Energy Consumption of 5G, Wireless Systems and
"A 5G base station is generally expected to consume roughly three times as much power as a 4G base station. And more 5G base stations are needed to cover
Get a quote
5G and Energy Efficiency
ussed in the literature. One of the main solutions highlighted in most of the studies on this subject is the possibility to put base stations in "sleep mode" – since base stations consume 80% of
Get a quote
Energy Efficiency for 5G and Beyond 5G: Potential,
Energy efficiency constitutes a pivotal performance indicator for 5G New Radio (NR) networks and beyond, and achieving optimal efficiency
Get a quote
5G Base Station Growth: How Many Are Active? | PatentPC
Energy efficiency improvements in 5G base stations are projected to reduce power consumption by 15-20% per year One of the biggest challenges with 5G is its high power consumption, but
Get a quote
Does 5G require electricity?
One 5G base station is estimated to consume about as much power as 73 households (6), and 3x as much as the previous generation of base stations (5),(7). Takedown request | View
Get a quote
How Much Power Does 5G Base Station Consume? | HuiJue
Have you ever wondered how much energy our hyper-connected world is consuming? 5G base stations, the backbone of next-gen connectivity, now draw 3-4 times more power than their 4G
Get a quote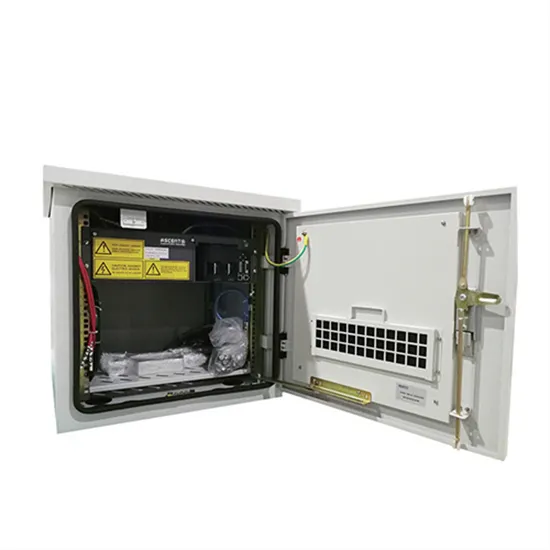
Front Line Data Study about 5G Power Consumption
The power consumption of a single 5G station is 2.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a single 4G station. The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power
Get a quote
Modelling the 5G Energy Consumption using Real-world
This paper proposes a novel 5G base stations energy con-sumption modelling method by learning from a real-world dataset used in the ITU 5G Base Station Energy Consumption Modelling
Get a quote
The power supply design considerations for 5G base
An integrated architecture reduces power consumption, which MTN Consulting estimates currently is about 5% to 6 % of opex. This percentage
Get a quote
Power consumption based on 5G communication
At present, 5G mobile traffic base stations in energy consumption accounted for 60% ~ 80%, compared with 4G energy consumption increased three times. In the future, high-density
Get a quote
Power Consumption of 4G and 5G Networks
Although RAN power consumption is reduced in 5G, it is still over 50% of the total 5G network infrastructure consumption. 📃Another trend worth
Get a quote
5G means Batteries. A lot of them
With the advent of 5G, not only that 4G base stations have to be upgraded or replaced, the number of base stations required for 5G also far exceeds that of
Get a quote
A technical look at 5G energy consumption and performance
To understand this, we need to look closer at the base station power consumption characteristics (Figure 3). The model shows that there is significant energy consumption in the
Get a quote
How much power does 5G consume?
One 5G base station is estimated to consume about as much power as 73 households (6), and 3x as much as the previous generation of base stations (5), (7). When base stations, data centers
Get a quote
What is the Power Consumption of a 5G Base Station?
