Does Connecting Batteries in Series Increase Amp-Hour (Ah)
When batteries are connected in series, their voltages add up, but their amp-hour capacity does not change. For example, if you connect two 12V batteries rated at 100Ah each
Get a quote
Battery Basics: Series & Parallel Connections for Voltage & Current
Series connections increase the total voltage and keep the current constant, while parallel connections increase the total current and keep the voltage constant.
Get a quote
How are energy storage batteries connected in series?
In series connections, batteries essentially act as a single unit. An increase in the total voltage results from the additive properties of each battery''s voltage, which means that
Get a quote
What happens when there are 2 batteries in a circuit?
What happens when batteries are in parallel? Parallel combination of battery increases output energy. In short, If batteries are
Get a quote
Series and Parallel Circuits in Power Sources
When loads or power sources are connected in series, the voltage increases. Series wiring does not increase the amperage produced. The image at right shows two modules wired in series
Get a quote
Do Amps Add Up in a Battery Series? Current Draw, Voltage, and
In a series battery configuration, the current (amps) remains the same across all batteries, while the voltage increases with each additional battery. This means that while the
Get a quote
Series and Parallel Circuits in Power Sources
When loads or power sources are connected in series, the voltage increases. Series wiring does not increase the amperage produced. The image at right
Get a quote
Why do series combinations of Batteries not increase
I''ve come to realize that batteries connected in series does not increase the capacity. But why is this so? This question explains that it doesnt
Get a quote
How are energy storage batteries connected in series?
In series connections, batteries essentially act as a single unit. An increase in the total voltage results from the additive properties of each
Get a quote
How are the energy storage cells connected in series?
In essence, a series configuration connects the output terminal of one cell to the input terminal of the subsequent cell. This process effectively increases the total voltage while
Get a quote
Complete Guide to Wiring Batteries in Series – PowMr
3 days ago· How to wire 12V batteries in series? This guide explains voltage, amp-hours, precautions, pros&cons, and steps for reliable series battery connections.
Get a quote
Why do series combinations of Batteries not increase Capacity?
I''ve come to realize that batteries connected in series does not increase the capacity. But why is this so? This question explains that it doesnt Adding mAh when wiring
Get a quote
Does Connecting Batteries in Series Increase Amp
When batteries are connected in series, their voltages add up, but their amp-hour capacity does not change. For example, if you connect two
Get a quote
Battery Basics: Series & Parallel Connections for
Series connections increase the total voltage and keep the current constant, while parallel connections increase the total current and keep the voltage constant.
Get a quote
How to Effectively Connect Batteries in Series and Parallel?
Connecting batteries in series or parallel affects voltage, capacity, and overall system performance. Understanding the proper methods and safety precautions ensures
Get a quote
Series and Parallel Battery Connections
Two or more batteries connected in a series increase the voltage of the battery system, but the amperage, or capacity stays the same. Two 6V batteries that
Get a quote
Wiring Two Batteries in Series: A Comprehensive Guide
What Does Wiring Two Batteries in Series Mean? Wiring two batteries in series involves connecting them end-to-end so that the positive
Get a quote
Batteries in Parallel vs. Series: What Are the Differences
Solar energy is a clean, sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, but its intermittent nature makes energy storage more important than ever. In home energy systems, batteries
Get a quote
Solar Battery Series & Parallel: Optimal Setup Guide
The voltage of the connected battery is equal to the sum of the voltage of each battery, and the current is equal to the current of the battery
Get a quote
Batteries in Series vs Parallel: Ultimate Guide
Series connection can increase energy loss due to higher resistance and voltage drop across batteries. Comparison of Current Distribution in Series and Parallel Configurations!
Get a quote
Series vs. Parallel: Understanding Battery Connections
Simple wiring setup. Disadvantages: Doesn''t increase capacity, limiting the total energy storage. If one battery fails, it can affect the entire series. Batteries in Parallel: Advantages and
Get a quote
What Happens If You Connect Different Batteries in
When you connect batteries in parallel, the voltage of each battery remains the same, but the current capacity is increased. This is because the
Get a quote
Batteries Series Vs Parallel Explained
Batteries series vs parallel: Understand the difference between series and parallel battery configurations, including voltage, capacity, and charging methods to optimize
Get a quote
Do Battery Amps Add Up In Series? Increase Output Amps With
Connecting batteries in series increases voltage without changing ampere capacity. For example, two 12V 30Ah batteries in series provide 24V but retain a 30Ah
Get a quote
How Much Current Is available in Series-Connected Batteries?
If 3 fully charged (3.7V (nom), 2.9Ah) li-ion batteries (rated for 2A max per cell), were placed in series to form a 3S battery pack, how much current could a maximum load
Get a quote
Series and Parallel Circuits in Power Sources
Series wiring connections are made at the positive (+) end of one module to the negative (-) end of another module. When loads or power sources are
Get a quote
If batteries are arranged in series in a closed circuit (I.e. with a
What people mean when they say "current doesn''t increase when batteries are in series" is that the maximum current you can get from the batteries doesn''t increase. All
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Does the current increase when batteries are connected in series in an energy storage cabinet ]
What happens if a battery is connected in series?
