Clean and renewable energy | Denmark leads the way
Solar panels are used to heat up buildings and produce district heating, and solar cells are used to produce electricity. In addition, Denmark has three
Get a quote
Customized ESD Series Stacked Solar Telecom Base Station Power Supply
EverExceed''s stacked solar telecom base station power supply delivers reliable, intelligent, and eco-friendly energy for modern telecom networks. With high-efficiency solar modules,
Get a quote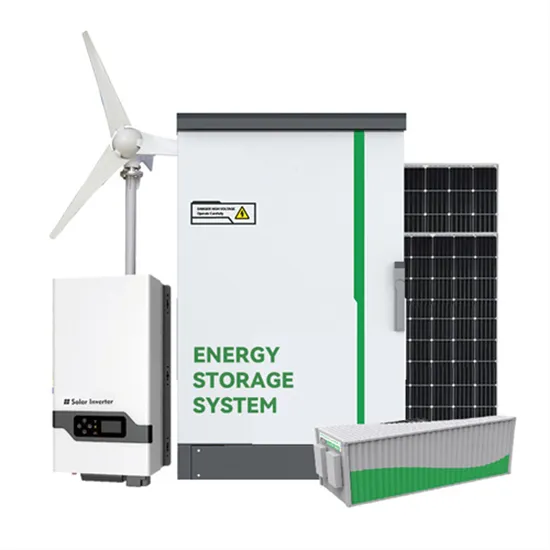
Sustainable Power Supply Solutions for Off-Grid Base
In the context of off-grid telecommunication applications, off-grid base stations (BSs) are commonly used due to their ability to provide radio
Get a quote
Renewable energy in Denmark
Denmark is a leading country in renewable energy production and usage. Renewable energy sources collectively produced 81% of Denmark''s electricity generation in 2022, [5] and are
Get a quote
Energy infomaps
Power production and transmission in Denmark, 2019 Most recent map of the Danish power infrastructure, including the main components of the transmission network, production sites,
Get a quote
Balancing green markets: Denmark sets the standard in Europe
Wind and solar power are becoming increasingly dominant in its energy mix. Coal and natural gas usage are declining, while heat pumps are increasingly popular for residential heating. This
Get a quote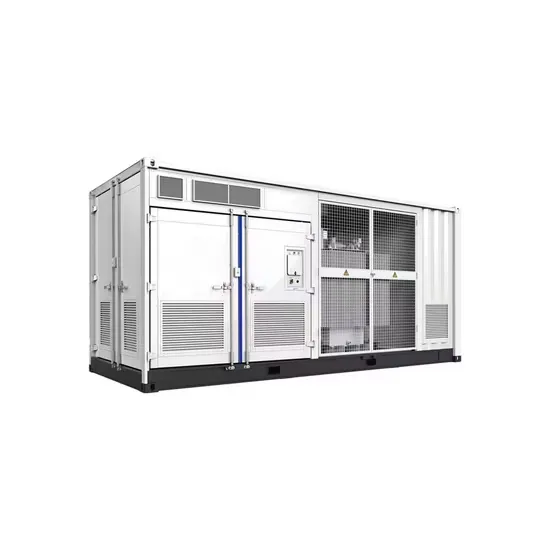
