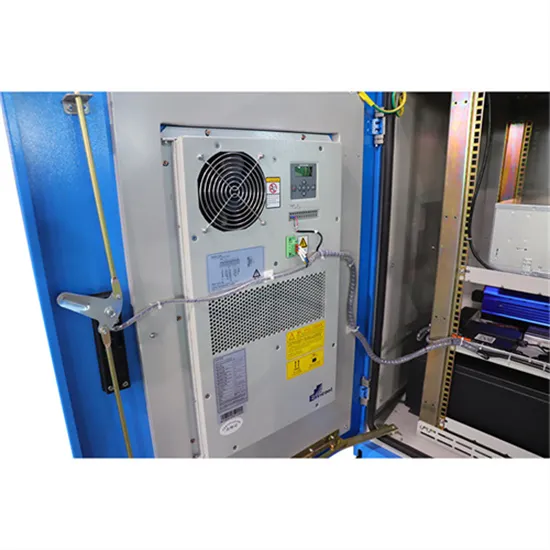

6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
Almost any solar systems of any scale include an inverter of some type to allow the power to be used on site for AC-powered appliances or on the grid. Different types of inverters are shown
Get a quote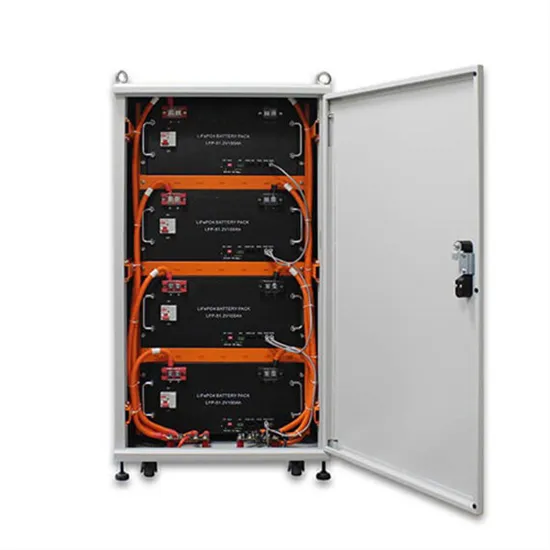
INVERTER
The machine can start The starting torque during inverter operation should be smaller than the torque during commercial power supply operation. Select appropriate capacities for the motor
Get a quote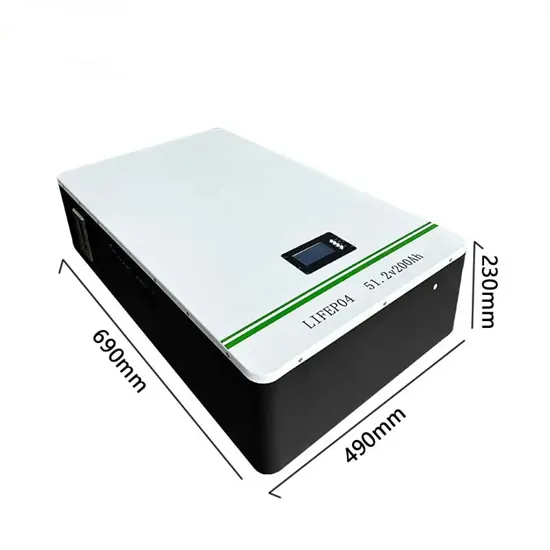
Inverter : Operating Principle,Circuit, Classification and Applications
Definition: The inverter is an electronic circuit that converts fixed DC supply to variable AC supply. The inverter is used to run the AC loads through a battery or control AC
Get a quote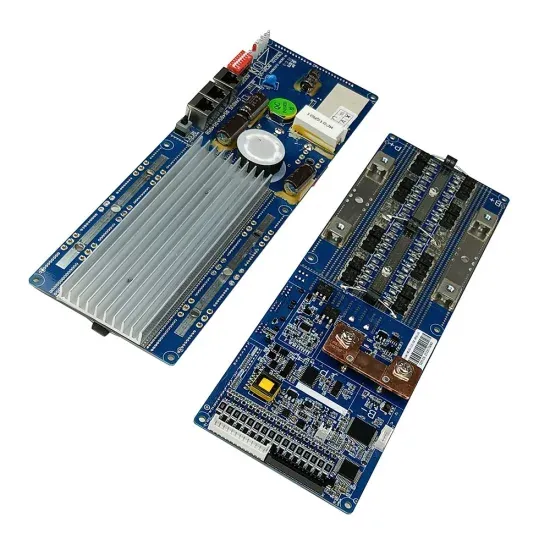
6.4. Inverters: principle of operation and parameters
Almost any solar systems of any scale include an inverter of some type to allow the power to be used on site for AC-powered appliances or on the grid.
