5G Network Evolution and Dual-mode 5G Base Station
The fifth generation (5G) networks can provide lower latency, higher capacity and will be commercialized on a large scale worldwide. In order to efficiently deploy 5G networks on the
Get a quote
Power Consumption: 5G Basestations Are Hungry, Hungry Hippos
The increased power consumption of next-generation basestations may be one of the dirty little secrets of 5G, which might not be a secret much longer as operators roll out
Get a quote
A technical look at 5G energy consumption and performance
To understand this, we need to look closer at the base station power consumption characteristics (Figure 3). The model shows that there is significant energy consumption in the
Get a quote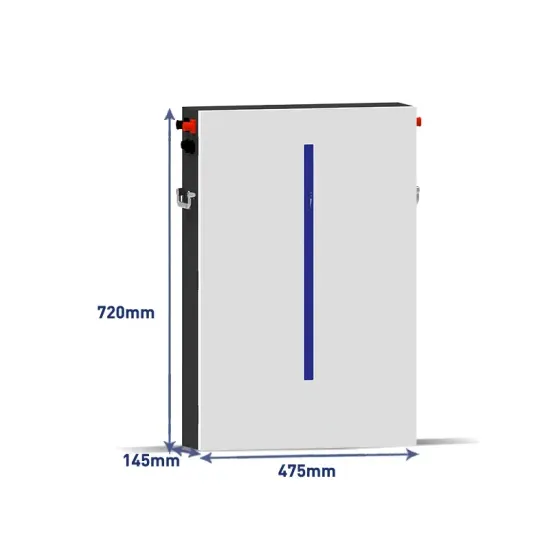
5G Transmit Power and Antenna radiation
Output power is typically limited by the EMF constraints of the site. In general, the nominal output power has to be defined by the cell size and the required data rate at the cell edge.
Get a quote
Electric Load Profile of 5G Base Station in Distribution Systems
This paper proposes an electric load demand model of the 5th generation (5G) base station (BS) in a distribution system based on data flow analysis. First, the electric load model of a 5G BS
Get a quote
Front Line Data Study about 5G Power Consumption
The power consumption of a single 5G station is 2.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a single 4G station. The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power
Get a quote
Renewable energy powered sustainable 5G network
Renewable energy is considered a viable and practical approach to power the small cell base station in an ultra-dense 5G network infrastructure to reduce the energy provisions
Get a quote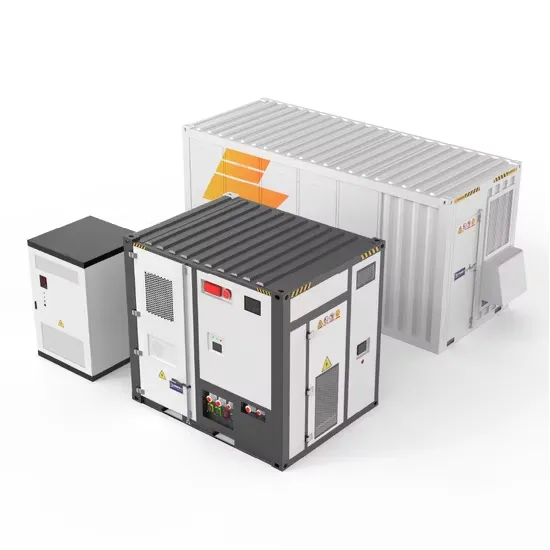
5G base stations use a lot more energy than 4G base stations: MTN
A typical 5G base station consumes up to twice or more the power of a 4G base station, writes MTN Consulting Chief Analyst Matt Walker in a new report entitled " Operators
Get a quote
Dynamic Power Management for 5G Small Cell Base Station
5G networks with small cell base stations are attracting significant attention, and their power consumption is a matter of significant concern. As the increase of the expectation, concern for
Get a quote
Learn What a 5G Base Station Is and Why It''s Important
A 5G base station is the heart of the fifth-generation mobile network, enabling far higher speeds and lower latency, as well as new levels of connectivity. Referred to as gNodeB, 5G base
Get a quote
5G base stations use a lot more energy than 4G base
A typical 5G base station consumes up to twice or more the power of a 4G base station, writes MTN Consulting Chief Analyst Matt Walker in a
Get a quote
Comparison of Power Consumption Models for 5G Cellular Network Base
Additional discussion of power models for radio access network, user equipment, and the system level as well as further remarks on base station power models can be found in
Get a quote
What is the Power Consumption of a 5G Base Station?