Ericsson has been able to innovate a 5G base station that consumes only 20% energy when the traffic is low compared to a normal setup. This achieves through advanced
Get a quote
Energy-efficient 5G for a greener future
Compared to earlier generations of communication networks, the 5G network will require more antennas, much larger bandwidths and a higher density of base stations. As a
Get a quote
5G and Energy Efficiency
The following aspects of 5G deployment are the main drivers expected to lead to higher energy consumption (up to 1000 times as much energy5): › A denser base station infrastructure than
Get a quote
5G Base Station Deployments; Open-RAN
Early 5G Use Cases and Applications: According to TrendForce ''s latest investigations, 5G use cases have been in telemedicine and industrial
Get a quote
5G base stations use a lot more energy than 4G base
Exact estimates differ by source, but MTN says the industry consensus is that 5G will double to triple energy consumption for mobile
Get a quote
Self-sufficient cell towers; when will cell sites go off-grid en masse?
But the analyst firm says a typical 5G base station consumes up to twice or more the power of a 4G base station; it notes that the industry consensus is that 5G will double to
Get a quote
5G Base Stations: The Energy Consumption Challenge
Early deployments indicate that 5G base stations require 2.5-3.5 times more power compared to a 4G one. Moreover, C-band, i.e., 3.4 GHz to 4.2 GHz, is deemed as the most popular 5G
Get a quote
Power Consumption of 4G and 5G Networks
Although RAN power consumption is reduced in 5G, it is still over 50% of the total 5G network infrastructure consumption. 📃Another trend worth noting is the rise in data center
Get a quote
5G base stations use a lot more energy than 4G base stations: MTN
Exact estimates differ by source, but MTN says the industry consensus is that 5G will double to triple energy consumption for mobile operators, once networks scale. Warnings
Get a quote
5G Base Station Architecture
A 5G Base Station is known as a gNode B (next ''generation'' Node B). This is in contrast to a 4G Base Station which is known as an eNode B (''evolved'' Node
Get a quote
Energy Consumption of 5G, Wireless Systems and the Digital
"A 5G base station is generally expected to consume roughly three times as much power as a 4G base station. And more 5G base stations are needed to cover the same area," -IEEE
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [How much electricity does a 5G base station in Switzerland use ]
How much power does a 5G station use?
The power consumption of a single 5G station is 2.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a single 4G station. The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power usage of the active antenna unit (AAU). Under a full workload, a single station uses nearly 3700W.
Are 5G base stations causing more energy consumption?
However, Li says 5G base stations are carrying five times the traffic as when equipped with only 4G, pushing up power consumption. The carrier is seeking subsidies from the Chinese government to help with the increased energy usage.
How much power will a 5G base station use in 2025?
The Small Cell Forum predicts the installed base of small cells to reach 70.2 million in 2025 and the total installed base of 5G or multimode small cells in 2025 to be 13.1 million. “A 5G base station is generally expected to consume roughly three times as much power as a 4G base station.
Why does 5G use more power than 4G?
The data here all comes from operators on the front lines, and we can draw the following valuable conclusions: The power consumption of a single 5G station is 2.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a single 4G station. The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power usage of the active antenna unit (AAU).
Which network consumes the most power in 5G?
Also, NextGalliance published a report with the below figure clearly illustrates that the RAN consumes the most power. Although RAN power consumption is reduced in 5G, it is still over 50% of the total 5G network infrastructure consumption. Another trend worth noting is the rise in data center power consumption in 5G.
Does China Mobile have a 5G base station?
China Mobile has tried using lower cost deployments of MIMO antennas, specifically 32T32R and sometimes 8T8R rather than 64T64R, according to MTN. However, Li says 5G base stations are carrying five times the traffic as when equipped with only 4G, pushing up power consumption.