Get a quote
INVERTER SCHOOL TEXT INVERTER BEGINNER
For the external operation, an inverter is operated with the control signal from outside the inverter according to the specification of the machine operation, and normally operated with a signal
Get a quote
What is a power inverter? Uses and operation
A power inverter is an electronic device. The function of the inverter is to change a direct current input voltage to a symmetrical alternating current output voltage, with the
Get a quote
INVERTER SCHOOL TEXT INVERTER PRACTICAL
A main characteristic of the inverter is the operation with various signals. This Chapter explains about operations (start, stop, speed variation) that can be made with the demonstration machine.
Get a quote
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
How do Inverters work? In this article we''ll be learning how inverters work, starting from the very basics. We''ll cover Pulse Width
Get a quote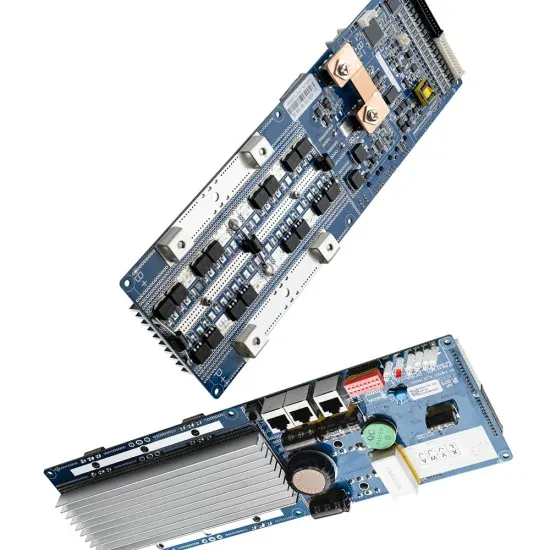
Confusion on meaning of Off Grid vs Grid-tie vs Zero Export
Since you are on grid, you want a grid-tie inverter. Since you do not want to sell any power to the power company, you want a zero export function, which puts current
Get a quote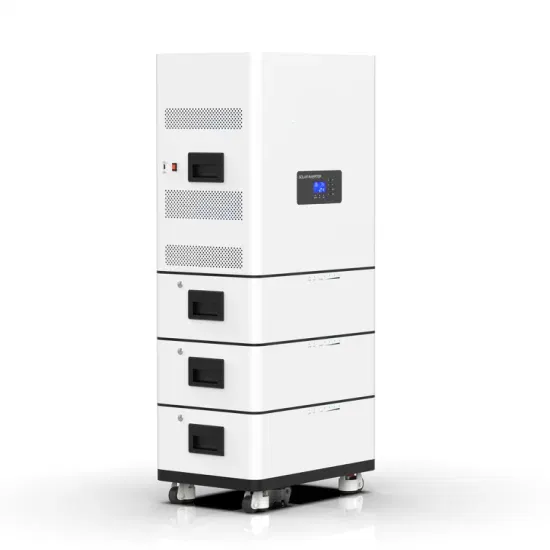
How to run an inverter without a battery
Battery backup systems are commonly used with inverters, but did you know you can run an inverter without one? In this guide, you''ll discover how to directly power your
Get a quote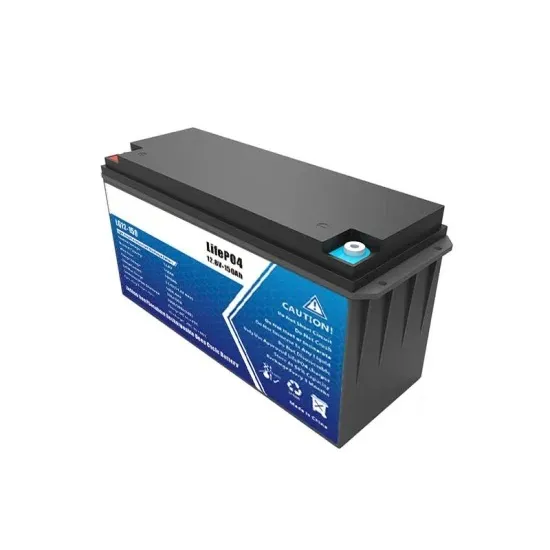
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To Power Conversion
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and expert insights.
