What is Rectifier? Types of Rectifiers and their Operation
A type of rectifier whose output voltage can be varied or changed is called controlled rectifier. The need for a controlled rectifier is apparent when we look into the shortcomings of an
Get a quote
What are the 4 main parts of a UPS power supply?
There are four main parts of an uninterruptible power supply: rectifier, inverter, battery, and static bypass switch. Rectifier: The rectifier is a device used to
Get a quote
Inverter Vs. Rectifier: The Battle of Power Conversion
In this article, you will find a detailed exploration of inverter vs. rectifier. We will dive into their core principles, examine how each functions, highlight their differences, and discuss their various
Get a quote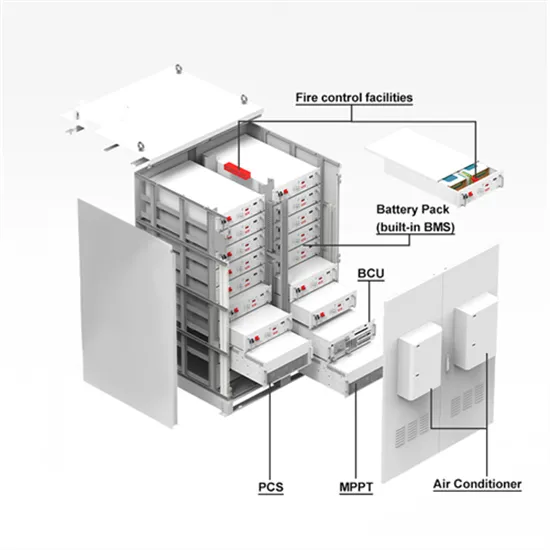
DSU User Manual | PDF | Rectifier | Power Inverter
The document is a user manual for diode supply modules ACS800-304 and ACS800-704. It describes how the diode supply units work, their
Get a quote
Explain UPS and its working function in detail
The rectifier-inverter system provides alternating current to the load while simultaneously charging the battery. When there is a break in the
Get a quote
The main difference between inverter vs rectifier – TYCORUN
This article will introduce the working principle and application scenarios of inverter and rectifier respectively, and then analyze the comparison of inverter vs rectifier, what are the
Get a quote
Rectiverter Creates New Category of Power System
Now there''s a more revolutionary way to meet the increasing power needs of these applications: the Rectiverter a breakthrough power system that
Get a quote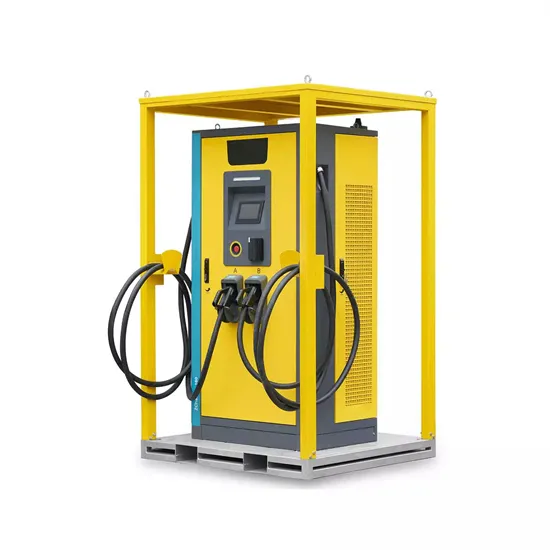
What Are the Main Components of a UPS System?
If there is a fault in the UPS system, the static bypass automatically connects the load to the mains supply and allows the incoming power to divert around the rectifier, batteries,
Get a quote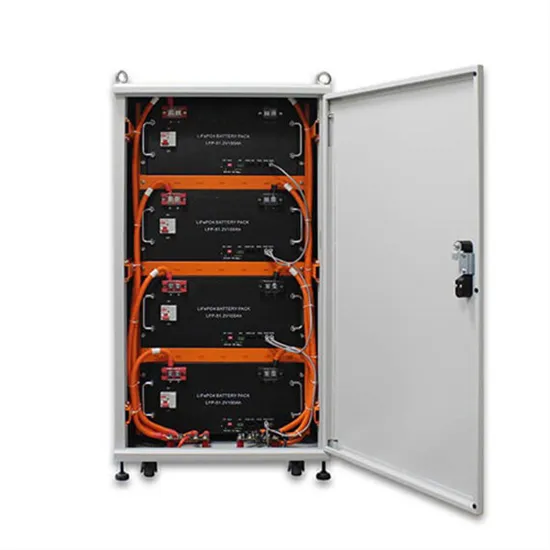
Inverter and Types of Inverters with their Applications
There are two types of single-phase H-bridge inverters and one famous type of three-phase inverter known as three-phase H-bridge inverter. These two types are discussed here.
