Unlocking the Power of Small Wind for Remote Telecom Towers
Small-scale wind turbines reduce reliance on fossil fuels like diesel. They help telecom companies lower carbon emissions, meeting client expectations and sustainability
Get a quote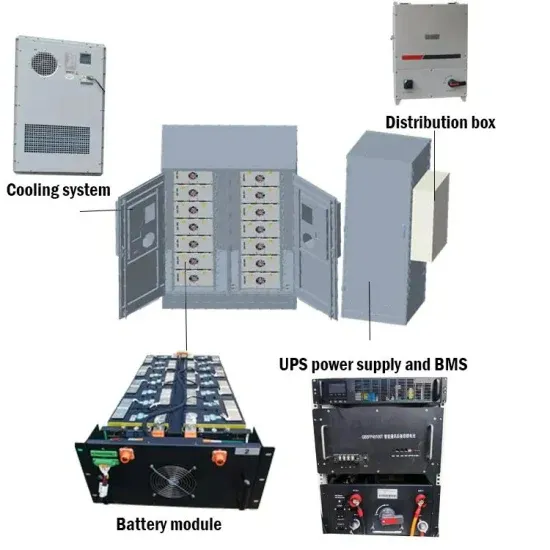
Research on Offshore Wind Power Communication System
Result After the completion of the 5G communication system based on PTN+ integrated small base station, IP transmission based on optical transmission, supporting
Get a quote
Explainer: Why are wind turbines so big – and could smaller be
Project developers are opting for bigger and bigger turbines, in a bid to reduce project footprints – and impact on the environment – while generating maximum power, and
Get a quote
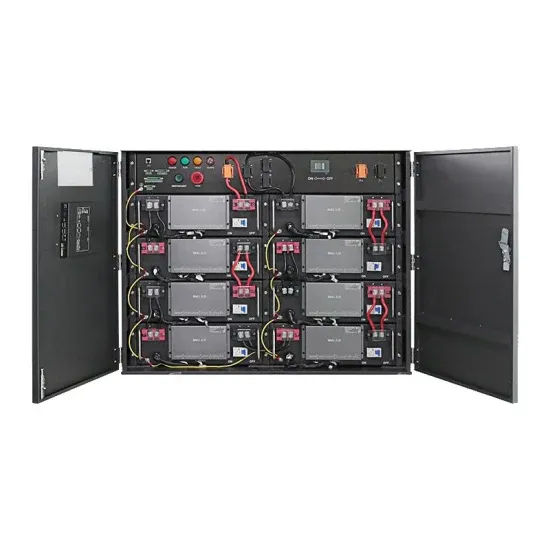
Cooling for Mobile Base Stations and Cell Towers
BackgroundUnattended base stations require an intelligent cooling system because of the strain they are exposed to. The sensitive telecom equipment is
Get a quote
Wind power''s rise: why it''s taking the world by storm
Unlike fossil fuel power plants, wind turbines don''t release harmful pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, and mercury. This results in significant public
Get a quote
WINDExchange: What Is Wind Power?
Wind power is the nation''s largest source of renewable energy, with wind turbines installed in all 50 states supplying more than 10% of total U.S electricity and
Get a quote
(PDF) Small windturbines for telecom base stations
The presentation will give attention to the requirements on using windenergy as an energy source for powering mobile phone base stations.
Get a quote
Towers of power: why wind turbines are getting taller
Hilly terrain (like a mountain ridge) may also distort the wind, requiring engineers to design the wind turbines to be even taller to catch the
Get a quote
What''s the carbon footprint of a wind turbine?
Power plants that burn natural gas are responsible for 437 to 758 grams of CO2-equivalent per kilowatt-hour — far more than even the most
Get a quote
Unlocking the Power of Small Wind for Remote
Small-scale wind turbines reduce reliance on fossil fuels like diesel. They help telecom companies lower carbon emissions, meeting client
Get a quote
Impact analysis of wind farms on telecommunication services
This paper presents a comprehensive review on the impact of wind turbines on the telecommunication services, with special dedication to the methodology to be applied in order
Get a quote
Technical Keys to Successful Network Modernization:
As wireless services continue to soar, providers are deploying more and more base station antennas, fiber connections and other equipment in order to meet the growing demand. The
Get a quote
Why Are Radio Communication Antennas Getting Smaller?