Get a quote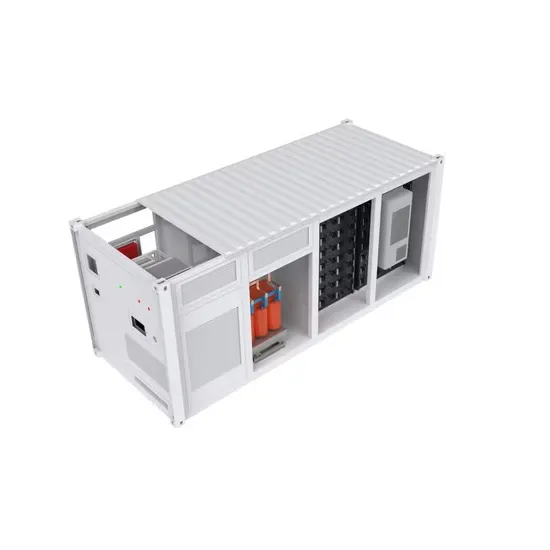
lecture12.DVI
VM= 2 V+ VIN Ideal inverter returns well defined logical outputs (0 or V +) even in the presence of considerable noise in (from voltage spikes, crosstalk, etc.) logic level restoration noise
Get a quote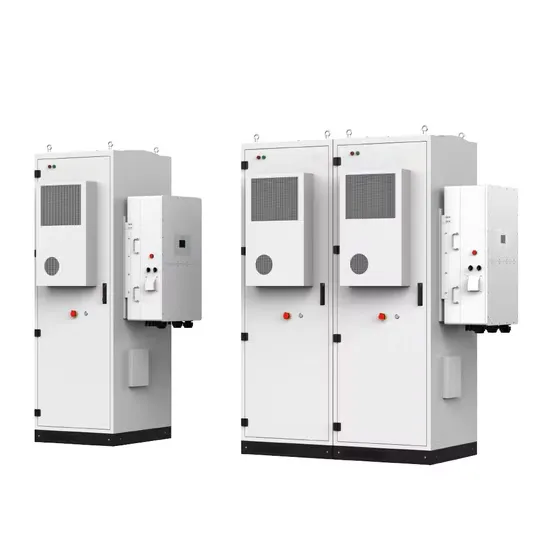
How does an inverter work?
We''ll start the introduction by explaining the inverter device''s mechanism in detail. The inverter device''s role is to control the voltage and frequency of the power
Get a quote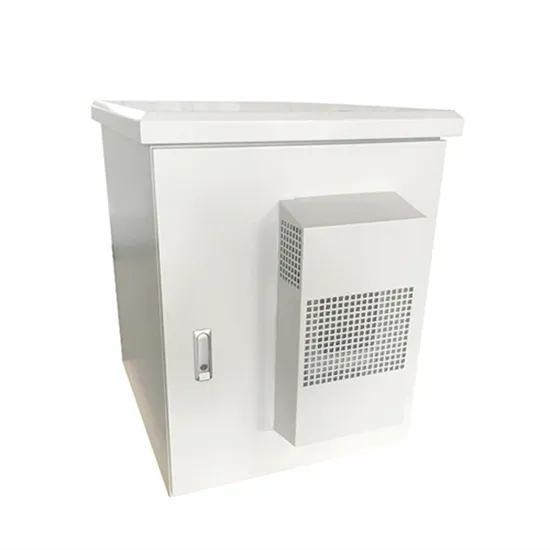
How Inverters Work
How do Inverters work? In this article we''ll be learning how inverters work, starting from the very basics. We''ll cover Pulse Width Modulation, PWM and variable frequency drives.