Get a quote
What is the difference between a rectifier and an
What is an Inverter? An inverter, on the other hand, performs the opposite function of a rectifier. It converts direct current (DC) into alternating
Get a quote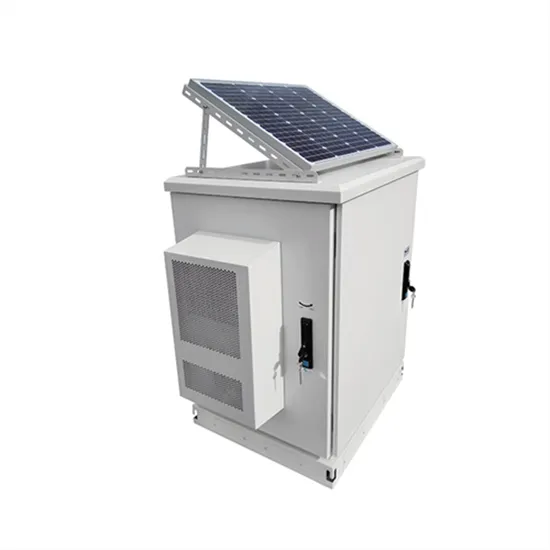
What is Rectifier? Types of Rectifiers and their Operation
When it comes to power conversion in electronic systems, two critical devices often come up: inverters and rectifiers. Both play vital roles in
Get a quote
What is the difference between a rectifier and an inverter?
When it comes to power conversion in electronic systems, two critical devices often come up: inverters and rectifiers. Both play vital roles in transforming electrical power, but they
Get a quote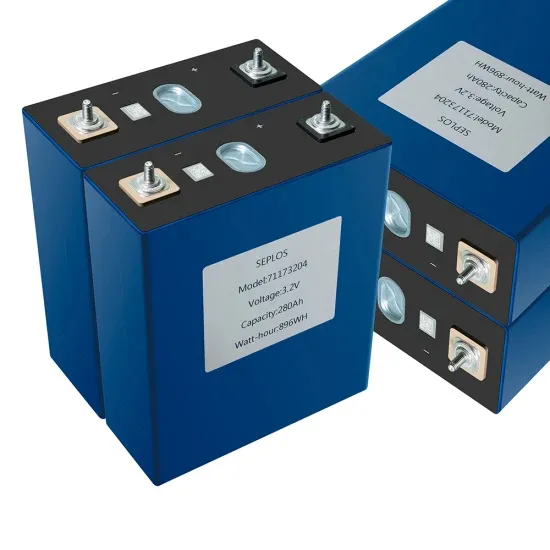
Difference Between Inverter And Rectifier Explained
In this quick read, you''ll learn the differences between inverter and rectifier. We''ll also discuss how they both function and give answers to some frequently asked questions.
Get a quote
Inverter vs rectifier
In the realm of power electronics, inverters and rectifiers play crucial roles, each serving distinct purposes in electrical systems. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of rack
Get a quote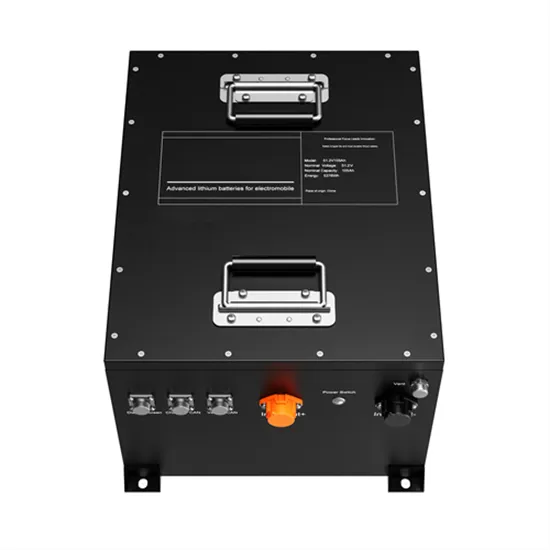
3 Types of Rectifiers + Pros & Cons: The Quick Guide
Found in devices such as laptop adapters, smartphone chargers, and large-scale power systems, rectifiers ensure that the appropriate current
Get a quote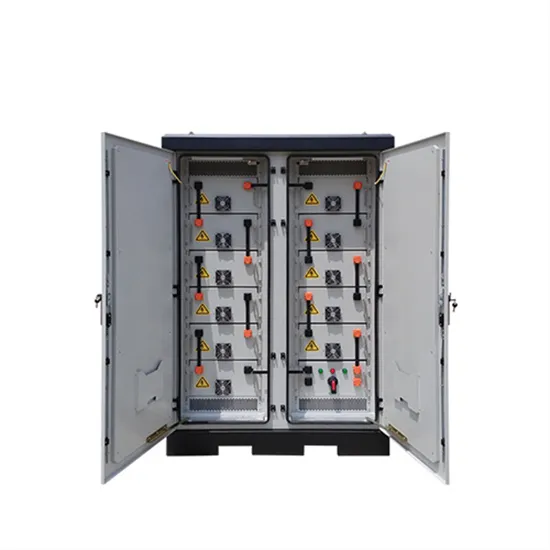
Inverter vs Rectifier
Confused between an inverter and rectifier? This blog explains the difference, how each works, and which one you need for your electrical system. Learn which device suits your
