5G Transmit Power and Antenna radiation
The use of such high frequencies is expected to increase the number of mobile antenna stations needed to cover the same geographical areas. But how are
Get a quote
Energy Consumption of 5G, Wireless Systems and the Digital
"A 5G base station is generally expected to consume roughly three times as much power as a 4G base station. And more 5G base stations are needed to cover the same area," -IEEE
Get a quote
A technical look at 5G energy consumption and performance
Today we see that a major part of energy consumption in mobile networks comes from the radio base station sites and that the consumption is stable.
Get a quote
Why does 5g base station consume so much power
5G base stations use high power consumption and high RF signals, which require more signal processing for digital and electromechanical units,
Get a quote
How much power does 5G consume?
One 5G base station is estimated to consume about as much power as 73 households (6), and 3x as much as the previous generation of base stations (5), (7). When base stations, data centers
Get a quote
How Much Power Does 5G Base Station Consume?
Have you ever wondered how much energy our hyper-connected world is consuming? 5G base stations, the backbone of next-gen connectivity, now draw 3-4 times more power than their 4G
Get a quote
5G base stations use a lot more energy than 4G base
A typical 5G base station consumes up to twice or more the power of a 4G base station, writes MTN Consulting Chief Analyst Matt Walker in a
Get a quote
Carbon emissions of 5G mobile networks in China
Here we develop a large-scale data-driven framework to quantitatively assess the carbon emissions of 5G mobile networks in China, where over 60% of the global 5G base
Get a quote
A Holistic Study of Power Consumption and Energy Savings
The power consumption of a 5G base station using massive MIMO is dominated by the power consumption of the radio units whose power amplifier(s) consume most of the energy, thus
Get a quote
Power consumption analysis of access network in 5G mobile
The architectural differences of these networks are highlighted and power consumption analytical models that characterize the energy consumption of radio resource
Get a quote
Front Line Data Study about 5G Power Consumption
The power consumption of a single 5G station is 2.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a single 4G station. The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power
Get a quote
Quantifying the energy cost savings from 2G/3G
Many telcos publish data on their energy consumption, and sometimes provide breakdowns for different parts of the network. But there are no existing
Get a quote
The 5G Dilemma: More Base Stations, More
According to recent research, the ultra-lean design that 5G networks are capable of will make it possible to put more components to sleep for a
Get a quote
What is the Power Consumption of a 5G Base Station?
These 5G base stations consume about three times the power of the 4G stations. The main reason for this spike in power consumption is the addition of massive MIMO and
Get a quote
5G means Batteries. A lot of them
In base stations and other network infrastructure, battery-based UPSs are most often used as backup power sources to keep the installations operational
Get a quote
The 5G Dilemma: More Base Stations, More Antennas—Less Energy?
According to recent research, the ultra-lean design that 5G networks are capable of will make it possible to put more components to sleep for a longer time, reducing energy
Get a quote
What is 5G Energy Consumption?
5G Base Station Power Consumption: With each base station carrying at least 5X more traffic and operating over more frequency bands, 5G base station power consumption is at least twice
Get a quote
Energy consumption optimization of 5G base stations considering
The explosive growth of mobile data traffic has resulted in a significant increase in the energy consumption of 5G base stations (BSs). However, the e
Get a quote
Power Consumption Modeling of 5G Multi-Carrier Base
However, there is still a need to understand the power consumption behavior of state-of-the-art base station architectures, such as multi-carrier active antenna units (AAUs), as well as the
Get a quote
Machine Learning and Analytical Power Consumption Models for 5G Base
The energy consumption of the fifth generation (5G) of mobile networks is one of the major concerns of the telecom industry. However, there is not currently an accurate and
Get a quote
Network energy consumption modeling and performance
5G - by design the most energy efficient cellular generation to date - evolves further with new features and solutions to further improve energy performance.
Get a quote
Energy Consumption of 5G, Wireless Systems and
"A 5G base station is generally expected to consume roughly three times as much power as a 4G base station. And more 5G base stations are needed to cover
Get a quote
Machine Learning and Analytical Power Consumption
Abstract—The energy consumption of the fifth generation (5G) of mobile networks is one of the major concerns of the telecom industry. However, there is not currently an accurate and
Get a quote
Why does 5g base station consume so much power and how to
5G base stations use high power consumption and high RF signals, which require more signal processing for digital and electromechanical units, and also put greater pressure
Get a quote
5G base stations use a lot more energy than 4G base stations: MTN
A typical 5G base station consumes up to twice or more the power of a 4G base station, writes MTN Consulting Chief Analyst Matt Walker in a new report entitled " Operators
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [5g base stations consume a lot of power]
Are 5G base stations causing more energy consumption?
