A technical look at 5G energy consumption and performance
Figure 3: Base station power model. Parameters used for the evaluations with this cellular base station power model. Energy saving features of 5G New Radio The 5G NR
Get a quote
Appliance Wattage Guide
How many watts does it take to power basic items in an average size house? In a typical home, essential items will average 5000 - 7500 watts of power to run. What is the difference between
Get a quote
Measurements and Modelling of Base Station Power
Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks significantly varies during a working or weekend
Get a quote
How Many Watts Does a Video Game Console Use?
The power consumption of the Xbox Series X typically ranges between 25 to 100 watts, while the Xbox Series S requires approximately 45 to 220 watts. Related Post:
Get a quote
How Many Watts Does a Laptop Use? Power
Wondering how many watts your laptop uses? Learn about laptop power consumption, including the factors that affect energy usage and tips to
Get a quote
Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Fields:
Although the FCC permits an effective radiated power (ERP) of up to 500 watts per channel (depending on the tower height), the majority of
Get a quote
How Many Watts Does a TV Use: 24, 32, 50, 55, 65 Inch TV and
TVs with 24- or 32-inch displays use virtually little power, while TVs with bigger displays can use up to 250 watts, based on their features and settings. Energy use is greatly
Get a quote
Philips Dreamstation power requirements
DreamStation Auto I see the power supply puts out a max of 12v @ 6.67A ( 80W ). Any idea on what power the CPAP actually draws? (no heated hose, no humidifier) I''m looking
Get a quote
DreamStation 2 12-volt power consumption : r/CPAP
I received my DreamStation2 under the recall replacement for my original DreamStation a little over two months go. I have a few questions and
Get a quote
Why bother to have a high power base station when mobile units
But the base station transmits a lot more power, and this compensates somewhat for the lack of diversity. The phone is about 1W, but if it''s close to the base station, it may be
Get a quote
7 Portable vs Base Station Ham Radio Setups That
Portable rigs typically output 5-20 watts and fit in backpacks, whereas base stations can transmit up to 1,500 watts and require dedicated
Get a quote
Maximum Wattage?
If those stations participated in conversation with mobile and/or portable stations, they would be considered base stations and would be authorized 50 watts to make up for the
Get a quote
Base stations and networks
The antenna output power level is typically between 20 watts and a few hundred watts for an outdoor base station. Television transmitters, by comparison, have 10-1000 times higher
Get a quote
Measurements and Modelling of Base Station Power Consumption under Real
Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks significantly varies during a working or weekend
Get a quote
What''s enough power for a base station? : r/gmrs
Like on the 2m band I''d say 50 watts is plenty, 75 watts is a hell of a lot, and 100 watts is for high up repeaters with important jobs. Just my own $0.02 on that but it tracks with
Get a quote
Efficient Freezer Use: Minimizing Energy Costs
Portable Freezers: These smaller units use less power, typically around 40-100 watts, with starting wattages potentially triple that amount (120
Get a quote
7 Portable vs Base Station Ham Radio Setups That Fit Your
Portable rigs typically output 5-20 watts and fit in backpacks, whereas base stations can transmit up to 1,500 watts and require dedicated space with proper ventilation.
Get a quote
Power Units Explained: Watts, Kilowatts, Megawatts
Megawatts (1,000,000 watts) are typically used to measure the output of small to medium power plants or large renewable energy installations like solar or wind
Get a quote
Power Base Station
Maximum base station power is limited to 24 dBm output power for Local Area base stations and to 20 dBm for Home base stations, counting the power over all antennas (up to four).
Get a quote
Electric Stove Energy Usage: Watts and Amps Explained
Learn how many watts and amps electric stoves use, how to calculate energy consumption, and how OUPES power stations can help support electric
Get a quote
How Much Power Does a 5G Base Station Consume? – Smart Solar
On average, a 5G base station consumes between 1,000 to 3,000 watts. This is significantly higher than 4G base stations, which typically consume 500 to 1,500 watts.
Get a quote
What''s enough power for a base station? : r/gmrs
Like on the 2m band I''d say 50 watts is plenty, 75 watts is a hell of a lot, and 100 watts is for high up repeaters with important jobs. Just my own $0.02 on that but it tracks with my experience.
