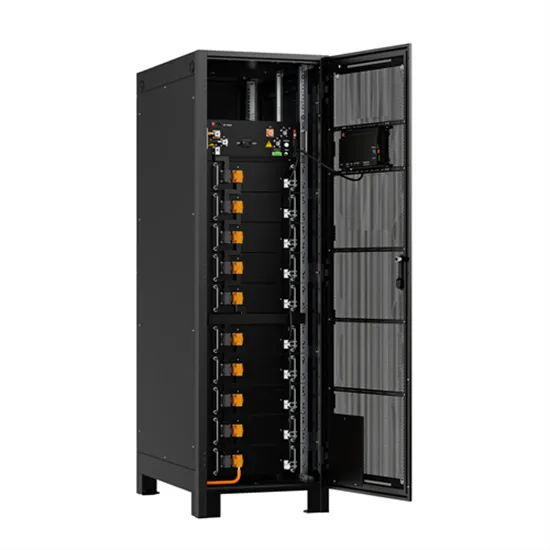

Solar Integration: Inverters and Grid Services Basics
Fundamentally, an inverter accomplishes the DC-to-AC conversion by switching the direction of a DC input back and forth very rapidly. As a result, a DC input becomes an AC output.
Get a quote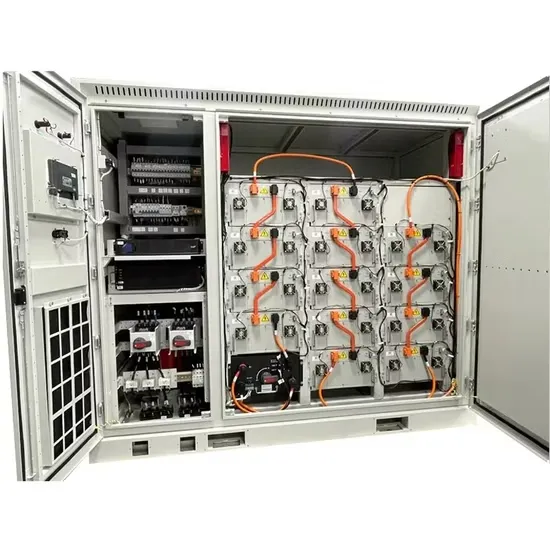
How to Start Inverter Manufacturing Business in 11 Steps
Fundamentally, an inverter accomplishes the DC-to-AC conversion by switching the direction of a DC input back and forth very rapidly. As a result, a DC input
Get a quote
How is the inverter manufactured?
In this article, Junchipower will introduce in detail the entire process of inverter production, from design planning to factory delivery, and gradually analyze the key steps and
Get a quote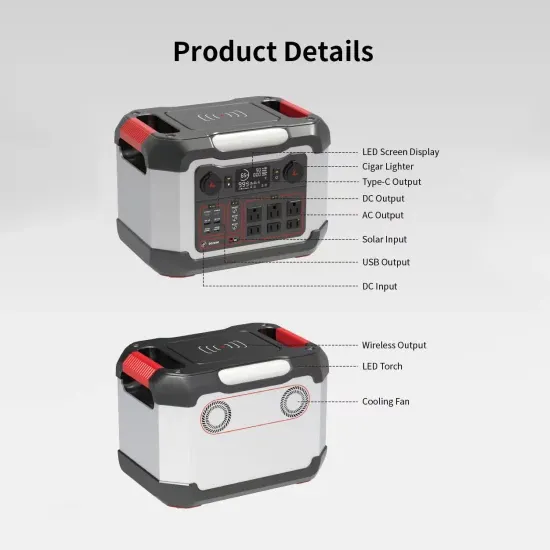
My Document
External production meter: A meter that is used for production metering of 3rd party generators, or for AC coupling with non-SolarEdge inverters. Site production meter: A meter that is installed
Get a quote
ARTICLE 705
Interconnected Electric Power Production Sources Part I. General Scope. This article covers installation of one or more electric power production sources operating in parallel
Get a quote
STEP 9: Install Energy Metering for the System
Standalone (AC-coupled) solar inverters must be metered by Backup Gateway 2 Meter Y or Tesla Remote Energy Meter. Site Metering for Backup Gateway 2
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
Inverters can be categorized based on the type of AC power they produce. AC power generated by the grid is of a pure sinusoidal shape and
Get a quote
Solar inverter sizing: Choose the right size inverter
Table 1: Annual energy production out of a 100 kW inverter as a function of DC-to-AC ratio. As the DC-to-AC ratio increases, so does the AC output and clipped
Get a quote
AN INTRODUCTION TO INVERTER-BASED RESOURCES
Consistent energy production levels from inverter-based resources (mainly renewable, variable energy resources) are still relatively low; however, even today, instantaneous penetrations* of
