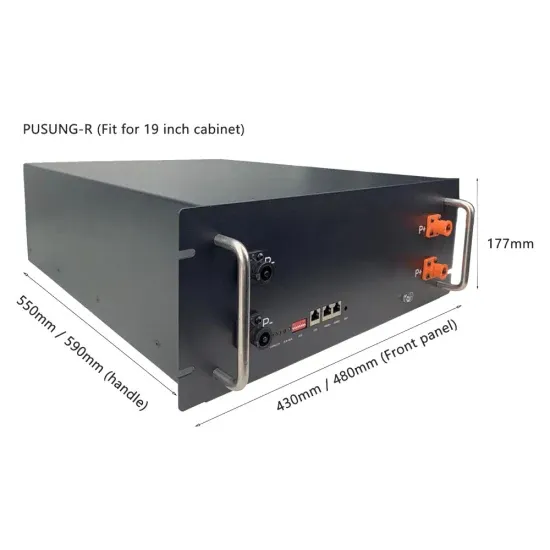
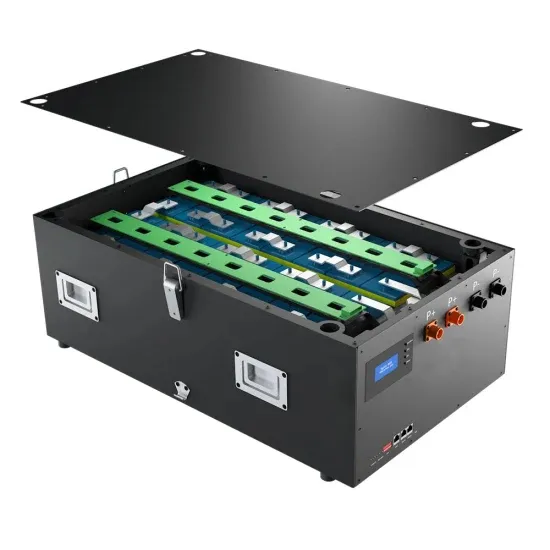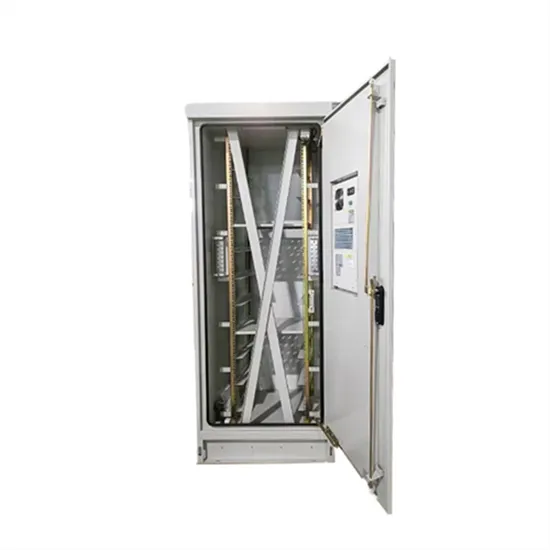
How Solar Energy Systems are Revolutionizing Communication Base Stations?
Energy consumption is a big issue in the operation of communication base stations, especially in remote areas that are difficult to connect with the traditional power grid,
Get a quote
Power consumption analysis of access network in 5G mobile communication
The architectural differences of these networks are highlighted and power consumption analytical models that characterize the energy consumption of radio resource
Get a quote
EFFICIENT POWER UTILIZATION IN COMMUNICATION
This parallel increase in usage of cellular phones has lead to implementation of communication towers called base stations.. The base stations comprises of electronic equipment and
Get a quote
Optimal energy-saving operation strategy of 5G base station with
To further explore the energy-saving potential of 5 G base stations, this paper proposes an energy-saving operation model for 5 G base stations that incorporates communication caching
Get a quote
Comparison of Power Consumption Models for 5G Cellular
The first step when modeling the energy consumption of wireless communication systems is to derive models of the power consumption for the main system components, which
Get a quote
Comparison of Power Consumption Models for 5G Cellular Network Base
The first step when modeling the energy consumption of wireless communication systems is to derive models of the power consumption for the main system components, which
Get a quote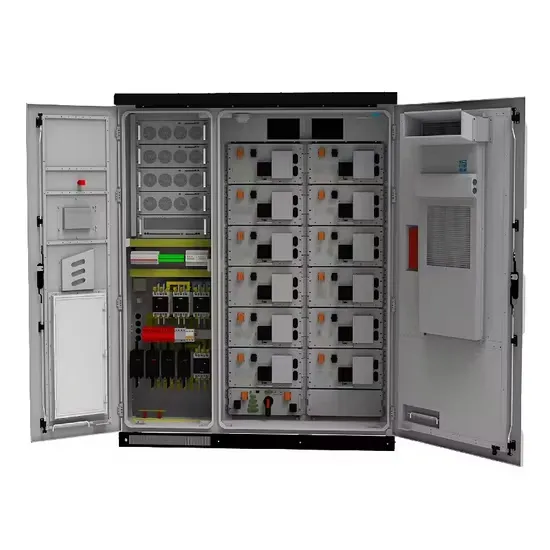
(PDF) INVESTIGATORY ANALYSIS OF ENERGY
This study examines the energy requirements of a multi-tenant BTS, focusing on power consumption patterns, key energy-intensive components, and optimization strategies.