In the world of wireless communication, one trend is impossible to ignore: antennas are getting smaller and smaller. From chunky VHF rods to tiny embedded patches, antenna
Get a quote
The role of communications and standardization in wind power
Increasing penetration of Wind Power Plants (WPPs) in power systems networks has necessitated the need for more efficient, reliable, and economic communication systems
Get a quote
Explainer: Why are wind turbines so big – and could
Project developers are opting for bigger and bigger turbines, in a bid to reduce project footprints – and impact on the environment – while
Get a quote
Exploiting Wind Turbine-Mounted Base Stations to Enhance
We investigate the use of wind turbine-mounted base stations (WTBSs) as a cost-effective solution for regions with high wind energy potential, since it could replace or even outperform
Get a quote
Why wind energy from the High Plains can''t get to other Texans
While wind farms in the region could help power and lower energy costs for at least 9 million homes, significant infrastructure upgrades would be needed to supply electricity from
Get a quote
The Pros and Cons of Wind Power for Data Center Sustainability
Discover the nuances of leveraging wind power for data centers, weighing its efficiency and reliability against other sustainable solutions.
Get a quote
Communications: Planning for wind turbines
Proposed wind farm developments often receive objections due to potential issues with regard to wireless communications systems. Objections
Get a quote
Bigger is not always better: how small scale wind
Conventional wisdom dictates that larger wind farms are more efficient and effective, but as wind power becomes a more significant component of the world''s energy mix,
Get a quote
How does onshore wind power work?
That''s much less than the steam turbine in a fossil-fuel power station, which is why wind turbines are grouped together to create a wind farm. The wind farm
Get a quote
Solutions to reduce effect of wind power on digital communications
Using methods developed by VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, wind farms can now be designed to minimize their effects on television broadcasting and mobile
Get a quote
How to make wind solar hybrid systems for telecom
Wind solar hybrid systems can fully ensure power supply stability for remote telecom stations. Meet the growing demand for communication services.
Get a quote
Why Are Wind Turbines Getting Larger?
Larger devices produce more emission-free electricity than smaller variants. Sustainability policies and regulations, like the United Nations (UN) Paris Agreement, may
Get a quote
3.5 kW wind turbine for cellular base station: Radar cross section
Due to dramatic increase in power demand for future mobile networks (LTE/4G, 5G), hybrid- (solar-/wind-/fuel-) powered base station has become an effective solution to reduce fossil fuel
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Why are wind power plants at communication base stations getting smaller and smaller ]
How can a small wind turbine help the telecom industry?
As the push for net-zero carbon emissions accelerates, the telecom sector must adopt innovative, renewable energy solutions for telecom sites. Small wind turbines provide a secure and cost-effective alternative. They ensure telecom towers run smoothly, even in remote and challenging environments.
Can wind energy be used to power mobile phone base stations?
Worldwide thousands of base stations provide relaying mobile phone signals. Every off-grid base station has a diesel generator up to 4 kW to provide electricity for the electronic equipment involved. The presentation will give attention to the requirements on using windenergy as an energy source for powering mobile phone base stations.
Do base station antennas reduce tower weight & wind load issues?
Performance factors aside, antennas with better frontal loading design and lesser weight will decrease overall tower weight and wind load issues. Base station antennas add load to the towers not only due to their mass, but also in the form of additional dynamic loading caused by the wind.
Why do telecom companies use wind power?
They help telecom companies lower carbon emissions, meeting client expectations and sustainability goals. Wind power enables companies to achieve these targets while reducing their carbon footprint. Small wind turbines generate electricity on-site, minimizing dependence on grid power and expensive diesel fuel.
Which telecommunication services are more sensitive to wind turbines?
The telecommunication services included in this review are those that have demonstrated to be more sensitive to nearby wind turbines: weather, air traffic control and marine radars, radio navigation systems, terrestrial television and fixed radio links.
Can wind turbines be used for telecom towers?
Natural disasters like bushfires and floods exacerbated the problem. To address this, Diffuse Energy, a Newcastle-based startup, developed small-scale wind turbines for telecom towers. Supported by $341,990 in funding from the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA), they installed turbines at 10 remote sites.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Where are the wind power plants for Yemeni communication base stations
Where are the wind power plants for Yemeni communication base stations
-
 About the height of wind power construction for communication base stations
About the height of wind power construction for communication base stations
-
 Wind power replacement plan for communication base stations
Wind power replacement plan for communication base stations
-
 Wind power costs for communication base stations
Wind power costs for communication base stations
-
 What types of wind power are there for cross-border communication base stations
What types of wind power are there for cross-border communication base stations
-
 What types of wind power equipment are there in communication base stations
What types of wind power equipment are there in communication base stations
-
 Large wind power supply for communication base stations
Large wind power supply for communication base stations
-
 How to move communication base stations away from wind power
How to move communication base stations away from wind power
-
 The role of wind power in communication base stations
The role of wind power in communication base stations
-
 Wind power generation for powering communication base stations
Wind power generation for powering communication base stations
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