Get a quote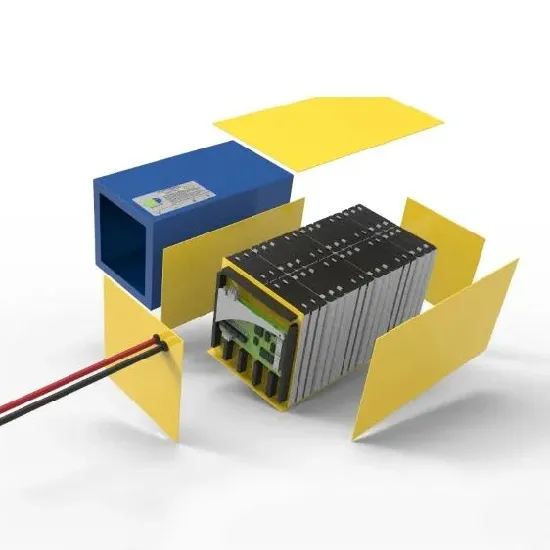
Inverter: Types, Circuit Diagram and Its Applications
What is an Inverter? An inverter can be defined as it is a compact and rectangular shaped electrical equipment used to convert direct current (DC) voltage to
Get a quote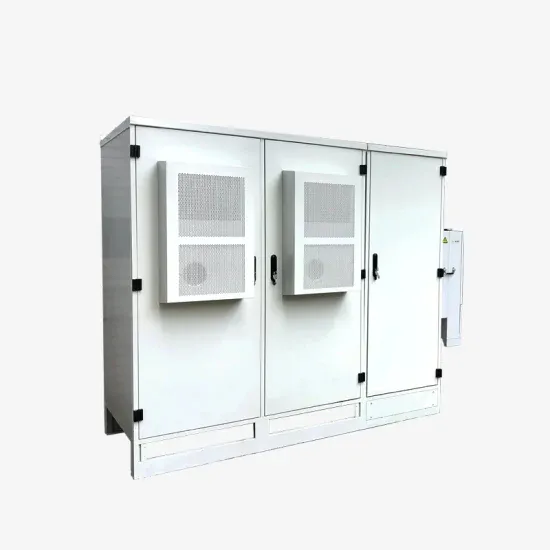
A Control Strategy for Suppressing Zero-Crossing Current of
In this paper, a control strategy to suppress the zero-crossing current of a single-phase half-bridge three-level active neutral-point-clamped inverter is proposed. The operating
Get a quote
How Much Power Does an Inverter Draw with no Load?
The no-load power consumption of an inverter, also known as standby power consumption or static power consumption, refers to the power that the inverter still needs to
Get a quote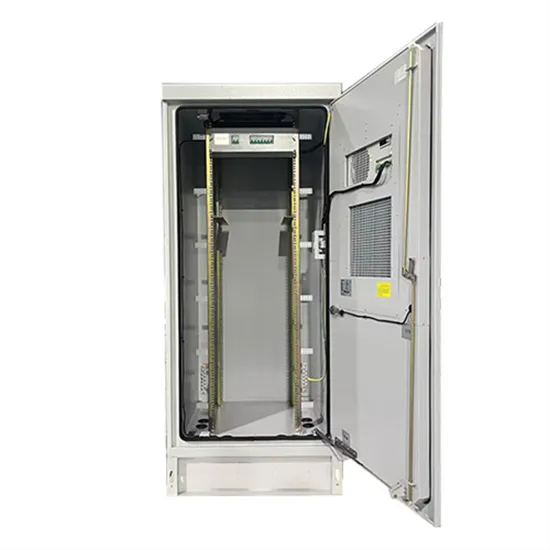
Okaya Advanced UPS/Inverter for Home – Buy at Best Price
Shop Okaya home inverters/UPS at best prices in India. True Sine Wave output, Super IntelliCharge fast charging & advanced smart protections. Range 700–2000 VA.
Get a quote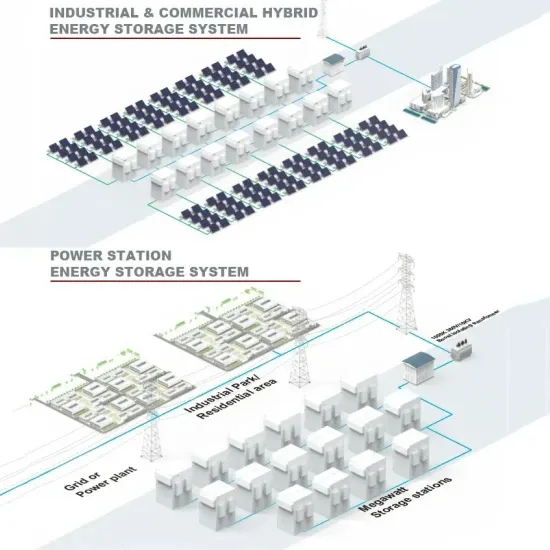
ECCE12 LoadMod ClassE full paper v11''
Abstract—Single-switch inverters such as the conventional class E inverter are often highly load sensitive, and maintain zero-voltage switching over only a narrow range of load resistances.