Get a quote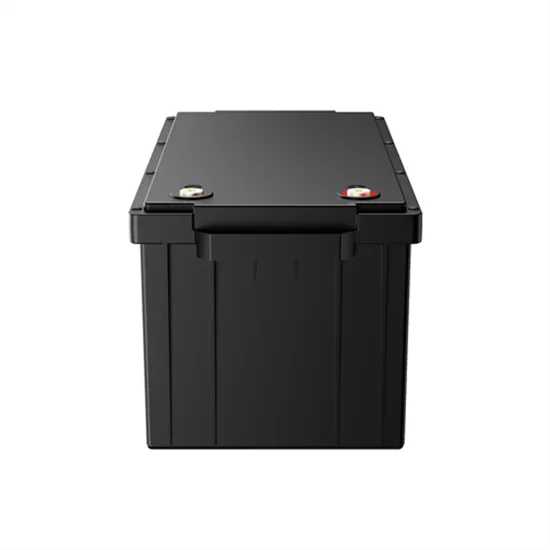
Different Types of Rectifiers – Single & Three Phase
A rectifier is an electronic circuit which converts Alternating Current into Direct Current. Based on the type of input supply, rectification and output
Get a quote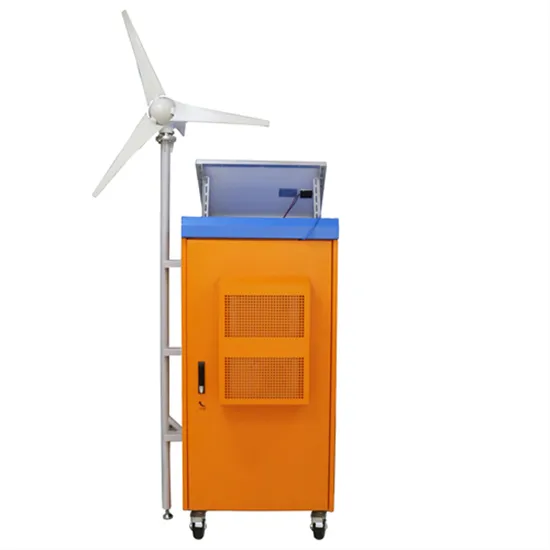
The Functions And Application Areas Of Rectifier
At the same time, the rectifier cabinet can also realize intelligent monitoring and control, making the operation of the equipment more reliable
Get a quote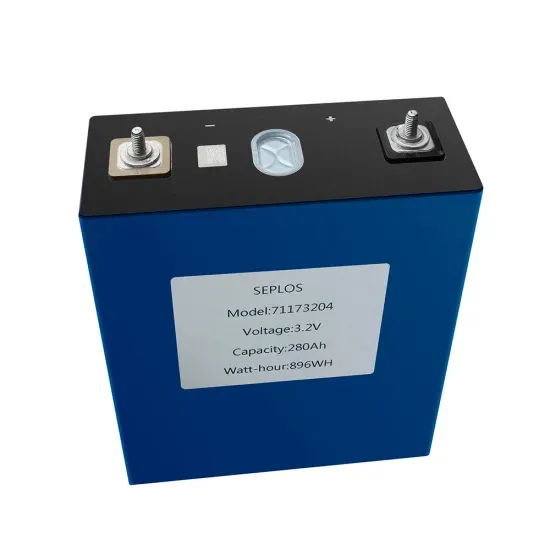
What types of rectifier and inverter cabinets belong to
fiers come in two basic types: half-wave and full-wave. A half-wave rectifier allows electricity of only one polarity (positive or negative) to pass through, while a full-wave
Get a quote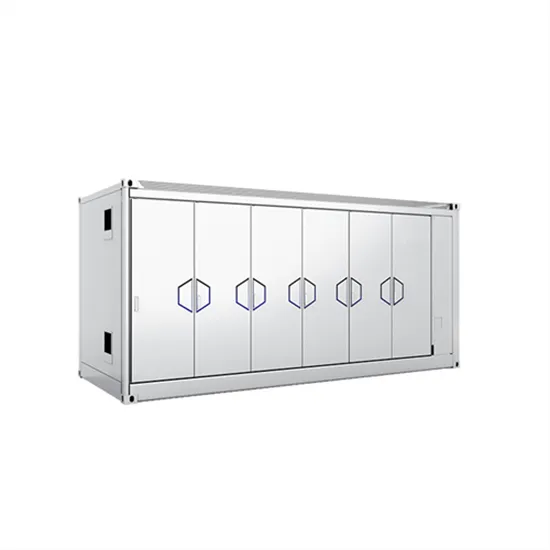
What is Rectifier? Types of Rectifiers and their Operation
Uncontrolled Rectifier Controlled Rectifier Bridge rectifiers are of many types and the basis for the classification can be many, to name a few, type of supply,
Get a quote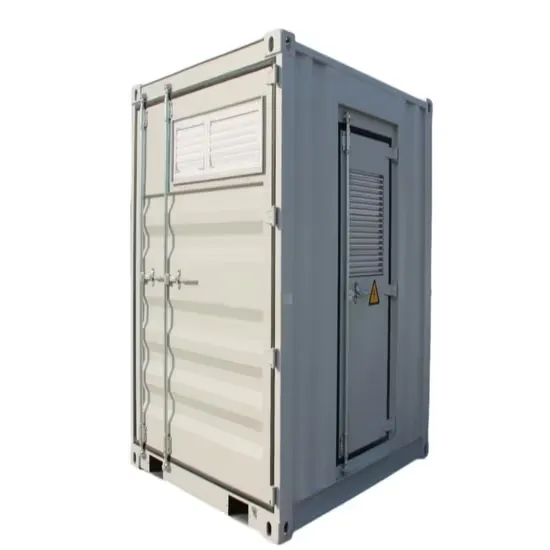
How Do Rectifiers Work? Types, Functions, and Key Applications
Learn about rectifiers, their types (half-wave, full-wave, bridge), working principles, and key applications in power supplies, electronics, and more.
Get a quote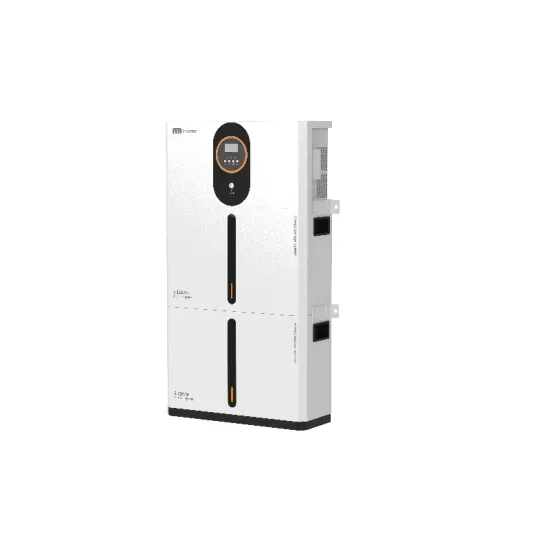
3 Types of Rectifiers + Pros & Cons: The Quick Guide
Found in devices such as laptop adapters, smartphone chargers, and large-scale power systems, rectifiers ensure that the appropriate current type is supplied. This post
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [What types of rectifier and inverter cabinets are there ]
What does a rectifier do in an inverter?
The alternating current output by the inverter can be applied to the power supply of various electrical appliances and equipment requiring alternating current. A rectifier is a power conversion device that converts alternating current to direct current. Its main function is to convert AC power to DC power.
Do I need an inverter or a rectifier?
In some cases, you might need both an inverter and a rectifier. This is common in power systems that work with both AC and DC currents. For example, a solar power system might require a rectifier to convert AC from the grid into DC for storage, and then an inverter to convert stored DC back into AC for use in your home.
What is the working state of inverter vs rectifier?
The working state of inverter vs rectifier: When the rectifier is working, the current direction is always the same, and the output is positive current; while the output current direction of the inverter can be reversed, and its output is alternating current, which has the characteristics of direction and frequency.
What is the difference between AC and rectifier?
AC is the form of electricity supplied by power grids and commonly used in household and industrial applications. However, many electronic devices, such as computers, phones, and industrial equipment, require proper DC power. Rectifiers are essential in providing this DC power from an AC source. Inverter Vs. Rectifier: Working Principle
Why is a rectifier more efficient than an inverter?