Get a quote
PV Production and System Issues
Look for the green LED: when it is on, the system is producing power, if it is flashing, this means the inverter has AC power and is in Standby mode. Look to see if the blue LED on: when this
Get a quote
How To Produce Inverter: A Step-by-Step Guide
They convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), enabling the use of stored energy in devices that require AC power. This article will explain how to produce inverter and the key
Get a quote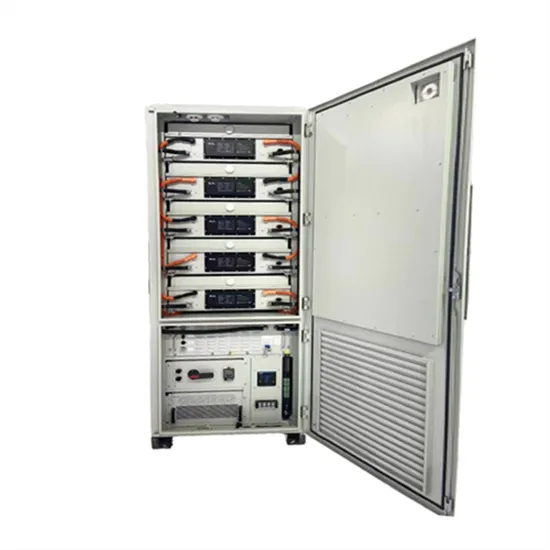
What Is an Inverter for Solar Panels and Why Does It
A solar inverter is an electrical device that converts the DC electricity generated by your solar panels into AC electricity. While solar
Get a quote
Solar Inverter Manufacturing Plant Report 2025 | Setup and Cost
Solar inverter is essential for facilitating the effective harnessing of solar energy, thus supporting clean and sustainable energy solutions. A solar inverter manufacturing plant is a facility
Get a quote
Power inverter
OverviewApplicationsInput and outputBatteriesCircuit descriptionSizeHistorySee also
An inverter converts the DC electricity from sources such as batteries or fuel cells to AC electricity. The electricity can be at any required voltage; in particular it can operate AC equipment designed for mains operation, or rectified to produce DC at any desired voltage. An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) uses batteries and an inverter to suppl
Get a quote
What Is an AC Battery Inverter? Understanding Its
An AC battery inverter is an essential component of home power systems, as it converts direct current (DC) electricity stored in accumulators
Get a quote
How to Start Inverter Manufacturing Business in 11 Steps
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to starting an inverter manufacturing business, covering essential aspects from market research to production setup and marketing
Get a quote
What is Solar Inverter Clipping?