These 5G base stations consume about three times the power of the 4G stations. The main reason for this spike in power consumption is the addition of massive MIMO and
Get a quote
5G Energy Efficiency Overview
Abstract It is a critical requirement for the future of 5G communication networks to provide high speed and significantly reduce network energy consumption. In the Fifth Generation (5G),
Get a quote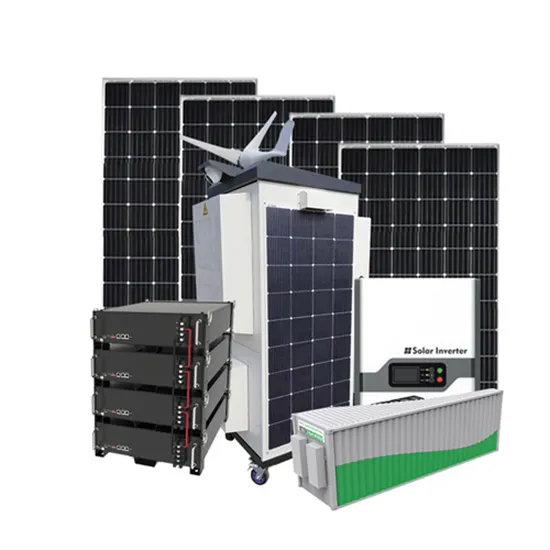
How Much Power Does a 5G Base Station Consume? – Smart Solar
On average, a 5G base station consumes between 1,000 to 3,000 watts. This is significantly higher than 4G base stations, which typically consume 500 to 1,500 watts.
Get a quote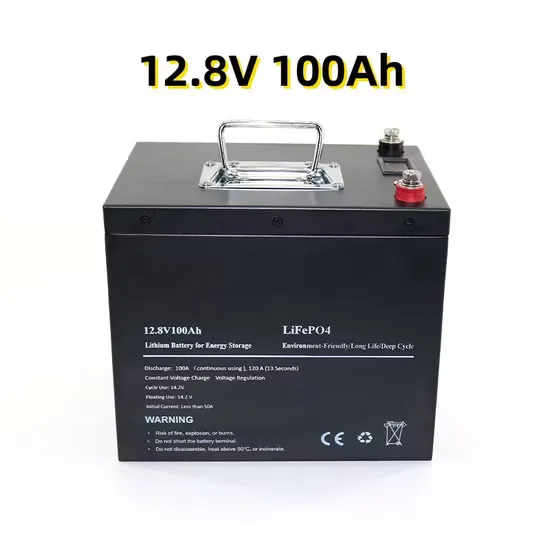
Size, weight, power, and heat affect 5G base station
Energy use will increase dramatically with 5G because a typical gNodeB uses at least twice as much electricity as its 4G counterpart, MTN
Get a quote
Energy consumption optimization of 5G base stations considering
The explosive growth of mobile data traffic has resulted in a significant increase in the energy consumption of 5G base stations (BSs). However, the existing energy conservation