However, Li says 5G base stations are carrying five times the traffic as when equipped with only 4G, pushing up power consumption. The carrier is seeking subsidies from the Chinese government to help with the increased energy usage.
How much power does a 5G station use?
The power consumption of a single 5G station is 2.5 to 3.5 times higher than that of a single 4G station. The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power usage of the active antenna unit (AAU). Under a full workload, a single station uses nearly 3700W.
Is 5G more energy efficient than 4G?
Although the absolute value of the power consumption of 5G base stations is increasing, their energy efficiency ratio is much lower than that of 4G stations. In other words, with the same power consumption, the network capacity of 5G will be as dozens of times larger than 4G, so the power consumption per bit is sharply reduced.
Will MIMO increase the energy consumption of 5G base stations?
As a result, there are many more hardware components per base station. Björnson believes this will probably increase the total energy consumption of 5G base stations compared to 4G. But as massive MIMO technology develops, its energy efficiency may also improve over time.
Does China Mobile have a 5G base station?
China Mobile has tried using lower cost deployments of MIMO antennas, specifically 32T32R and sometimes 8T8R rather than 64T64R, according to MTN. However, Li says 5G base stations are carrying five times the traffic as when equipped with only 4G, pushing up power consumption.
Why does 5G use so much power?
The main factor behind this increase in 5G power consumption is the high power usage of the active antenna unit (AAU). Under a full workload, a single station uses nearly 3700W. This necessitates a number of updates to existing networks, such as more powerful supplies and increased performance output from supporting facilities.
Guess what you want to know
-
 5g base stations consume power and power is cut off at night
5g base stations consume power and power is cut off at night
-
 Do 5G base stations consume more power
Do 5G base stations consume more power
-
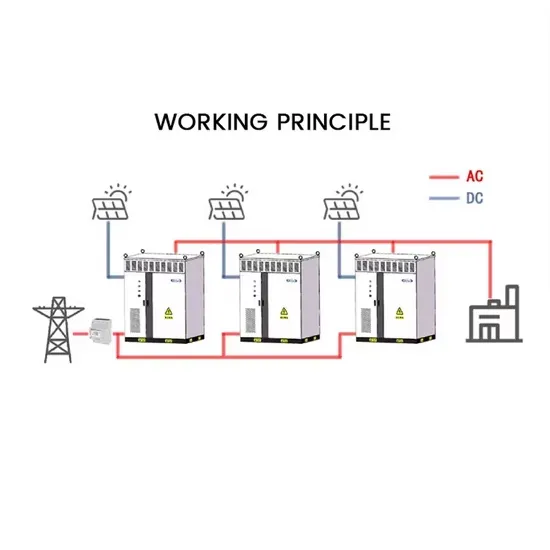 Photovoltaic power generation and 5G base stations
Photovoltaic power generation and 5G base stations
-
 Domestic power supply for 5G base stations
Domestic power supply for 5G base stations
-
 Hydrogen power supply for 5G base stations in the Netherlands
Hydrogen power supply for 5G base stations in the Netherlands
-
 5G base stations are built on the power grid
5G base stations are built on the power grid
-
 Solar power generation solves the power consumption of 5G base stations
Solar power generation solves the power consumption of 5G base stations
-
 Distributed power generation at 5G communication base stations
Distributed power generation at 5G communication base stations
-
 Analysis of power supply market of communication base stations
Analysis of power supply market of communication base stations
-
 Sophia Communications and 5G base stations
Sophia Communications and 5G base stations
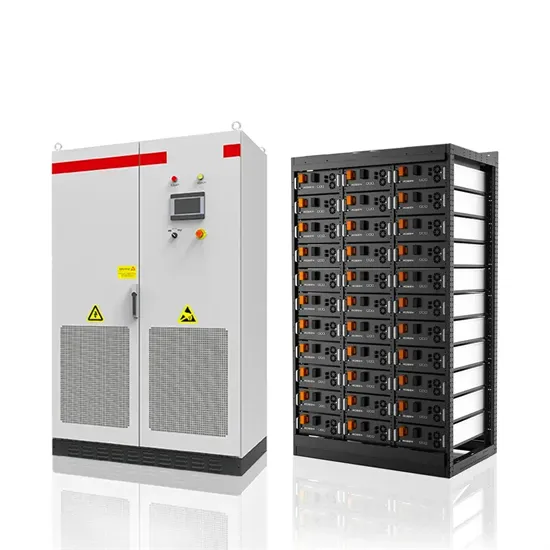
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