Guess what you want to know
-
 How much electricity does a 5G base station use
How much electricity does a 5G base station use
-
 How much electricity does a communication base station use
How much electricity does a communication base station use
-
 How many watts of voltage does a 5G base station use
How many watts of voltage does a 5G base station use
-
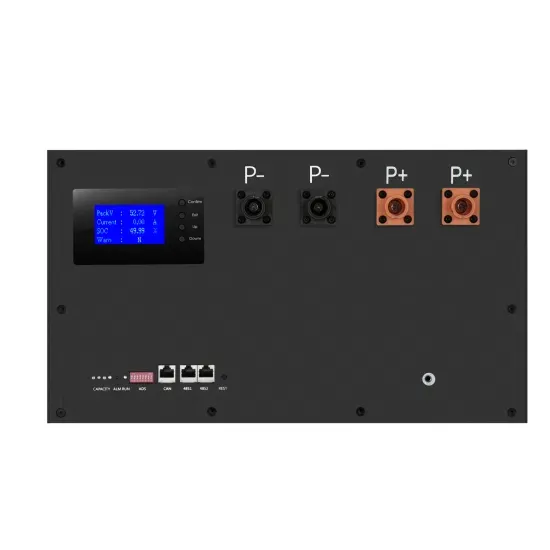
 How much electricity does a communication base station use in a year
How much electricity does a communication base station use in a year
-
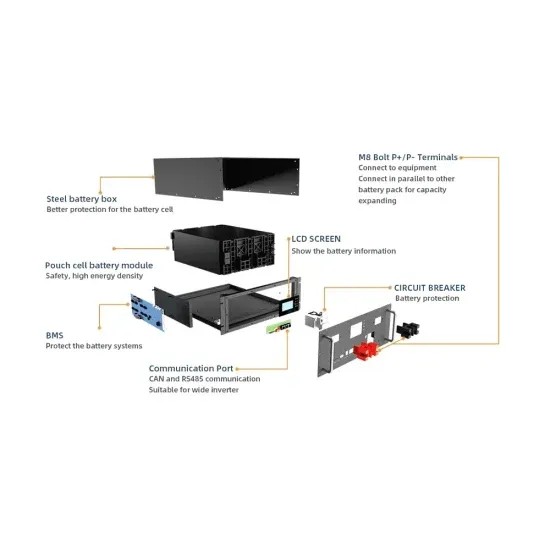 How to use Huawei s 5G base station communication energy storage cabinet
How to use Huawei s 5G base station communication energy storage cabinet
-
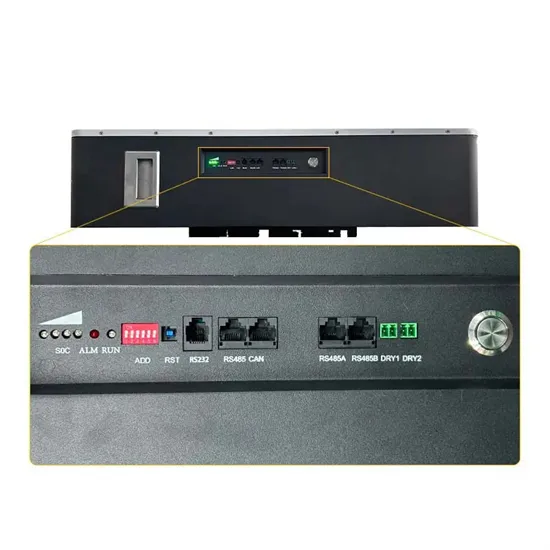
 How much electricity does a 5G base station have
How much electricity does a 5G base station have
-
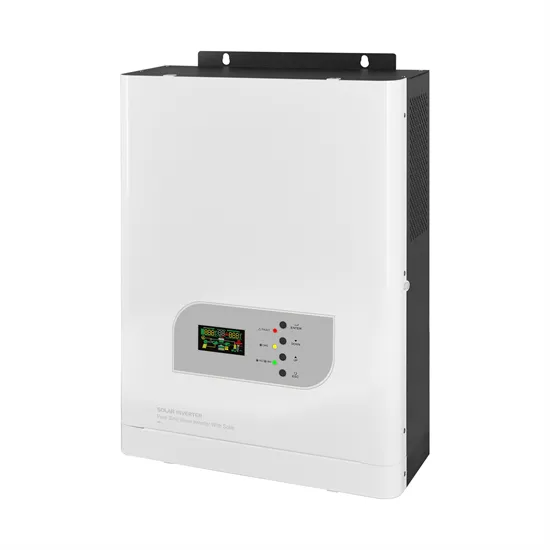 How to use the electric power remote mobile base station
How to use the electric power remote mobile base station
-
 How much power does Oman Communications 5G base station generate
How much power does Oman Communications 5G base station generate
-
 Does Colombia s 5G base station consume electricity
Does Colombia s 5G base station consume electricity
-
 5g energy base station electricity fee
5g energy base station electricity fee
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