Get a quote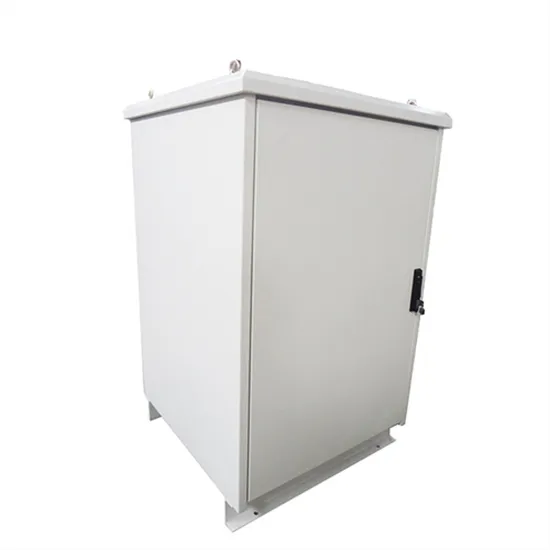
Do Cell Phone Towers Cause Cancer? | American
This could result in the antennas being closer to people, although small cells typically operate at much lower power levels than the larger (macro) base
Get a quote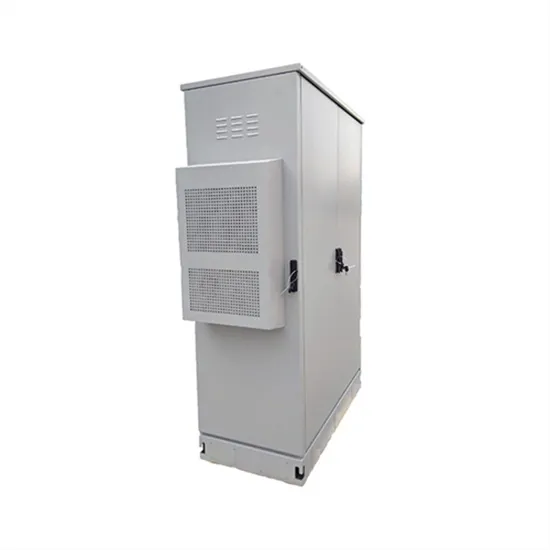
Size, weight, power, and heat affect 5G base station designs
Energy use will increase dramatically with 5G because a typical gNodeB uses at least twice as much electricity as its 4G counterpart, MTN says. Higher opex makes it difficult
Get a quote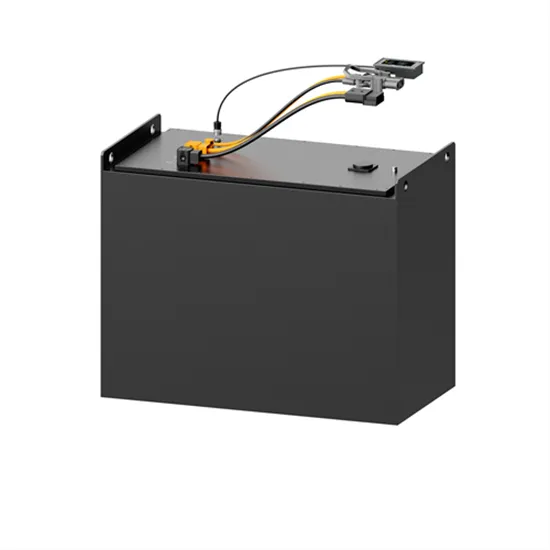
5g base station architecture
5G (fifth generation) base station architecture is designed to provide high-speed, low-latency, and massive connectivity to a wide range of devices. The architecture is more
Get a quote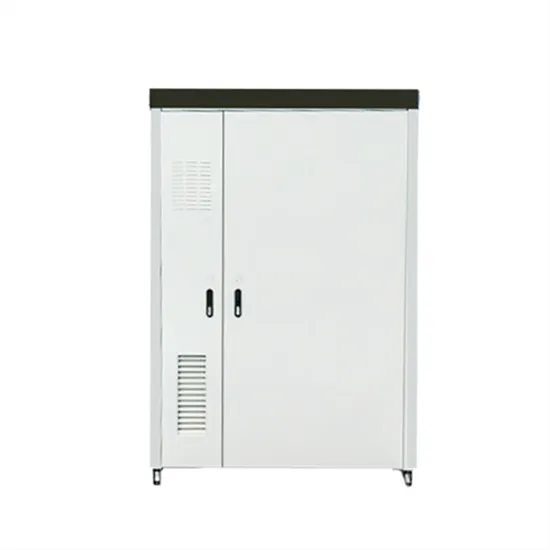
The 5G Dilemma: More Base Stations, More
A lurking threat behind the promise of 5G delivering up to 1,000 times as much data as today''s networks is that 5G could also consume up to
Get a quote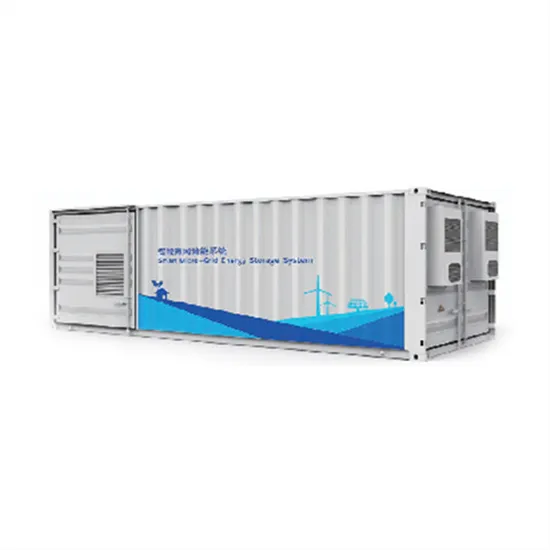
How much power does 5G consume?
