24v or 48v considering as far as I know few appliances use
The big advantage of 12v are the innumerous 12v appliances you can find. But if I don''t want 12v what are the reasons to pick 24v over 48v? Looking at prices, 48v systems seems to be
Get a quote
How many panels can I wire in series for 48V system
I have a 48V DC to 120V AV 5000W inverter. I''m a bit confused about how many panels I can wire in series. I''m assuming that I can wire four 12V panels in series (to get 48V),
Get a quote
24v to 48v Conversion
We lost our 24V Outback inverter to lightning. It was a simple plug and play to get the updated inverter, having the Midnite Solar back panel with necessary bus bars and
Get a quote
The Differences Between 24v and 48v Inverter: Which is Better?
In standard off-grid solar systems, RVs, or mobile power installations, choosing between 24V and 48V inverters can be a difficult decision. This article will analyze the key
Get a quote
The Pros and Cons of 12V DC, 24V DC, and 48V DC Systems –
Increased Complexity: A 48V system, while efficient, is generally more complex to set up and maintain compared to a 12V or 24V system. Components Needed for 48V System
Get a quote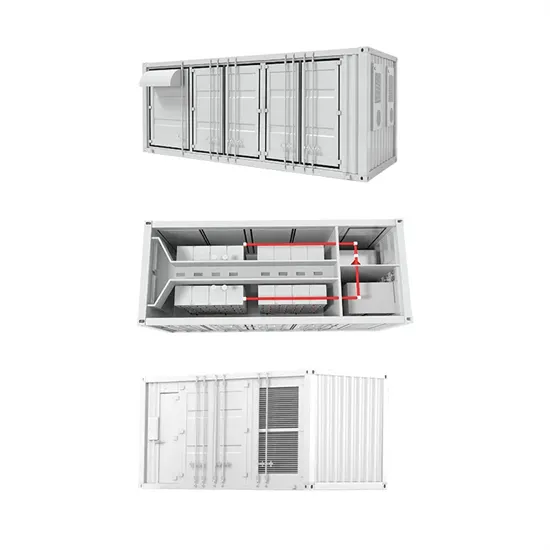
How to Connect Solar Panels to 48v inverter?
Otherwise the life span of your solar system will be greatly reduced. Summarize The connection between solar panels and 48v inverter is roughly
Get a quote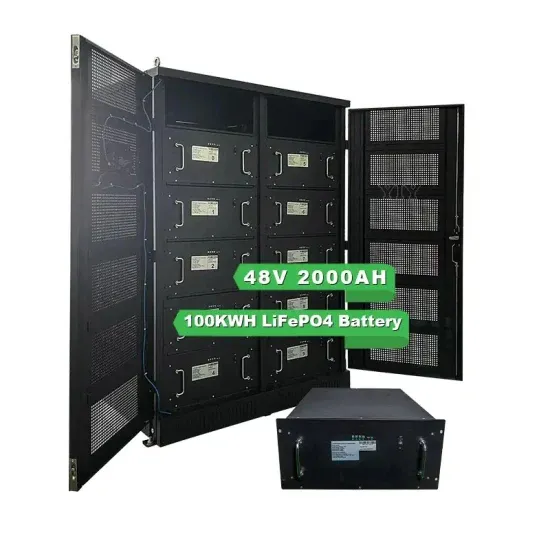
Can you convert 24V to 48V?
Yes, converting 24V to 48V is achievable through series wiring of two 24V batteries, DC-DC boost converters, or motor/controller rewiring. However, success depends
Get a quote
Can I Attach My Small Inverter Directly to the Battery?
For example, a 12V inverter won''t work with a 24V battery bank; the excess voltage can instantly destroy the inverter''s circuitry. Conversely, a 24V inverter connected to a 12V
Get a quote
24v Battery to 48v Inverter
Good Day Everyone, please I am new to this forum and I noticed that a discussion about the question I wanted to ask was discussed already, which is it''s not possible to use a
Get a quote
Can I connect a 12V inverter to work with a bank of Two 12V
It charges fine. Instead of a 24V inverter on the ends, Can I connect a 12V inverter to work by attaching the 12V inverter to the+ and - to of ONLY ONE of the 12V Batteries in the
Get a quote
Can a 48V Inverter Work with a 24V Battery?