Wind, Solar, and Batteries to Anchor Denmark''s Future Power
As traditional power stations become increasingly marginal, new installations—particularly offshore wind farms and solar arrays—must be equipped to handle
Get a quote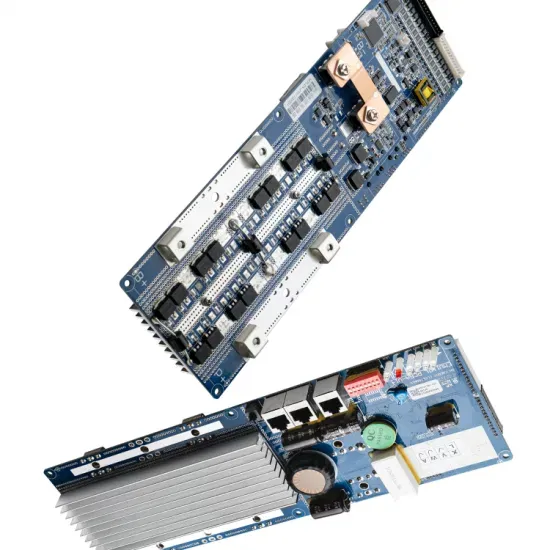
Baseload power is a myth: even intermittent
The old myth was based on the incorrect assumption that base-load demand can only be supplied by base-load power stations; for example,
Get a quote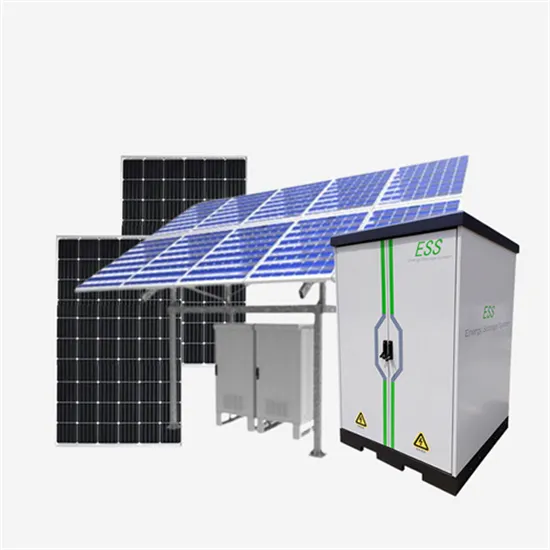
5G telecommunication base station solar power system
5G telecommunication base station solar power system Power plant or substation power for controlling, protection and automatic device, emergency lighting, communications, steam
Get a quote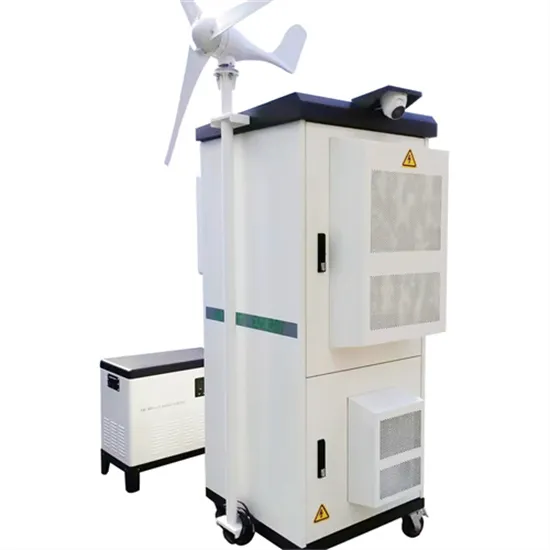
NorSea Denmark Install Solar Panels to Electrify Base Operations
By 2025, NorSea Denmark wants to be the first zero emissions offshore base operation in the world. To propel forward this objective, 1,708 solar panels have been set up
Get a quote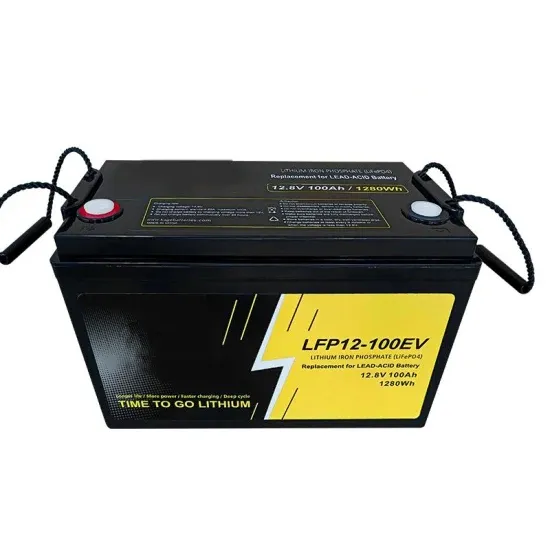
Electricity
The electricity supply is secured by a combination of central power plants, small-scale decentralized CHP plants, wind power, solar PV cells, the electricity network, as well as
Get a quote
Clean and renewable energy | Denmark leads the way | denmark.dk