One 5G base station is estimated to consume about as much power as 73 households (6), and 3x as much as the previous generation of base stations (5), (7). When base stations, data centers
Get a quote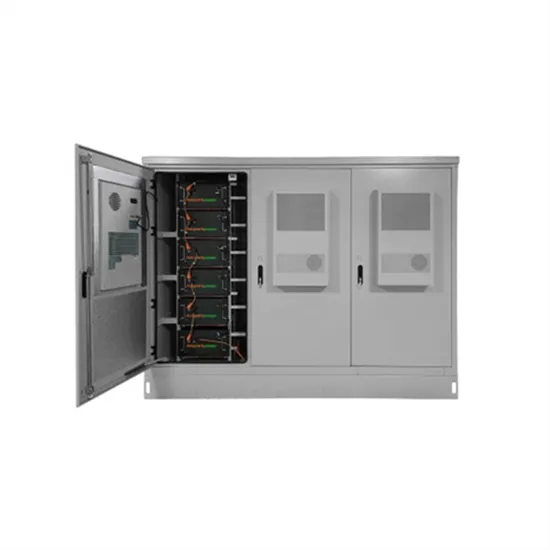
6 FAQs about [How much power does Oman Communications 5G base station generate ]
How much power does a 5G station use?
The power consumption of a single 5G station is 2.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a single 4G station. The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power usage of the active antenna unit (AAU). Under a full workload, a single station uses nearly 3700W.
Are 5G base stations causing more energy consumption?
However, Li says 5G base stations are carrying five times the traffic as when equipped with only 4G, pushing up power consumption. The carrier is seeking subsidies from the Chinese government to help with the increased energy usage.
Does Oman have a 5G network?
In Oman, the TRA has implemented measures to promote infrastructure sharing among mobile operators, which can enhance the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of 5G network deployments.
Why does 5G use more power than 4G?
The data here all comes from operators on the front lines, and we can draw the following valuable conclusions: The power consumption of a single 5G station is 2.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a single 4G station. The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power usage of the active antenna unit (AAU).
How many 5G base stations will Omantel have?
Omantel launched its 5G network in December 2019, utilizing the 3.4 – 3.6 GHz frequency band. 1 The Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (TRA) had set a target for operators to deploy 4,400 5G base stations over a five-year period starting in October 2019.