No, a 48V inverter cannot work directly with a 24V battery without additional modifications. The key reason for this is the difference in voltage. Inverters are designed to
Get a quote
Can I Use a 24V Inverter on a 48V Battery?
Connecting a 24V inverter to a 48V battery can cause the inverter to fail immediately, leading to permanent damage. Additionally, it can pose safety risks, such as
Get a quote
Can a 24v inverter run from half of a 48 volt bank?
I want to connect the two banks in series to create 1 big 48 volt bank. I have a 24 volt Samlex 1000 I wanted to connect to one of the banks. Would that work or would the samlex see the
Get a quote
Can charge my battery bank with 24v and use with 12v old inverter
I can add another panel only if i add another battery and make it 24v system (MPPT can charge 1440W@24v). I am just curious if I can use the old 12v inverter with 24v
Get a quote
Can I connect two 24v phoenix 3000vac inverters on single 48v
With that in mind, the VE.Bus port would be damaged when you connect the two inverters with the RJ45 cable because one will be 24V higher than the other port. The better
Get a quote
24V vs 48V Solar Systems
When we speak about 24V or 48V solar systems, the voltage in the name can refer to many components. In some cases, it can refer to the voltage of the solar panels, the voltage of the
Get a quote
Advice needed, Converting inverter from 48v to 24v
you need the 24V in series to make 48V and then using Voltage as the charging method on the 5.5kw. Which inverter do you? Deye or Sunsynk? Also check if the batteries
Get a quote
Can A 48V Inverter Connect To A 24V Battery? Compatibility And
No, a 48V inverter cannot recognize a 24V input. 48V inverters are designed to work with a specific input voltage range. The difference in voltage means that the inverter will
Get a quote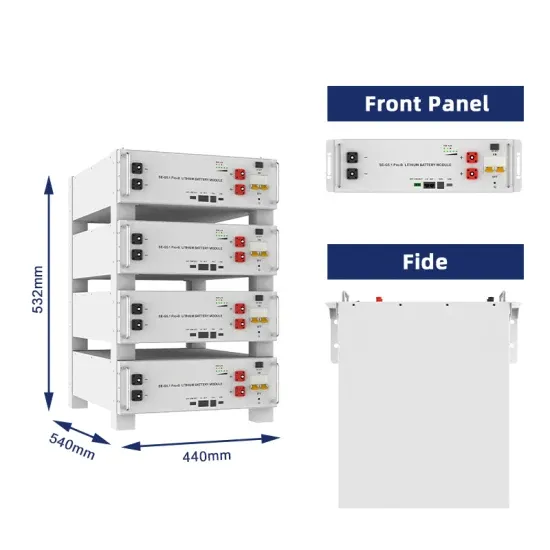
The Differences Between 24v and 48v Inverter: Which
In standard off-grid solar systems, RVs, or mobile power installations, choosing between 24V and 48V inverters can be a difficult
Get a quote
Can a 48V Inverter Work with a 24V Battery? – A Comprehensive
No, a 48V inverter cannot directly work with a 24V battery. Inverters are designed to work with specific input voltage levels, and a 48V inverter is built to operate with a 48V
Get a quote
24v to 48v Conversion
My suggestion is to stick with your inverter until it falters. Purchase LFP batteries in a configuration that will allow you to use them as a 24V system OR 48V. (not an odd
Get a quote
Can I Use A 24V Inverter On A 48V Battery? Compatibility And
Using a 24V inverter with a 48V battery is generally incompatible due to voltage mismatches. The inverter is designed to operate within a specific voltage range, and
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Can a 24v inverter be connected to a 48v]
Can a 24V inverter run a 48v battery?
Explore the basics of using a 24V inverter on a 48V battery setup to understand its compatibility and potential advantages and disadvantages: Inverter Functionality: Inverters convert DC power from batteries into AC power, crucial for running household devices off-grid or during power outages.
Should I use a 48 volt inverter?
You may decide to use them even for appliances that are 2000Watts. When you use a 48-Volts inverter, you can use regular and more flexible connectors to connect the inverter to the battery bank. This is so because the thinner the wire, the higher the resistance.
How much power does a 24V inverter consume?