Solar panels are used to heat up buildings and produce district heating, and solar cells are used to produce electricity. In addition, Denmark has three geothermal energy facilities in operation,
Get a quote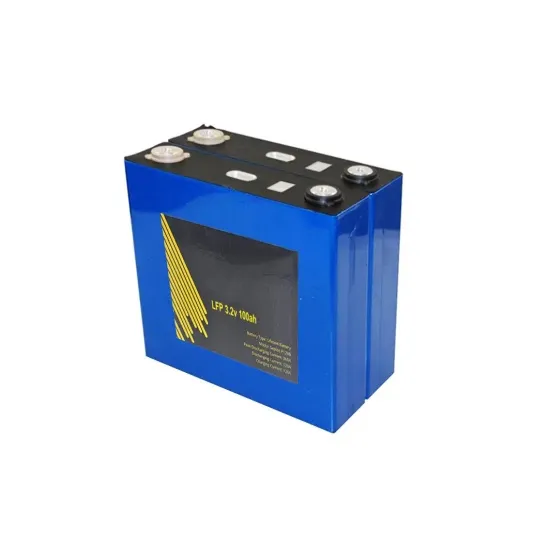
Balancing green markets: Denmark sets the standard
Wind and solar power are becoming increasingly dominant in its energy mix. Coal and natural gas usage are declining, while heat pumps are increasingly
Get a quote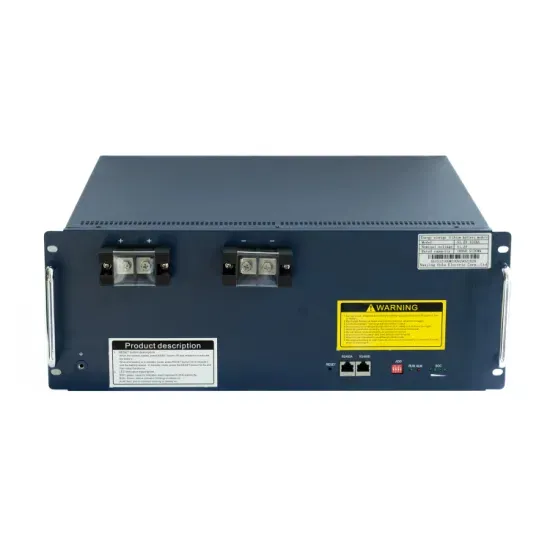
Optimum sizing and configuration of electrical system for
The rising demand for cost effective, sustainable and reliable energy solutions for telecommunication base stations indicates the importance of integration and exploring the
Get a quote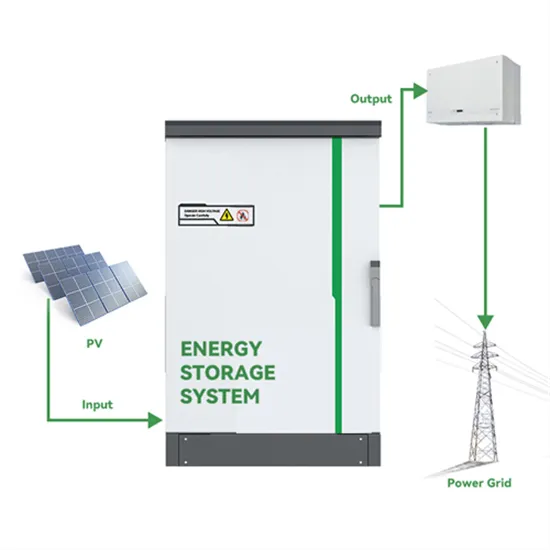
Green energy | Read why the Danish solutions are at front
Today, 50% of electricity in Denmark is supplied by wind and solar power. By 2030, the goal set by the Danish parliament, is that the electricity system in Denmark will be completely
Get a quote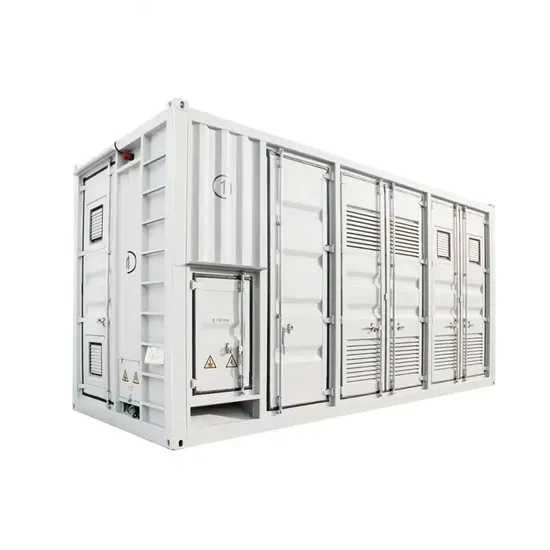
Hybrid Power System; Solar and Diesel for Mobile Base
Description of Project Contents: Project overview In Indonesia, the number of mobile base stations is increasing and telecommunications network traffic is becoming heavier, so that the
Get a quote
Solar Powered Cellular Base Stations: Current
Cellular base stations powered by renewable energy sources such as solar power have emerged as one of the promising solutions to these issues.