Get a quote
Power Consumption Modeling of Different Base Station
In this work the electrical input power of macro and micro base stations in cellular mobile radio networks is characterized and quanti ed in dependence of the load level. The model
Get a quote
Energy-efficiency schemes for base stations in 5G heterogeneous
In today''s 5G era, the energy efficiency (EE) of cellular base stations is crucial for sustainable communication. Recognizing this, Mobile Network Operators are actively prioritizing EE for
Get a quote
Multi-objective interval planning for 5G base station
Large-scale deployment of 5G base stations has brought severe challenges to the economic operation of the distribution network, furthermore,
Get a quote
Measurements and Modelling of Base Station Power Consumption under Real
Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks significantly varies during a working or weekend
Get a quote
The electric power consumption when installed the
The high electric power consumption of air conditioning in communication base station needs to be solved urgently. This paper presents a new technology to
Get a quote
Power consumption based on 5G communication
This paper proposes a power control algorithm based on energy efficiency, which combines cell breathing technology and base station sleep technology to reduce base station energy
Get a quote
Power Base Station
Base station power refers to the output power level of base stations, which is defined by specific maximum limits (24 dBm for Local Area base stations and 20 dBm for Home base stations)
Get a quote
Coordinated scheduling of 5G base station energy storage for
Auxiliary equipment includes power supply equipment, monitoring and lighting equipment. The power supply equipment manages the distribution and conversion of electrical
Get a quote
Power Consumption Modeling of 5G Multi-Carrier Base
However, there is still a need to understand the power consumption behavior of state-of-the-art base station architectures, such as multi-carrier active antenna units (AAUs), as well as the
Get a quote
Key Factors Affecting Power Consumption in Telecom Base Stations
Discover the key factors influencing power consumption in telecom base stations. Optimize energy efficiency and reduce operational costs with our expert insights.
Get a quote
Domain Ontology Modeling of Communication Base Station Energy Consumption
Given the limitations of decision analysis caused by the inability to efficiently integrate and describe large-scale heterogeneous data in current research on communication base station
Get a quote
Measurements and Modelling of Base Station Power
Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks significantly varies during a working or weekend
Get a quote
Key Factors Affecting Power Consumption in Telecom
Discover the key factors influencing power consumption in telecom base stations. Optimize energy efficiency and reduce operational costs with
Get a quote
Energy Consumption Assessment of Mobile Cellular Networks
II. BASE STATION SITE POWER CONSUMPTION MODEL Since the energy efficiency metrics of a mobile cellular network cannot be formulated with an understanding of the power
Get a quote
Low-Carbon Sustainable Development of 5G Base Stations in China
Many countries have made significant investments in digital infrastructure, including 5G base stations which have become a critical component of this infrastructure. However, due
Get a quote
Front Line Data Study about 5G Power Consumption
The two figures above show the actual power consumption test results of 5G base stations from different manufacturers, ZTE and HUAWEI, in Guangzhou and Shenzhen, by an anonymous
Get a quote
Power consumption modeling of different base station types in
In wireless communications micro cells are potentially more energy efficient than conventional macro cells due to the high path loss exponent. Also, heterogeneous
Get a quote
Measurements and Modelling of Base Station Power
Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks
Get a quote
Front Line Data Study about 5G Power Consumption
The two figures above show the actual power consumption test results of 5G base stations from different manufacturers, ZTE and HUAWEI, in Guangzhou and
Get a quote
Measurements and Modelling of Base Station Power Consumption
Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks significantly varies during a
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Communication base station electricity consumption]
What is a base station power consumption model?
In recent years, many models for base station power con-sumption have been proposed in the literature. The work in proposed a widely used power consumption model, which explicitly shows the linear relationship between the power transmitted by the BS and its consumed power.
How do base stations affect mobile cellular network power consumption?
Base stations represent the main contributor to the energy consumption of a mobile cellular network. Since traffic load in mobile networks significantly varies during a working or weekend day, it is important to quantify the influence of these variations on the base station power consumption.
Do base stations dominate the energy consumption of the radio access network?
Furthermore, the base stations dominate the energy consumption of the radio access network. Therefore, it is reasonable to focus on the power consumption of the base stations first, while other aspects such as virtualization of compute in the 5G core or the energy consumption of user equipment should be considered at a later stage.
Is there a direct relationship between base station traffic load and power consumption?
The real data in terms of the power consumption and traffic load have been obtained from continuous measurements performed on a fully operated base station site. Measurements show the existence of a direct relationship between base station traffic load and power consumption.
What is the largest energy consumer in a base station?
The largest energy consumer in the BS is the power amplifier, which has a share of around 65% of the total energy consumption . Of the other base station elements, significant energy consumers are: air conditioning (17.5%), digital signal processing (10%) and AC/DC conversion elements (7.5%) .
Which base station elements consume the most energy?
Of the other base station elements, significant energy consumers are: air conditioning (17.5%), digital signal processing (10%) and AC/DC conversion elements (7.5%) . New research aimed at reducing energy consumption in the cellular access networks can be viewed in terms of three levels: component, link and network.
Guess what you want to know
-
 5g communication base station power consumption calculation
5g communication base station power consumption calculation
-
 Communication base station energy storage system reduces energy consumption at night
Communication base station energy storage system reduces energy consumption at night
-
 How much electricity does a communication base station use in a year
How much electricity does a communication base station use in a year
-
 How much electricity does a communication base station use
How much electricity does a communication base station use
-
 China s 5G base station electricity consumption ranking
China s 5G base station electricity consumption ranking
-
 Energy consumption of communication base station inverter equipment
Energy consumption of communication base station inverter equipment
-
 Manton 5G base station electricity consumption
Manton 5G base station electricity consumption
-
 Lithium iron phosphate battery for communication base station energy storage
Lithium iron phosphate battery for communication base station energy storage
-
 Virtual Power Plant Communication Base Station
Virtual Power Plant Communication Base Station
-
 Communication base station lead-acid battery transmission construction
Communication base station lead-acid battery transmission construction
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.