Does China Mobile have a 5G base station?
China Mobile has tried using lower cost deployments of MIMO antennas, specifically 32T32R and sometimes 8T8R rather than 64T64R, according to MTN. However, Li says 5G base stations are carrying five times the traffic as when equipped with only 4G, pushing up power consumption.
Guess what you want to know
-
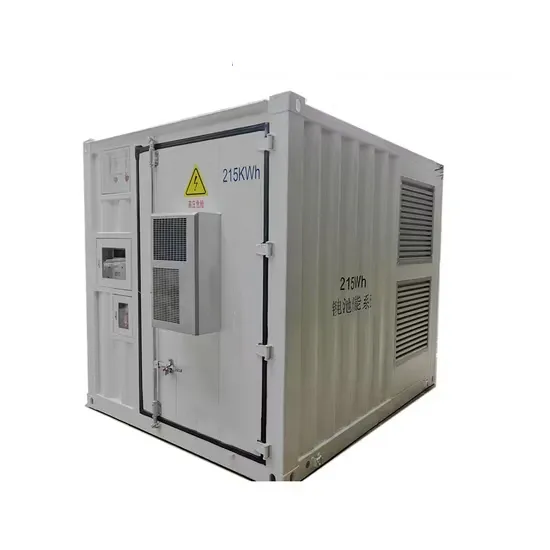 How much hybrid power supply does a 5G communication base station have
How much hybrid power supply does a 5G communication base station have
-
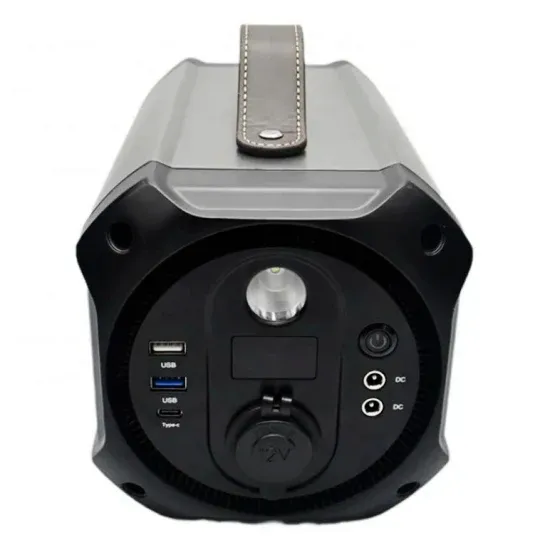 How much power can a French telecommunications base station generate from liquid flow batteries
How much power can a French telecommunications base station generate from liquid flow batteries
-
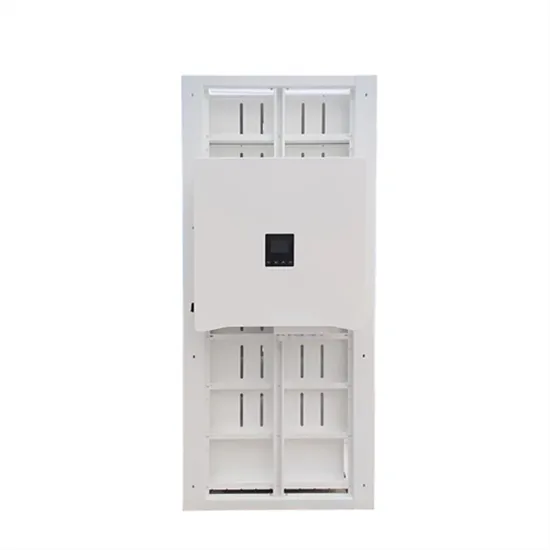 France Communications 5G base station hybrid power supply
France Communications 5G base station hybrid power supply
-
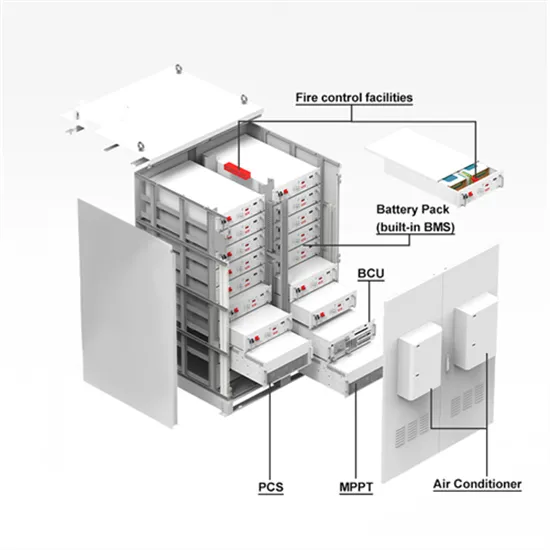 Guyana Communications 5G base station total hybrid power supply
Guyana Communications 5G base station total hybrid power supply
-
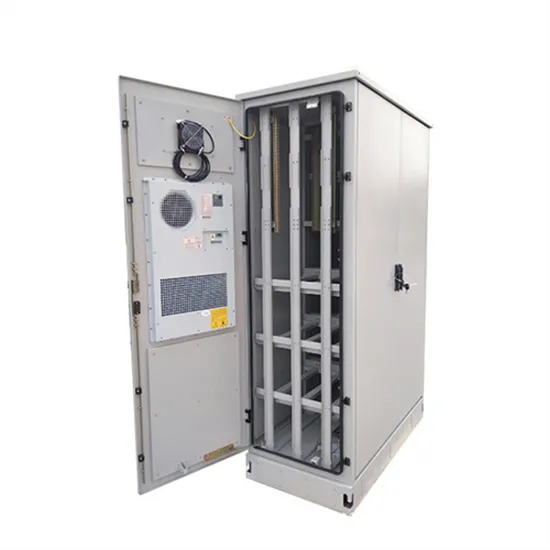 How many power supplies are usually provided with a base station
How many power supplies are usually provided with a base station
-
 What power supply does a 5G base station require
What power supply does a 5G base station require
-
 How many volts is the base station power supply
How many volts is the base station power supply
-
 Huawei s only 5G base station power supply supplier
Huawei s only 5G base station power supply supplier
-
 Photovoltaic area of the Maldives 5G communication base station power supply project
Photovoltaic area of the Maldives 5G communication base station power supply project
-
 5G base station new power system
5G base station new power system
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