Get a quote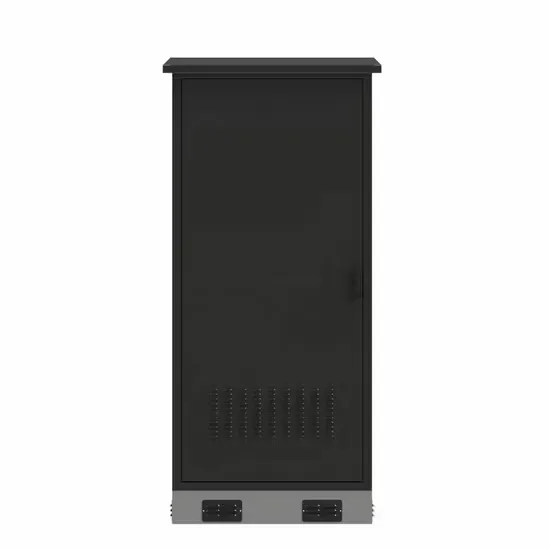
Power Inverters: What Are They & How Do They Work?
An inverter is a static device that converts one form of electrical power into another but cannot generate electrical power. This makes it a converter, not a generator. It can be
Get a quote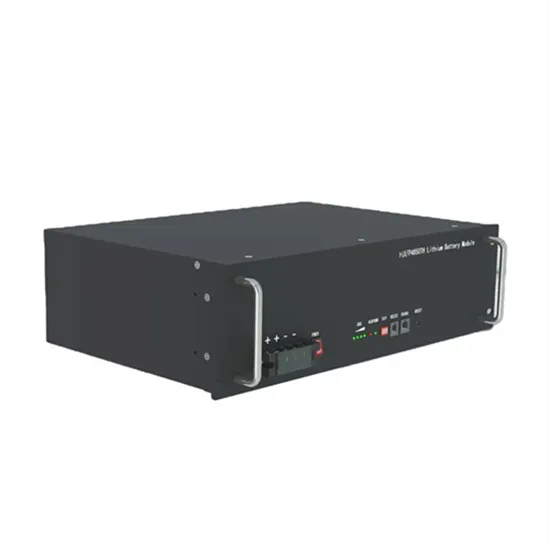
What Does An Inverter Do? Complete Guide To
Learn what inverters do, how they convert DC to AC power, types available, and applications. Complete guide with sizing tips, safety advice, and
Get a quote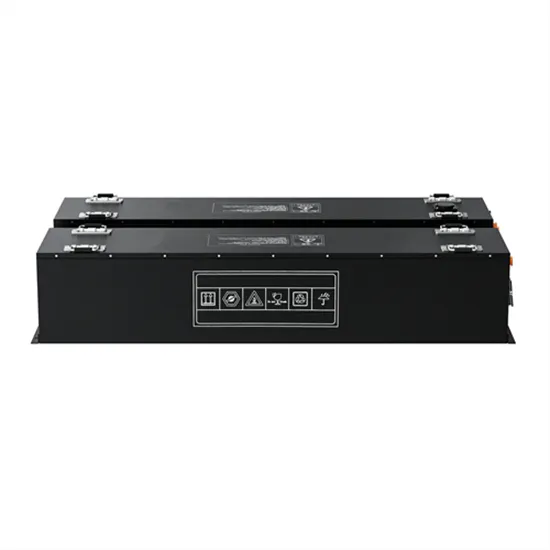
How Much Power Does an Inverter Draw with no Load?
The no-load power consumption of an inverter, also known as standby power consumption or static power consumption, refers to the power
Get a quote
Felicity 10kva Solar Inverter – Silent Operation
The Felicity Solar Hybrid Inverter 10000VA/8000W IVPM10048 is a versatile and powerful energy solution designed for residential and commercial applications. Combining the functionalities of
Get a quote
Inverter : Operating Principle,Circuit, Classification
Definition: The inverter is an electronic circuit that converts fixed DC supply to variable AC supply. The inverter is used to run the AC loads
Get a quote
6 FAQs about [Inverter 0 power operation]
Is an inverter a generator or a converter?
An inverter is a static device that converts one form of electrical power into another but cannot generate electrical power. This makes it a converter, not a generator. It can be used as a standalone device such as solar power or back power for home appliances.
What are inverters used for?
