What are the five principal wind turbine parts?
What are the main parts of a wind turbine and what are their functions? A wind turbine consists of five main parts and many smaller parts.
Get a quote
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile Connectivity
It consists of electronic equipment, including transceivers, antennas, and signal processors, that manage the communication within a specific geographical area or "cell."
Get a quote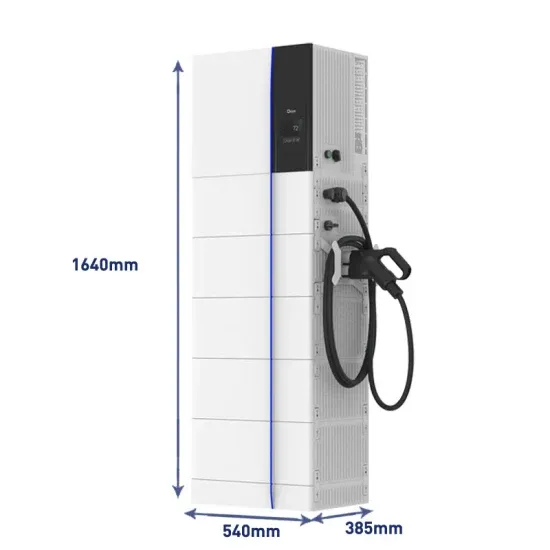
(PDF) Small windturbines for telecom base stations
The presentation will give attention to the requirements on using windenergy as an energy source for powering mobile phone base stations.
Get a quote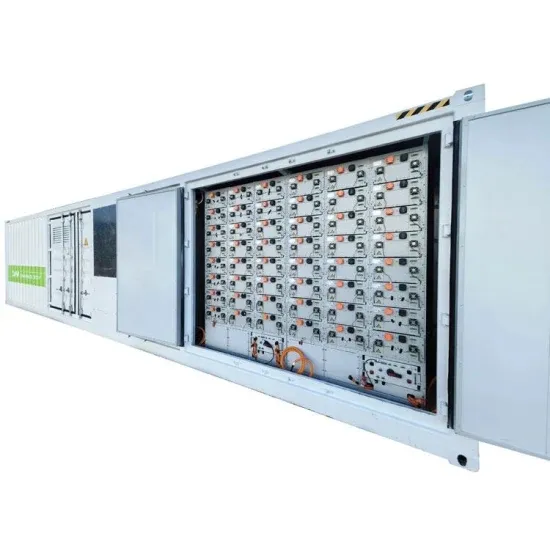
Basic Electronics
Each mobile communicates via radio with one of the base stations and may be handed off to any other base station throughout the duration of the call. Each mobile station consists of a
Get a quote
Wind turbine: what it is, parts and working | Enel
What is a wind turbine? A wind turbine, or wind generator or wind turbine generator, is a device that converts the kinetic energy of wind (a natural and
Get a quote
Base Stations
Base stations form a key part of modern wireless communication networks because they offer some crucial advantages, such as wide coverage, continuous communications and
Get a quote
3.5 kW wind turbine for cellular base station: Radar cross section
Due to dramatic increase in power demand for future mobile networks (LTE/4G, 5G), hybrid- (solar-/wind-/fuel-) powered base station has become an effective solution to reduce fossil fuel
Get a quote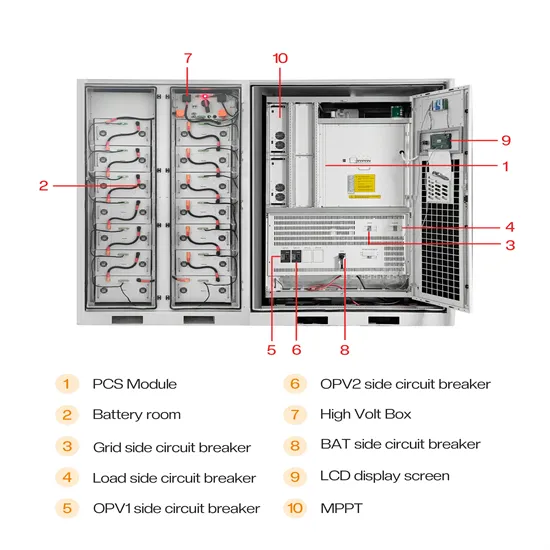
BSS (Base Station Subsystem)
Base Station Subsystem (BSS) is an essential component of the GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) network architecture. It is responsible for managing the
Get a quote
Why Telecom Base Stations?
