course, the pure sine technology can be used in a hybrid inverter or standard (non-hybrid) inverter. What''s the Difference Between
Get a quote
Difference Between Digital Inverter & Sine Wave Inverter
Digital inverters and sine wave inverters are unrelated electrical devices. Digital inverters flip the one and zeros in binary signals. Sine wave inverters use direct current (DC)
Get a quote
Sine Wave vs Normal Inverter: What''s the Difference
Waveform quality: Sine wave inverters provide a smooth and consistent power output, while normal inverters produce a rough square wave, which can be harmful to sensitive
Get a quote
difference between cheap and expensive pure sine wave inverters?
I highly doubt you can get a 4kW inverter for 40$, let alone that being pure sine wave. That''d like be a unit capable of maybe 200-400W at best square wave.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [The difference between inverter and sine wave]
What is the difference between pure sine wave inverter and modified sine wave?
Pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters are two common types of inverters. They have some differences in working principle, performance characteristics, application field, waveform, and compatibility. Next, we will explain the differences between pure sine wave inverters and modified sine wave inverters in various aspects.
What is a pure sine wave inverter?
Pure sine wave inverter: It produces a smooth, continuous waveform that closely resembles the AC power provided by the utility grid. The waveform is a true sine wave with a smooth and rounded shape. Modified sine wave inverter: It produces a waveform that is more like a stepped approximation of a sine wave.
Why is my inverter NOT a pure sine wave?
That's likely because the inverter is producing a rougher waveform, not a pure sine wave. Appliances like laptops, refrigerators, and microwave ovens are designed to function optimally on clean power. A pure sine wave inverter respects that design.
What does a sine wave inverter look like?
If you chart it out, it looks like a sine wave at first, but if you look closely, there are jagged stair steps in the waveform as the inverter crudely flips between polarities rather than the smooth wave seen above. Devices designed to run from an AC power source will all generally run on a modified sine wave.
Should I buy a sine wave inverter?
While this depends on your electrical system and what you’re powering, in most cases you’ll want to choose a pure sine wave inverter, especially if you’re using it as a main power source in a campervan, RV, or tiny home. If you just need to power basic electronics on a camping trip or road trip, modified sine is fine.
How does a sine wave inverter work?
As you can see in this diagram, when you plot out AC and DC current polarity, AC power forms a smooth wave. This is known as an AC sinusoidal or "sine" wave. An inverter's job is to reproduce that wave from a DC power source, and there are two answers to this problem. A modified sine wave inverter produces an approximation of a real AC sine wave.
Guess what you want to know
-
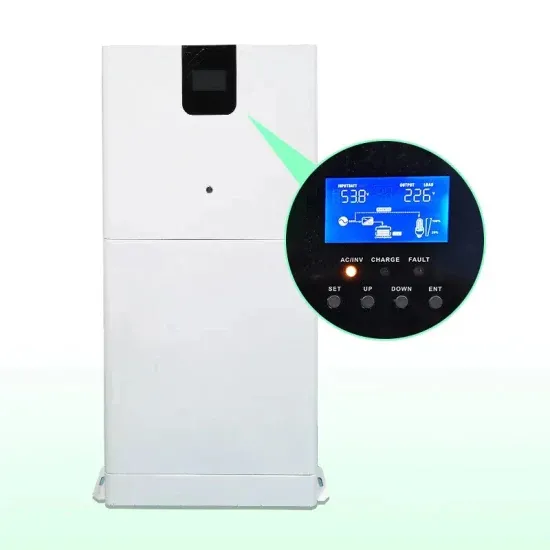 The difference between inverter and sine wave
The difference between inverter and sine wave
-
 48v inverter sine wave
48v inverter sine wave
-
 Brand new pure sine wave inverter from Poland
Brand new pure sine wave inverter from Poland
-
 5v inverter produces sine wave
5v inverter produces sine wave
-
 Power frequency sine wave inverter 65-150v
Power frequency sine wave inverter 65-150v
-
 Sine wave inverter structure
Sine wave inverter structure
-
 Ghana pure sine wave inverter
Ghana pure sine wave inverter
-
 Canadian pure sine wave inverter export
Canadian pure sine wave inverter export
-
 Inverter with sine wave
Inverter with sine wave
-
 Sine wave inverter intelligence
Sine wave inverter intelligence
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