Get a quote
Solar energy
Today, we use solar energy in Denmark in two ways: in the form of rooftop solar panels that can produce heat and district heating, and solar cells that can produce electricity.
Get a quote
Security of electricity supply with high shares wind power
Ensuring adequate flexibility in the energy system; More analysis on the risk of extreme events in a future with low production from solar and wind power. More analysis on scenarios with large
Get a quote
Solar Power Plants in Denmark (Map)
Today, we use solar energy in Denmark in two ways: in the form of rooftop solar panels that can produce heat and district heating, and solar cells that can
Get a quote
Solar power in Denmark
Denmark has lower solar insolation than many countries closer to Equator, but lower temperatures increase production. Modern solar cells decrease production by 0.25% per year.
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Solar power supply for base stations in Denmark]
How do we use solar energy in Denmark?
Today, we use solar energy in Denmark in two ways: in the form of rooftop solar panels that can produce heat and district heating, and solar cells that can produce electricity. Why is solar energy important?
How many solar heating plants are there in Denmark?
At the end of 2017, there were 296 solar heating plants (solar heating plants with solar panel areas over 500 square metres) in operation worldwide, 111 of which were located in Denmark. Read also: Denmark at global front within solar heating. Solar heating covers approx. 2% of Denmark’s district heating production.
Why is solar heating important in Denmark?
Solar heating covers approx. 2% of Denmark’s district heating production. One of the big challenges of solar heating is energy storage, because the sun provides the most energy in the summer, when we need it the least to heat buildings. Heat storage is therefore a major research area at DTU.
How many new PV installations are there in Denmark?
In 2013 PV deployment reached 216 MW of new installations, down 32 percent from the previous year. 2012 In 2012, new photovoltaic installations had surged to unprecedented levels in Denmark.
Will solar heating cover 10% of Denmark's heating Consumption by 2050?
The researchers estimate that solar heating can cover 10% of Denmark’s heating consumption by 2030 and 40% by 2050, if the expansion of solar heating plants with thermal heat storage pits continues to develop as it did between 2012-2019.
How does a solar district heating system work in Braedstrup?
In Braedstrup, the community's solar district heating system stores heat in a borehole STES (BTES) facility that uses 19,000 cubic metres of underground strata as a heat battery. It can hold 500 MWh of heat at a temperature of 65 °C. Two water tanks provide additional heat storage.