Inverters are essential components in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and whole-house backup systems. They provide seamless power during outages by converting stored battery power to AC electricity. Critical applications include:
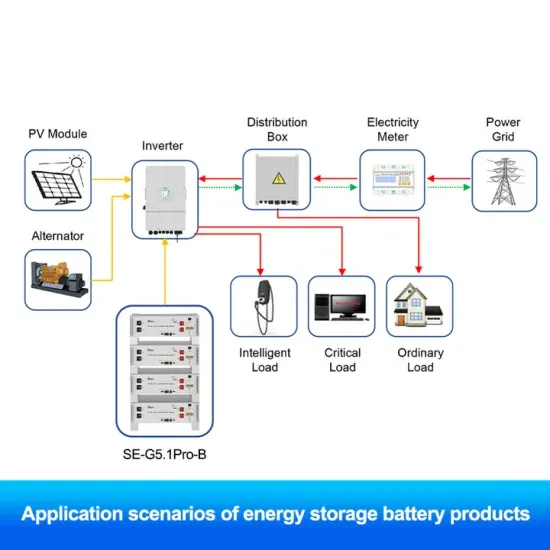
What is an inverter & how does it work?
An inverter is an electronic device that converts direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Think of it as a translator between two different electrical languages – your solar panels, batteries, and car electrical systems speak “DC,” while your home appliances, power grid, and most electronics speak “AC.”
What is a DC inverter?
Inverter Definition: An inverter is defined as a power electronics device that converts DC voltage into AC voltage, crucial for household and industrial applications. Working Principle: Inverters use power electronics switches to mimic the AC current’s changing direction, providing stable AC output from a DC source.
How efficient are inverters?
The available inverter models are now very efficient (over 95% power conversion efficiency), reliable, and economical. On the utility scale, the main challenges are related to system configuration in order to achieve safe operation and to reduce conversion losses to a minimum. Figure 11.1.
What are the different types of inverters?
Types of Inverters: Inverters are categorized by their output waveforms (square wave, modified sine wave, and sine wave) and by their load type (single-phase and three-phase). Applications: Inverters in power electronics are used in UPS systems, solar power, HVDC transmission, and for controlling motor speeds in various devices.
Guess what you want to know
-
 Inverter High Power Ranking
Inverter High Power Ranking
-
 Inverter power generation price
Inverter power generation price
-
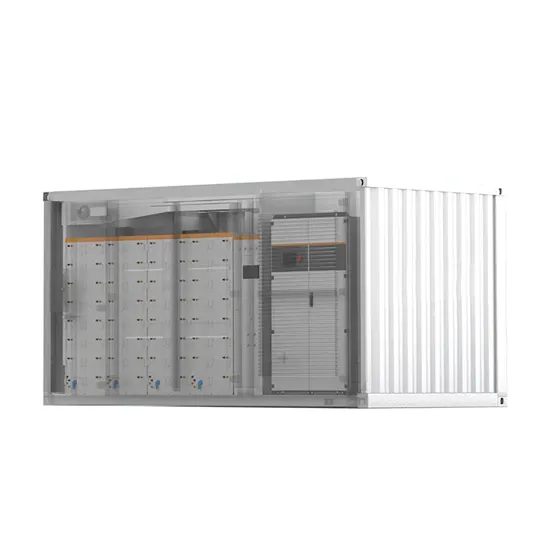 Saint Lucia Photovoltaic Inverter Power Supply
Saint Lucia Photovoltaic Inverter Power Supply
-
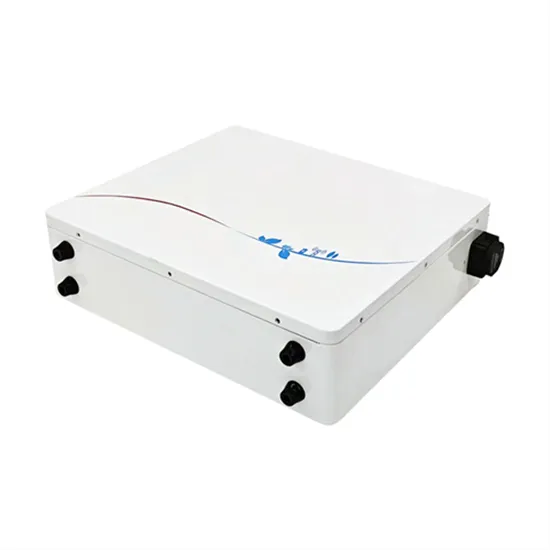 High power inverter power generation
High power inverter power generation
-
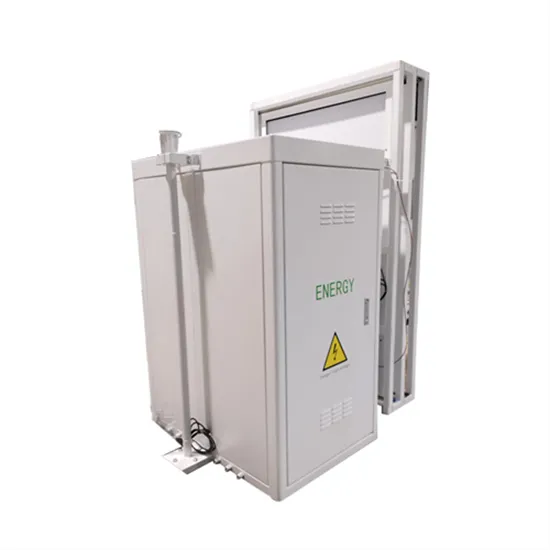 Cook Islands Photovoltaic Power Generation Equipment Inverter
Cook Islands Photovoltaic Power Generation Equipment Inverter
-
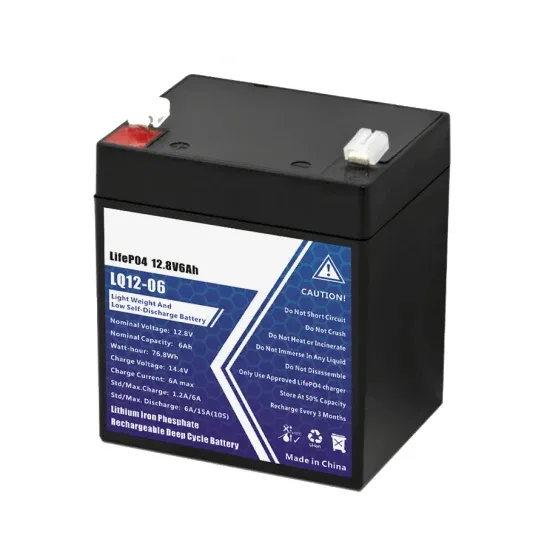 PV inverter power time
PV inverter power time
-
 Inverter outdoor power supply
Inverter outdoor power supply
-
 Photovoltaic inverter classification power conversion level
Photovoltaic inverter classification power conversion level
-