When batteries are connected in series, the voltage increases while the current stays constant. This is because the current that flows through all components in a series circuit is the same. If you have two 12V batteries, they will provide 24V at the same current as one battery.
Does connecting batteries in series increase battery capacity?
Connecting batteries in series does not increase their amp-hour (Ah) capacity; instead, it increases the overall voltage while keeping the Ah rating constant. This means that while you can achieve higher voltage for your applications, the total energy storage capability, measured in Ah, remains the same as that of a single battery.
Do batteries in series increase voltage and keep ampere capacity the same?
Current Draw, Voltage, and Practical Insights Connecting batteries in series increases voltage but keeps ampere capacity the same. For example, two 12V 30Ah batteries in series produce a combined voltage of 24V. The ampere capacity remains 30Ah, as the positive and negative terminals increase voltage without changing the current capacity.
What is a series battery configuration?
In a series battery configuration, the current (amps) remains the same across all batteries, while the voltage increases with each additional battery. This means that while the total voltage adds up, the current capacity does not increase. In a series configuration, several key points explain how amps work:
How does a series configuration affect battery life?
This definition emphasizes that while series configurations increase voltage, the current draw impacts how long the battery supply lasts. Higher current draw reduces battery life due to increased energy consumption. For instance, if a series configuration experiences a significant current draw, it depletes the batteries faster.
What is the relationship between current draw and battery life?
The relationship between current draw and battery life in series configurations refers to how the amount of electrical current drawn influences the duration a battery can supply power. In a series configuration, batteries are connected end-to-end, and the voltage increases while the current remains the same across all batteries.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Energy storage cabinet batteries are high current batteries
Energy storage cabinet batteries are high current batteries
-
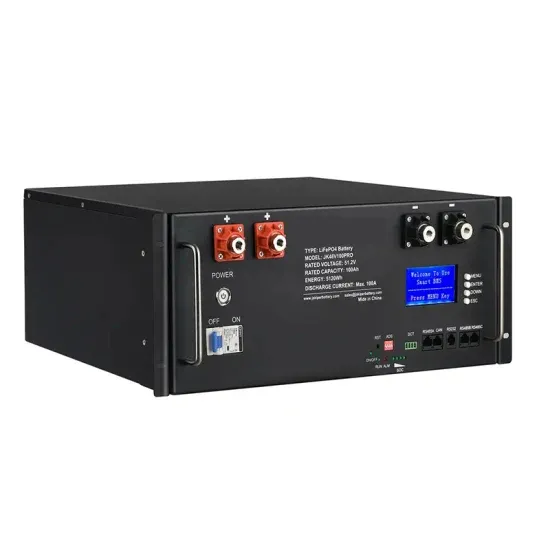 Should the energy storage batteries be connected in series or in parallel
Should the energy storage batteries be connected in series or in parallel
-
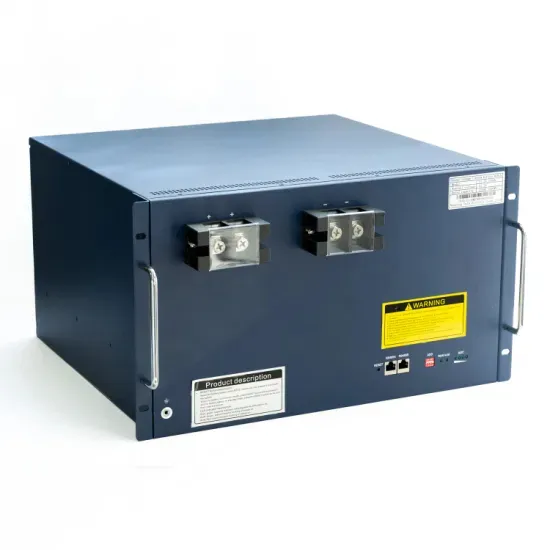 Energy storage cabinets connected in series with batteries
Energy storage cabinets connected in series with batteries
-
 What is the price of energy storage cabinet batteries
What is the price of energy storage cabinet batteries
-
 Are energy storage cabinet batteries alkaline manganese batteries
Are energy storage cabinet batteries alkaline manganese batteries
-
 Conditions for becoming an agent for energy storage cabinet batteries
Conditions for becoming an agent for energy storage cabinet batteries
-
 Liquid-cooled energy storage cabinet with batteries
Liquid-cooled energy storage cabinet with batteries
-
 The connection methods of energy storage cabinet batteries are
The connection methods of energy storage cabinet batteries are
-
 Production time of energy storage cabinet batteries
Production time of energy storage cabinet batteries
-
 Charging voltage and current of energy storage container batteries
Charging voltage and current of energy storage container batteries
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