Guess what you want to know
-
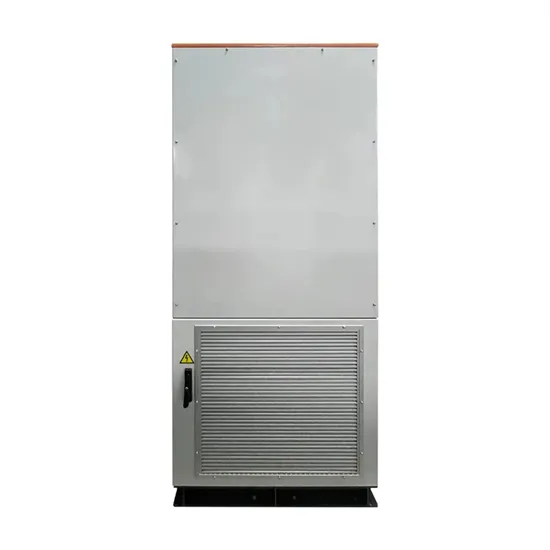 Which solar panel power supply for communication base stations is the most affordable
Which solar panel power supply for communication base stations is the most affordable
-
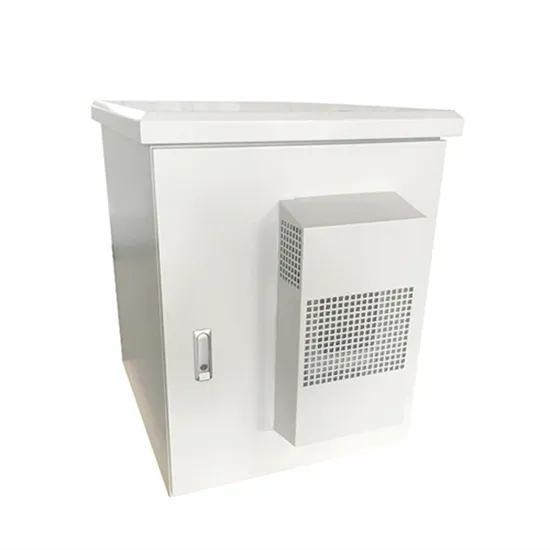 The total hybrid power supply of wind and solar complementary power for national communication base stations
The total hybrid power supply of wind and solar complementary power for national communication base stations
-
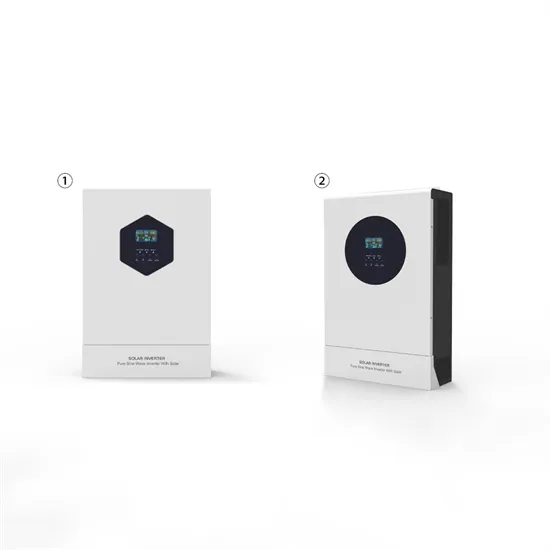 Customized solar power supply price for communication base stations
Customized solar power supply price for communication base stations
-
 Solar power generation hours for communication base stations
Solar power generation hours for communication base stations
-
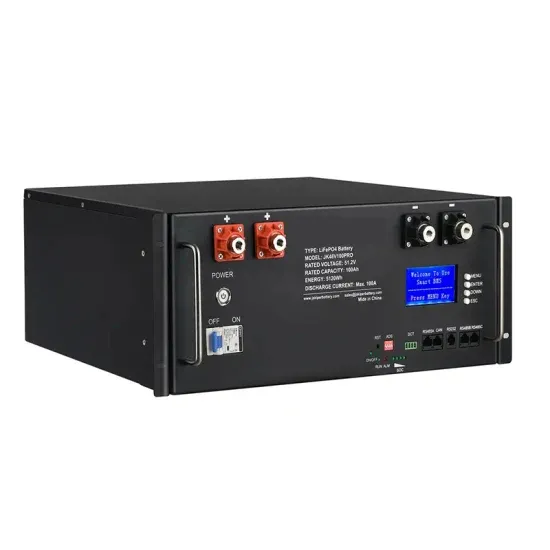 Morocco s communication base station wind and solar hybrid power supply
Morocco s communication base station wind and solar hybrid power supply
-
 Embedded wind power supply for communication base stations
Embedded wind power supply for communication base stations
-
 Detailed introduction of power supply equipment for communication base stations
Detailed introduction of power supply equipment for communication base stations
-
 Power supply price for 5G base stations
Power supply price for 5G base stations
-
 Wholesale price of large solar power for communication base stations
Wholesale price of large solar power for communication base stations
-
 Belize s mobile base station equipment solar hybrid power supply
Belize s mobile base station equipment solar hybrid power supply
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