 100kw inverter power 30kw
100kw inverter power 30kw
-
 Togo communication base station power operation
Togo communication base station power operation
Industrial & Commercial Energy Storage Market Growth
The global industrial and commercial energy storage market is experiencing unprecedented growth, with demand increasing by over 350% in the past three years. Energy storage cabinets and lithium battery solutions now account for approximately 40% of all new commercial energy installations worldwide. North America leads with a 38% market share, driven by corporate sustainability goals and federal investment tax credits that reduce total system costs by 25-30%. Europe follows with a 32% market share, where standardized energy storage cabinet designs have cut installation timelines by 55% compared to custom solutions. Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing region at a 45% CAGR, with manufacturing innovations reducing system prices by 18% annually. Emerging markets are adopting commercial energy storage for peak shaving and energy cost reduction, with typical payback periods of 3-5 years. Modern industrial installations now feature integrated systems with 50kWh to multi-megawatt capacity at costs below $450/kWh for complete energy solutions.
Energy Storage Innovations & Industrial Cost Benefits
Technological advancements are dramatically improving energy storage cabinet and lithium battery performance while reducing costs for commercial applications. Next-generation battery management systems maintain optimal performance with 45% less energy loss, extending battery lifespan to 18+ years. Standardized plug-and-play designs have reduced installation costs from $900/kW to $500/kW since 2022. Smart integration features now allow industrial systems to operate as virtual power plants, increasing business savings by 35% through time-of-use optimization and grid services. Safety innovations including multi-stage protection and thermal management systems have reduced insurance premiums by 25% for commercial storage installations. New modular designs enable capacity expansion through simple battery additions at just $400/kWh for incremental storage. These innovations have significantly improved ROI, with commercial projects typically achieving payback in 4-6 years depending on local electricity rates and incentive programs. Recent pricing trends show standard industrial systems (50-100kWh) starting at $22,000 and premium systems (200-500kWh) from $90,000, with flexible financing options available for businesses.