The efficiency of the inverter is low, because the electrical energy conversion must be performed during the voltage conversion process, and there is a certain loss. A rectifier, on the other hand, is more efficient because the electrical energy only needs to be converted once to get the required current. In Carrying Capacity Aspects
What does a rectifier do in a computer?
Computers:Computers rely on rectifiers to convert grid power into the DC voltages required for their internal circuits. What is an Inverter? An inverter, on the other hand, performs the opposite function of a rectifier. It converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
Guess what you want to know
-
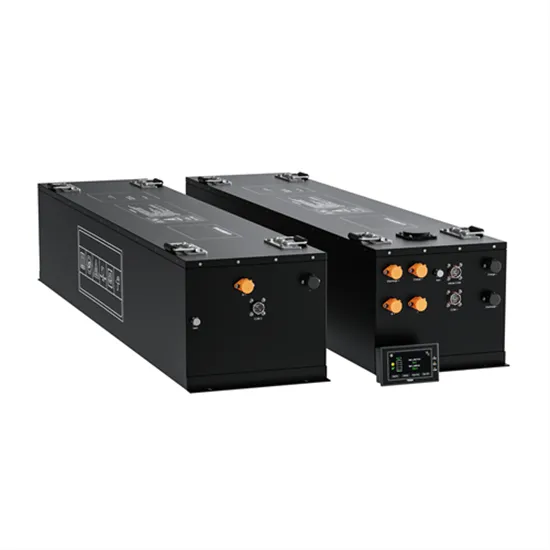 What types of liquid-cooled energy storage battery cabinets are included
What types of liquid-cooled energy storage battery cabinets are included
-
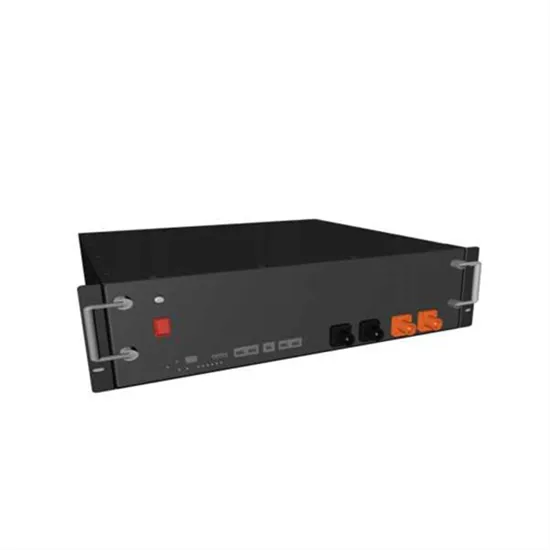 Huawei rectifier and inverter cabinets
Huawei rectifier and inverter cabinets
-
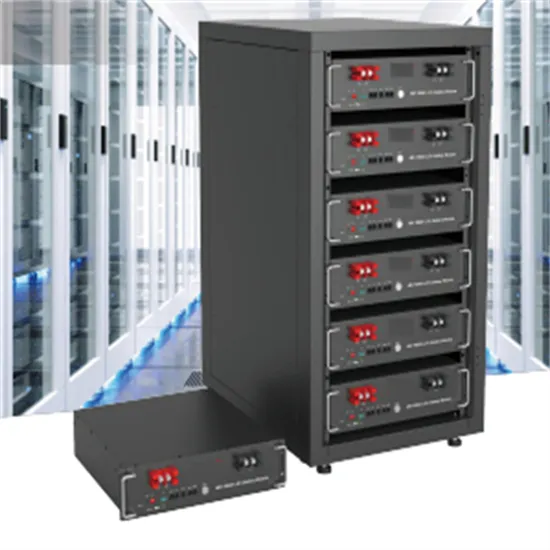 What types of outdoor inverter components are there
What types of outdoor inverter components are there
-
 What does the Uzbekistan communication base station inverter include
What does the Uzbekistan communication base station inverter include
-
 What are the uses of photovoltaic energy storage cabinets
What are the uses of photovoltaic energy storage cabinets
-
 How many types of batteries are there in energy storage cabinets
How many types of batteries are there in energy storage cabinets
-
 Types of Base Station Battery Cabinets
Types of Base Station Battery Cabinets
-
 What are the bidding requirements for energy storage cabinets
What are the bidding requirements for energy storage cabinets
-
 What frequency does a high-frequency inverter require
What frequency does a high-frequency inverter require
-
 What voltage does the inverter change
What voltage does the inverter change
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