Each inverter has a maximum output rating. This is the greatest amount of AC power the inverters can pump out at one time. If the solar panels'' energy
Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Inverters/Variable Frequency Drives
There are a number of different types of inverters but we will be discussing the type that is used to control electric motors in electrical engineering. These can also be known as
Get a quote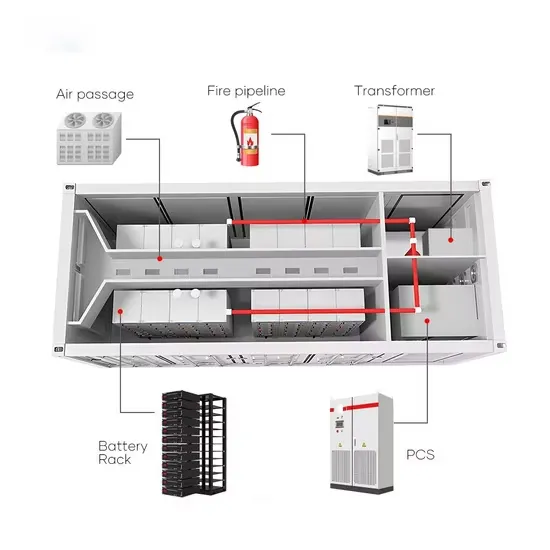
Inverter Manufacturing Plant Project Report 2025: Setup and Cost
An inverter manufacturing plant is a facility designed to produce electronic devices that convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), essential for various applications such as
Get a quote
Inverter Basics | inverter
Unless you have a basic system that offers a low-voltage DC power source, the inclusion of an inverter becomes essential. An inverter takes input from a DC (direct current)
Get a quote
Converting DC to AC: Basic Principles of Inverters
Inverters can be categorized based on the type of AC power they produce. AC power generated by the grid is of a pure sinusoidal shape and alternates smoothly between
Get a quote
Why array oversizing makes financial sense
This inverter clipping, or power limiting, ensures the inverter is operating within its capabilities but results in lost energy production during peak production hours. All UL 1741-certified inverters
Get a quote
Inverter Making Process
It aims to serve as a comprehensive resource for engineers, manufacturers, researchers, and enthusiasts interested in the detailed lifecycle of inverter production.
Get a quote
How to Monitor Performance of 3kW String Inverters
2 days ago· The inverter not only facilitates the conversion of DC to AC but also plays a role in maximizing energy production through features like Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT).
Get a quote
Power inverter
The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source. A power inverter can be entirely electronic or maybe a combination of mechanical effects (such as a
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [AC inverter production]
How does an inverter convert DC to AC?
Fundamentally, an inverter accomplishes the DC-to-AC conversion by switching the direction of a DC input back and forth very rapidly. As a result, a DC input becomes an AC output. In addition, filters and other electronics can be used to produce a voltage that varies as a clean, repeating sine wave that can be injected into the power grid.
What is inverter manufacturing business?
An inverter is an electric device that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). This conversion may be accomplished by electromechanical means namely motor and generator sets, which are entirely by electronic means.
How do inverters work?
Inverters are just one example of a class of devices called power electronics that regulate the flow of electrical power. Fundamentally, an inverter accomplishes the DC-to-AC conversion by switching the direction of a DC input back and forth very rapidly. As a result, a DC input becomes an AC output.
What is the AC output voltage of a power inverter?
The AC output voltage of a power inverter is often regulated to be the same as the grid line voltage, typically 120 or 240 VAC at the distribution level, even when there are changes in the load that the inverter is driving. This allows the inverter to power numerous devices designed for standard line power.
What is a power inverter?
A power inverter, inverter, or invertor is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). The resulting AC frequency obtained depends on the particular device employed. Inverters do the opposite of rectifiers which were originally large electromechanical devices converting AC to DC.
Does a static inverter produce power?
The inverter does not produce any power; the power is provided by the DC source. A power inverter can be entirely electronic or maybe a combination of mechanical effects (such as a rotary apparatus) and electronic circuitry. Static inverters do not use moving parts in the conversion process.
Guess what you want to know
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


 60V battery inverter can drive AC
60V battery inverter can drive AC
 AC 220 inverter
AC 220 inverter
 High-voltage DC to AC inverter
High-voltage DC to AC inverter
 Inverter DC to AC 380V high power 9kw
Inverter DC to AC 380V high power 9kw
 Substation AC system inverter
Substation AC system inverter
 AC power connection inverter
AC power connection inverter
 DC inverter to AC
DC inverter to AC
 5v DC to AC inverter
5v DC to AC inverter
 Huawei Uruguay inverter production
Huawei Uruguay inverter production