A good sized 24V inverter could use about as much power just being on as your lights do. If the lights consume 45 watts and run for 12 hours a day, the total power usage would be 45 watts x 12 hours = 540 watts. The battery power required for losses plus the load could double that. The lights themselves may be DC, using a small transformer (wall wart) to go from 120Vac to (likely) 12Vdc.
What are the disadvantages of a 24V inverter?
Efficiency Loss: An inherent disadvantage is efficiency loss. Mismatched voltages, such as using a 24V inverter on a 48V battery, can result in power loss, impacting overall system performance. Compatibility Issues: Mixing different voltage components may lead to compatibility problems.
Is a 24V inverter better than a 48V?
At 48V it drops to a more reasonable 66A. This is actually better than you might think because power loss is proportional to current squared, so if you use your existing wiring and connectors the loss in them will be 4 times higher. A 24V inverter might be a bit cheaper, but you should consider the cost of replacing your wiring and fuses etc.
What is the difference between 24v and 48V?
And that is why I asked about the power rating. The advantage of 48V over 24V is that only half as much current is required to get the same power. Assuming 95% converter efficiency, for 3kW output at 24V your battery wiring has to handle 132A! At 48V it drops to a more reasonable 66A.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Convert 24V to 48V inverter
Convert 24V to 48V inverter
-
 Can a 1kW 48v inverter be connected to 60v
Can a 1kW 48v inverter be connected to 60v
-
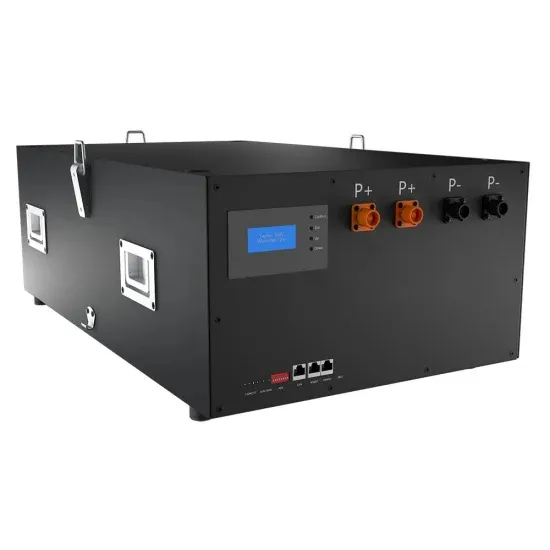
 Energy storage inverter connected to 48v lithium battery
Energy storage inverter connected to 48v lithium battery
-
 Which is better to connect to the inverter 12v 24v 48v
Which is better to connect to the inverter 12v 24v 48v
-
 Can a 24v inverter be used with 48v
Can a 24v inverter be used with 48v
-
 How big of an inverter can a 48v lead-acid battery be connected to
How big of an inverter can a 48v lead-acid battery be connected to
-
 How many watts does a 48v inverter use
How many watts does a 48v inverter use
-
 How big of an inverter can a 12A 48V battery power
How big of an inverter can a 12A 48V battery power
-
 Can a 48V inverter be used with 36V voltage
Can a 48V inverter be used with 36V voltage
-
 Inverter 48v 60v 72v universal
Inverter 48v 60v 72v universal
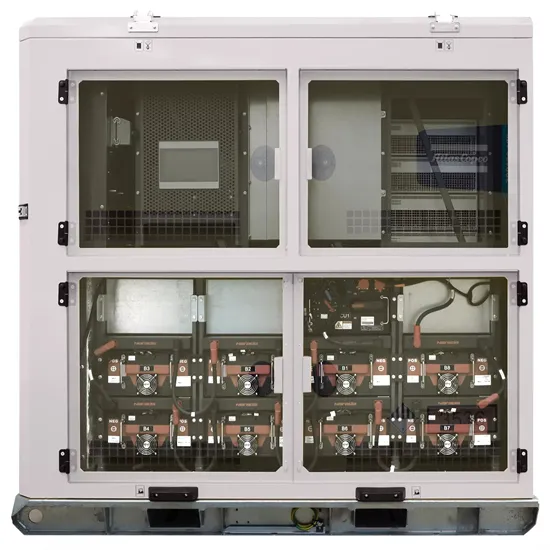
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