Variable Speed Operation to improve fuel eficiency Reduces Fuel Consumption (typically by 50 - 80%) PV and small-scale wind generators can be easily incorporated to supplement the
Get a quote
Base Stations and Cell Towers: The Pillars of Mobile
It consists of electronic equipment, including transceivers, antennas, and signal processors, that manage the communication within a
Get a quote
Communication Base Station Energy Power Supply System
The wind-solar-diesel hybrid power supply system of the communication base station is composed of a wind turbine, a solar cell module, an integrated controller for hybrid energy
Get a quote
What is Telecommunication Base Station | China Hop
In addition to these visible parts, the base station also includes many invisible parts. Communication base stations are usually composed of the following
Get a quote
What is Telecommunication Base Station | China Hop
In addition to these visible parts, the base station also includes many invisible parts. Communication base stations are usually composed of the following main components: In the
Get a quote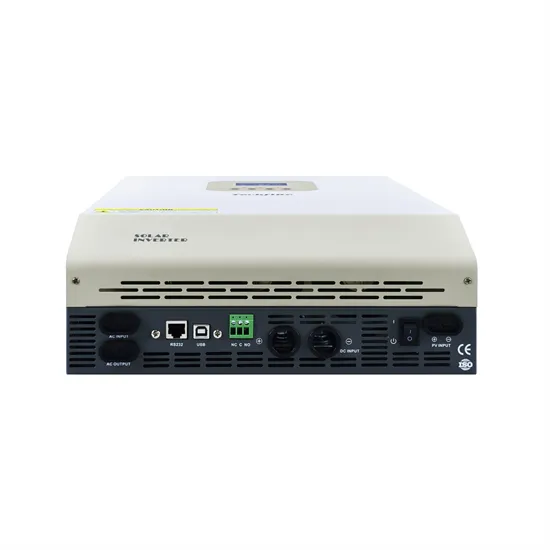
Research on Offshore Wind Power Communication System
Result After the completion of the 5G communication system based on PTN+ integrated small base station, IP transmission based on optical transmission, supporting
Get a quote
CN111836120A
The communication antenna is further hung high, so that the network coverage range is enlarged, the communication of the land and offshore wind power is realized, the construction strength...
Get a quote
Wind Load Test and Calculation of the Base Station Antenna
Among wind load measurement tests, the wind tunnel test simulates the environment most similar to the actual natural environment of the product and therefore is the most accurate test method.
Get a quote
What is a Base Station?
The electromagnetic waves emitted by base stations and mobile phones are like air, filling us all around. Everyone knows mobile phones, however, the base station, the hero
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [The wind power of communication base station consists of five parts]
Can wind energy be used to power mobile phone base stations?
Worldwide thousands of base stations provide relaying mobile phone signals. Every off-grid base station has a diesel generator up to 4 kW to provide electricity for the electronic equipment involved. The presentation will give attention to the requirements on using windenergy as an energy source for powering mobile phone base stations.
What are the components of a base station?
Power Supply: The power source provides the electrical energy to base station elements. It often features auxiliary power supply mechanisms that guarantee operation in case of lost or interrupted electricity, during blackouts. Baseband Processor: The baseband processor is responsible for the processing of the digital signals.
How do base stations work?
Base stations use antennas mounted on cell towers to send and receive radio signals to and from mobile devices within their coverage area. This communication enables users to make voice calls, send texts, and access data services, connecting them to the wider world. Network Management and Optimization
What is a base station in a cellular network?
Base Stations A base station, often housed within a cell site, is the central point in a cellular network where signals are transmitted and received from mobile devices. It consists of electronic equipment, including transceivers, antennas, and signal processors, that manage the communication within a specific geographical area or “cell.”
What are base stations & cell towers?
Base stations and cell towers are critical components of cellular communication systems, serving as the infrastructure that supports seamless mobile connectivity. These structures facilitate the transmission and reception of signals between mobile devices and the wider network, enabling voice calls, text messages, and data services.
What is a block diagram of a base station?
The block diagram of a base station typically includes the following key components: Baseband Processor: The baseband processor too deals with different communication protocols and interfaces with mobile network infrastructure. Duplexer: The duplexer enables the employment of a single antenna for both transmission and reception.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Communication Base Station Wind Power Construction and Maintenance Company
Communication Base Station Wind Power Construction and Maintenance Company
-
 Integrated wind power without communication base station
Integrated wind power without communication base station
-
 Photovoltaic communication base station wind power installation
Photovoltaic communication base station wind power installation
-
 Austria communication base station wind power photovoltaic
Austria communication base station wind power photovoltaic
-
 Approval before setting up wind power station for communication base station
Approval before setting up wind power station for communication base station
-
 Palestine communication base station solar and wind power generation
Palestine communication base station solar and wind power generation
-
 Base station communication equipment wind power
Base station communication equipment wind power
-
 Tajikistan communication wind power base station quotation
Tajikistan communication wind power base station quotation
-
 Guatemala 5G communication base station wind power planning
Guatemala 5G communication base station wind power planning
-
 Wind power station for communication base station built in North African desert
Wind power station for communication base station built in North African desert
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
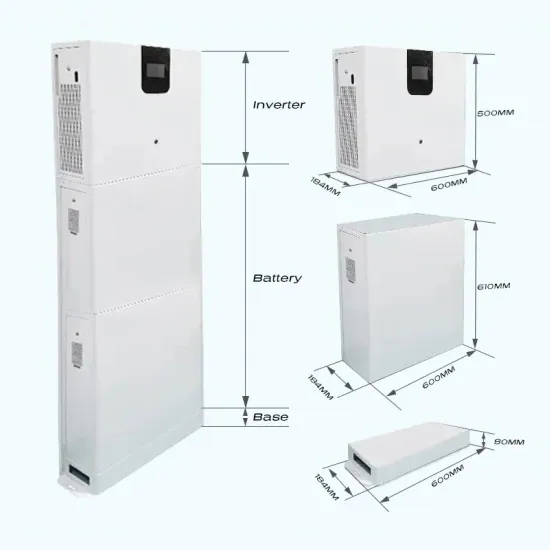
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.