Get a quote
How Many Watts Does A Gas Furnace Use? (Blower
For heat production, gas furnaces do use natural gas or propane. The main running cost associated with gas furnaces is the price of this fuel. Electric
Get a quote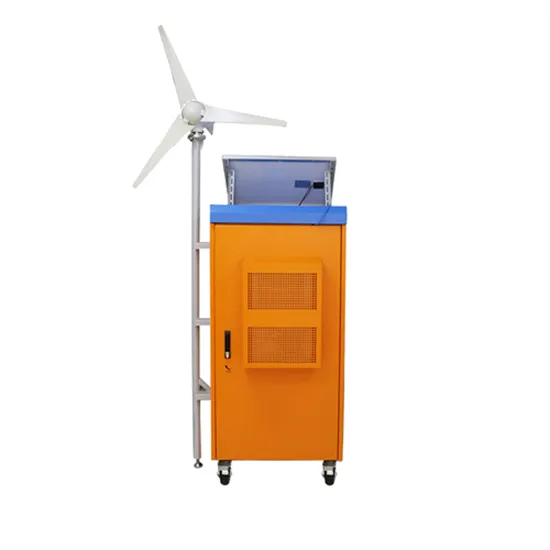
Human Exposure to Radio Frequency Fields: Guidelines for
Although the FCC permits an effective radiated power (ERP) of up to 500 watts per channel (depending on the tower height), the majority of cellular or PCS cell sites in urban and
Get a quote
what is power consumption of base station?
I haven''t run tests on just those but previously I had measured about 40 watts total for my cable modem, Asus RT-N66U router, base station and a dormant USB hard drive to
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [How many watts of power does a base station typically use ]
How much power does a cellular base station use?
This problem exists particularly among the mobile telephony towers in rural areas, that lack quality grid power supply. A cellular base station can use anywhere from 1 to 5 kW power per hour depending upon the number of transceivers attached to the base station, the age of cell towers, and energy needed for air conditioning.
How do base stations affect mobile cellular network power consumption?
Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks significantly varies during a working or weekend day, it is important to quantify the influence of these variations on the base station power consumption.
How many watts can a fixed station transmit?
95.1767 (a) (1) Transmitter power of mobile, repeater, and base stations must not exceed 50 watts. This is for the "main" (a/k/a repeater input/output) channels. It seems that the term "fixed station" is no longer defined by the new rules, so that 15 watt limit seems meaningless.
How much power does an antenna use?
The antenna output power level is typically between 20 watts and a few hundred watts for an outdoor base station. Television transmitters, by comparison, have 10-1000 times higher output power than outdoor base stations. Antennas mounted indoors use very low power levels, typically around a few watts or less.
Which base station elements consume the most energy?
Of the other base station elements, significant energy consumers are: air conditioning (17.5%), digital signal processing (10%) and AC/DC conversion elements (7.5%) . New research aimed at reducing energy consumption in the cellular access networks can be viewed in terms of three levels: component, link and network.
What type of generator does a base station use?
The air conditioning of the base station runs at 220 VAC. These base stations can be powered by two types of diesel generators. The first is the conventional type where 220 VAC is converted to 48 VDC to charge the batteries and power the communication equipment.
Guess what you want to know
-
 How to use the Vaduz mobile communication wind power base station
How to use the Vaduz mobile communication wind power base station
-
 How many watts of power are sufficient for a general base station
How many watts of power are sufficient for a general base station
-
 How much watts of electricity does a mobile base station device use
How much watts of electricity does a mobile base station device use
-
 How many watts of voltage does a 5G base station use
How many watts of voltage does a 5G base station use
-
 How much electricity does a 5G base station use
How much electricity does a 5G base station use
-
 How many volts does China Mobile s base station power supply have
How many volts does China Mobile s base station power supply have
-
 How much electricity does a communication base station use in a year
How much electricity does a communication base station use in a year
-
 How is the photovoltaic power generation of Estonia s green base station
How is the photovoltaic power generation of Estonia s green base station
-
 How much hybrid power supply does a 5G communication base station have
How much hybrid power supply does a 5G communication base station have
-
 How much electricity does a 5G base station in Switzerland use
How much electricity does a 5G base station in Switzerland use
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


